Lecture12 6 13
- 1. Accessory Structures of the Eye Figure 17–3
- 2. Neural Tunic (Retina) Figure 17–4c
- 3. Retina • Rods, cones are types of photoreceptors Figure 17–6
- 4. Rods • Highly sensitive to light, do not discriminate colors • Rods dominate peripheral areas of retina • Provide low-resolution black–and–white vision in dimly lit environments Cones • Sensitive to colored light • Densely clustered in fovea • Provide high–resolution color vision in brightly lit environments
- 6. • Rods and cones synapse with neurons called bipolar cells • Bipolar cells then synapse with neurons called ganglion cells Figure 17–6a
- 7. Horizontal Cells • Where receptors synapse with bipolar cells Amacrine Cells • Where bipolar cells synapse with ganglion cells • Both facilitate or inhibit communication between photoreceptors and ganglion cells • Alter sensitivity of retina
- 8. Optic Disc • Circular region just medial to fovea • Origin of optic nerve Figure 17–6b, c
- 10. Visual Pigments • Where light absorption occurs • Derivatives of rhodopsin (opsin plus retinal) • Retinal: synthesized from vitamin A Figure 17–13b
- 11. Phototransduction 1) Photon strikes retinal portion of rhodopsin 2) Opsin is activated: – Goes from 11-cis form to 11-trans form 3) Opsin activates transducin (G protein), then activates phosphodiesterase (PDE) 4) Cyclic-GMP (cGMP) levels decline; gated sodium channels close 5) Dark current is reduced; neurotransmitter release declines
- 12. In dark, photoreceptors are activated (stimulated) Dark Current In light, photoreceptors are inactivated (inhibited) Figure 17–14
- 13. Bleaching • Rhodopsin molecule breaks down into retinal and opsin Figure 17–15
- 14. Dark-Adapted State • Pupil dilates • Most pigments can be activated • A single photon can be detected Light-Adapted State • Pupil constricts • Bleaching of visual pigments occurs • “Blinding” when go from dark to light room
- 15. Pupillary Muscle Reflexes Figure 17–5
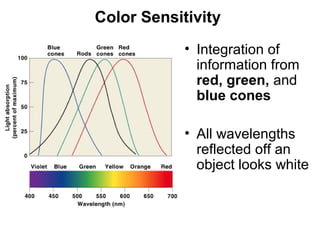
- 16. Color Sensitivity • Integration of information from red, green, and blue cones • All wavelengths reflected off an object looks white Figure 17–16
- 17. Color Blindness • Inability to detect certain colors Figure 17–17
- 18. Visual Pathway • Begins at photoreceptors • Ends at visual cortex of cerebral hemispheres • Message crosses 2 synapses before goes toward brain: –photoreceptor --> bipolar cell –bipolar cell --> ganglion cell (sensory neuron) “processing in retina”
- 19. Convergence • Each ganglion cell receives input from many photoreceptors • Therefore, Receptive field of ganglion cell is monitored by many photoreceptors
- 20. M Cells • ganglion cells that monitor rods • Provide information about: –general form of object –motion –shadows in dim lighting P Cells • ganglion cells that monitor cones • Provide information about: –edges –fine detail –color
- 21. Visual Pathway 1. Axons from ganglion cells converge on optic disc 2. Penetrate wall of eye 3. Proceed toward diencephalon as optic nerve (II) 4. 2 optic nerves (1 for each eye) reach diencephalons at optic chiasm Figure 17–19
- 22. Optic Tracts 5. Axons from both eyes projecting from optic chiasm to lateral geniculi Optic Radiations 6. Bundles of projection fibers from lateral geniculates to visual cortex
- 23. Visual Cortex 7. Info from right or left fields of vision arrive at visual cortex of opposite occipital lobe: – left half arrives at right occipital lobe – right half arrives at left occipital lobe
- 24. Depth Perception • By comparing relative positions of objects between left–eye and right–eye images But, at great distances: - Previous familiarity - Occlusion - Perspective - Motion parallax - Shadows and light Figure 17–19