Ch01 sociological perspective
- 1. Chapter 1 Developing a Sociological Perspective
- 2. Chapter Outline What is Sociology? The Sociological Imagination The Significance of Diversity The Development of Sociology Theoretical Frameworks in Sociology
- 3. What Is Sociology? The study of human behavior in society. A scientific way to think about society and its influence on humans. Includes the study of social behavior and social change.
- 4. Question What do the following people have in common? Dan Akroyd (actor; comedian) Debra Winger (actress) Saul Bellow (novelist; Nobel Prize recipient) Joe Theissman (NFL quarterback) Rev. Jesse Jackson Robin Williams (comedian; actor) Rev. Martin Luther King, Jr. Ronald Reagan
- 5. Answer They were all sociology majors.
- 6. Disciplines of Sociology Psychology analyzes human behavior. Anthropology is the study of human cultures. Political Science is the study of politics.
- 7. Disciplines of Sociology Economics studies the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services. Social Work uses the social sciences to serve people in need.
- 8. The Sociological Imagination Ability to see societal patterns that influence life. C. Wright Mills wrote about sociological perspective in The Sociological Imagination. Sociology can reveal how society shapes our lives.
- 9. Troubles and Issues Troubles are private problems in an individual’s life. Issues affect large numbers of people Issues shape the context within which troubles arise.
- 10. Debunking Studying the patterns and processes that shape behavior. Questioning actions and ideas that are usually taken for granted. Acting as “an outsider within.”
- 11. Understanding Diversity Understanding diversity is critical to understanding society because patterns of social change and social structure are influenced by diverse group experiences. Diversity includes: the shaping of social institutions by different social factors the formation of group and individual identity the process of social change
- 12. Share of Minorities in the U.S. Population
- 13. America’s Diversity: % White
- 14. America’s Diversity: % African American
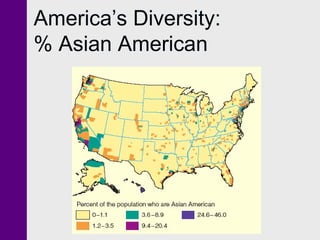
- 16. America’s Diversity: % Asian American
- 17. America’s Diversity: % American Indian
- 18. Sociology and the Enlightenment Faith in the ability of human reason to solve society’s problems. Belief that natural laws and processes in society are used for the general good.
- 19. Influence of the Enlightenment Positivists - society could be studied using the natural sciences. Humanitarianism - human reason can direct social change for the betterment of society.
- 20. Sociology in Europe: Comte French philosopher Coined the term sociology Believed sociology could discover laws of human social behavior and help solve society’s problems
- 21. Sociology in Europe: Tocqueville French citizen who traveled to the United States 1831 Wrote an analysis of U.S. democratic culture and society. In the United States the tyranny of kings was replaced by the “tyranny of the majority.”
- 22. Sociology in Europe: Martineau British citizen who toured the United States in 1834. Wrote Society in America, an analysis of social customs she observed. Wrote first sociological methods book on participant observation.
- 23. Classical Sociological Theory: Durkheim Viewed society as an entity larger than the sum of its parts. Conceptualized social facts as social patterns external to individuals. Discovered the social basis of human behavior.
- 24. Classical Sociological Theory: Marx Work was devoted to explaining how capitalism shaped society. Profit is produced through the exploitation of the working class. Considered the economic organization of society the most important influence on what humans think and how they behave.
- 25. Classical Sociological Theory: Weber Theorized that society had three dimensions: political, economic,and cultural. Believed that to understand social behavior one had to understand the meaning that a behavior had for social actors.
- 26. Sociology in America American sociologists believed sociology could help solve social problems. The Chicago School - concerned with the relationship of individual to society and society as a human laboratory.
- 27. Key Sociological Concepts Social structure Organized pattern of social relationships and institutions that together constitute society Social institutions Established and organized systems of social behavior with a recognized purpose.
- 28. Key Sociological Concepts Social change The alteration of society over time. Social interaction A behavior between two or more people that is given meaning.
- 29. Sociological Theory: Individual and Society Functionalism Individuals occupy fixed social roles. Conflict Theory Individuals subordinated to society. Symbolic Interaction Individual and society are interdependent.
- 30. Sociological Theory: View of Inequality Functionalism Inevitable; functional for society Conflict Theory Result of struggle over scarce resources. Symbolic Interaction Inequality demonstrated through meaning of status symbols.
- 31. Sociological Theory: Basis of Social Order Functionalism Consensus on common values. Conflict Theory Power; coercion Symbolic Interaction Collective meaning systems; society created through social interaction
- 32. Sociological Theory: Source of Social Change Functionalism Disorganization and adjustment to achieve equilibrium. Conflict Theory Struggle; competition Symbolic Interaction Ever-changing web of relationships and meaning of things.
- 33. Sociological Theory: Criticisms Functionalism A conservative view of society that underplays power differences among and between groups. Conflict Theory Understates the degree of cohesion and stability in society. Symbolic Interaction There is little analysis of inequality and it overstates the subjective basis of society.
- 34. Polling Question Which sociological perspective do you think is generally the weakest in explaining things in our society? A.) Functionalist B.) Conflict Theory C.) Symbolic interaction
- 35. Polling Question Which sociological perspective do you think explains the concept of inequality in our society the most accurately? A.) Functionalist B.) Conflict Theory C.) Symbolic interaction
- 36. Quick Quiz
- 37. 1. Sociology is the study of: a. personality types b. political philosophy c. human behavior d. the distribution of goods and services
- 38. Answer: c Sociology is the study of human behavior.
- 39. 2. The ability to see the societal patterns that influence individual and group life is referred to as: a. commonsense b. social speedup c. Wright's Theorem d. the sociological imagination
- 40. Answer: d The ability to see the societal patterns that influence individual and group life is referred to as the sociological imagination.
- 41. 3. The sociologist that first coined the term sociology is: a. Auguste Comte b. Emile Durkheim c. Karl Marx d. Harriet Martineau
- 42. Answer: a The sociologist that first coined the term sociology is Auguste Comte.
- 43. 4. According to Karl Marx, the most important influence on what humans think and how they behave is: a. the socio-emotional organization of society b. the economic organization of society c. the political organization of society d. the religious organization of society
- 44. Answer : b According to Karl Marx, the most important influence on what humans think and how they behave is the economic organization of society.
- 45. 5. Symbolic interactionism emphasizes: a. the role of coercion and power b. class struggles c. face-to-face contact d. the interdependent parts of society
- 46. Answer: c Symbolic interactionism emphasizes face-to-face contact.