clostridium.perfringenes
- 1. Clostridium 1 Dr . Milad Shaini
- 2. Physiology and Structure Large Gram positive Straight or slightly curved rods with slightly rounded ends Anaerobic bacilli Spores are wider than bacillary body, giving bacillus a swollen appearance resembling spindle; hence named so (Kolster meaning spindle ) Spore do not germinate and growth does not normally proceed unless a suitably low redox potential Eh exists 2
- 3. Physiology and Structure Saprophytes Most clostridia are motile by peritrichous flagella.(except C.tetani Type VI & C.perfringens) C.perfringens & C.butyricum are capsulated; others are non-capsulated Some are commensals of the animal & human gut which invade the blood and tissue when host die and initiate the decomposition of the corpse (dead body) Causes diseases such as gas gangrene, tetanus, botulism & pseudo- membranous colitis by producing toxins which attack the neurons pathways 3
- 4. Spores The shape & position of spores varies in different spp. & thus useful in their identification. Spores may be: o Central or equatorial in C.bifermentans(Spindle shaped) o Sub terminal in C.perfringens(club shaped) o Oval and terminal in C.tertium(resembling tennis racket) o Spherical and terminal in C.tetani( drum sticks ) 4
- 5. Cultural characteristics Clostridia are anaerobic. Optimum temp. for growth is 37°C;pH 7-7.4. Robertson’s cooked meat broth is useful medium. Most species produce gas in this medium 5
- 6. Resistance Spores of C.botulinum survive boiling after 3-4 hrs. Even at 105°C are not killed completely. Spores of C.perfringens are destroyed by boiling in 5 minutes. Spores of C.tetani persist for years in dry soil, while few strains resist boiling for 15-90 min. All species are killed by autoclaving at 121°C for 20 minutes. Halogens are effective;1% aq of Iodine kills spores within 3 hrs.2% glutaraldehyde kills spores 6
- 8. • Large Gram-positive bacilli with straight, parallel sides & slightly rounded ends. • Measure 4-6x1μm in size, occuring singly or in chains • Pleomorphic, capsulated & non-motile. • Spores are central or sub terminal. Spores are rarely seen in culture media or material from pathogenic lesions, a characteristic morphologic feature Morphology 8
- 9. Toxins 9
- 10. α-Toxin Produced in large amounts by type A strains, α-toxin is a phospholipase C (EC 3.1.4.3) and appears to play a major role in gas gangrene. It hydrolyzes phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin, but not other phospholipids. It is a zinc metal protein and requires calcium ions for interaction with substrate. It is responsible for the lecithinase reaction on egg yolk agar and for the hazy zone of hemolysis on blood agar. The gene encoding α-toxin has been cloned and sequenced. The results show that the gene product is a 399-amino acid peptide with a molecular mass of 43 kDa; Immunization of guinea-pigs with α-toxin protects them against gas gangrene when challenged with C. perfringens and toxin. 10
- 11. β-Toxin β-Toxin is a major lethal toxin produced by type B and C toxin types. It is responsible for the lesions of necrotic enteritis of pig-bel. The toxin purified by affinity chromatography has a molecular mass of 40 kDa and an isoelectric pH of 5.6. Nucleotide sequencing of the gene encoding the β-toxin reveals an open reading frame of 1 008 nucleotides that encodes a protein of 336 amino acids with a molecular mass of 34.9 kDa 11
- 12. ε-Toxin ε-Toxin is a prototoxin that is activated by proteolytic enzymes and is produced by both type B and type D strains. It increases the permeability of the intestine, thus enhancing its own uptake, and acts systemically as a lethal toxin. In the circulation, it causes swollen, hyperemic kidneys, edema in the lungs, and excess pericardial fluid. The nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding ε-toxin shows that the mature prototoxin consists of 297 amino acids with a molecular mass of 33 kDa. A 13 amino acid N-terminal peptide is cleaved during activation. 12
- 13. ι-Toxin ι-Toxin is a binary toxin consisting of two subunits, ι-a and ι-b, which are immunologically and biochemically distinct. The gene sequences encoding these subunits have been determined and the deduced amino acid sequences for the functionally active proteins correspond to peptides with molecular masses of about 40 and 81 kDa, respectively. A mixture of both components is needed to demonstrate biological activity by mouse lethality or dermonecrosis. The light chain (ι-a) is an enzyme that ADP-ribosylates polyarginine and skeletal muscle and nonmuscle actin. ι-a must gain entrance into the target cell before it can have any effect, but cannot do this of itself; ι-b recognizes a binding site on the cell membrane, binds to the site, and interacts with ι-a to facilitate its entry. ι-Toxin of C. perfringens is similar to ι-toxin of C. spiroforme in serological, biological, and enzymatic activities. 13
- 14. Minor Toxins θ toxin δ toxin κ toxin λ toxin μ toxin ν Toxin 14
- 15. Enterotoxin Enterotoxin produced by C.perfringens is responsible for food-borne diarrhea which occurs after consumption of foods containing large numbers of the vegetative organism. It has been found in toxin types A, C, and D, but type B and E strains have not been sufficiently tested to establish whether they also produce it. 15
- 16. Enzymes Neuraminidase destroys myxovirus receptors on red cells Hemagglutinin active against red cells of humans Fibrinolysin Hemolysin Bursting factor has specific action on muscle tissue, responsible for muscle lesions in gas gangrene. Circulatory factor causes an increase in adrenaline sensitivity of capillary bed ,also inhibits phagocytosis 16
- 17. Pathogenicity Three Clinical conditions produced include: 1.Simple wound contamination: Slow wound healing 2.Anaerobic or clostridial cellulitis: Clostridiae invade fascial planes(fasciitis) with minimal toxin production but no invasion of muscle tissue. Lesions vary from limited ‘gas abscess’ to extensive involvement of limbs. Seropurulent discharges with offensive odor produced 17
- 18. Pathogenicity 3.Anaerobic myositis or myonecrosis or gas gangrene Most serious complication of clostridial invasion of healthy muscle tissue . Abundant formation of exotoxin & production of gas. GG is disease of war. In civilian life it follows road accidents or injuries with crushing of muscle mass. GG is rarely infection of single clostridium; several species found in association with anaerobic streptococci & facultative anaerobes (E.coli,Stap,Proteus) Among pathogenic clostridiae,C.perfringens is most frequently encountered(60%) followed by C.Novyi & C.septicum(20-40%). Three Clinical conditions produced include: 18
- 19. Pathophysiological events of gas gangrene Calcium salts & salicic acid in soil cause necrosis. Crushing tissue/tearing of arteries produce anoxia of muscle. Extravasation of blood increase pressure on capillaries. reducing further blood supply. Eh & pH of damaged tissues falls. Carbohydrates in tissue are fermented producing gas. Proteins are broken down into amino acids. Extravasated hemoglobin & myohemoglobin are reduced & they cease to act as oxygen carriers. 19
- 20. Pathophysiological events of gas gangrene The Clostridia multiply & elaborate different toxins. Lecithinases damage cell membranes. α-toxin causes lysis of erythrocytes-hemolytic anemia Collagenases destroy collagen barriers in the tissue Hyaluronidases breakdown intercellular substance Abundant gas production reduces blood supply 20
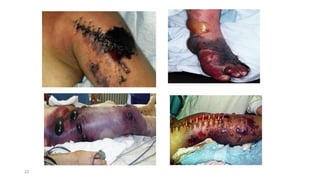
- 21. Clinical presentation (IP 6 hrs. to 6 weeks) Increasing pain, tenderness & edema of affected part with blackening of tissue & foul smelling serous exudes • Crepitus due to accumulation of gas bubbles • Death occurs due to circulatory failure. 21
- 22. 22
- 23. Other infections Food poisoning: usually caused by Type A strains Gangrenous appendicitis: C.perfringens Type A & occasionally by Type D Necrotizing enteritis: caused by Type C strains Biliary tract infection: Rare but serious Endogenous gas gangrene of intra-abdominal origin Brain abscess & meningitis: Rare Panophthalmitis: Rare Thoracic infections Urogenital infections- usually follow UT surgery 23
- 24. Laboratory diagnosis A. Hematological investigation: Not significant B. Bacteriological Investigation: Specimen: Wound swabs, necrosed tissue, muscle fragments, exudates from active parts etc. 1.Microscopy: • Gram positive, non-motile, capsulated bacilli. • Spores are rarely observed in C.perfringens 24
- 25. Laboratory diagnosis 2.Culture: On RCM(Robertson’s cooked meat broth)→ meat turned pink but not digested On blood agar → target hemolysis Stormy fermentation of lactose in litmus milk; the acid coagulates casein-acid clot. 25
- 26. 3. Biochemical reactions Laboratory diagnosis Glucose Indole Negative Lactose Fermented MR Positive Maltose VP Negative H2S prodn & Nitrate redn Positive 26
- 27. Laboratory diagnosis 4.Nagler’s Reaction Rapid detection of C.perfringens from clinical sample Done to detect the lecithinase activity of alpha toxin Characteristics opalescence is produced around colonies in positive test due to breakdown of lipoprotein complex in the medium 27
- 28. Laboratory diagnosis 5.Reverse CAMP Test Used for differentiation of C.perfringens from other clostridium species. CAMP positive Group B Streptococcus is streaked in SBA & C.perfringens is streaked perpendicular to it “arrowhead”(enhanced) hemolysis is seen between growth of C.perfringens & Group B streptococcus 28
- 29. Prophylaxis and Treatment 1.Surgery: All damaged tissue should be removed, wounds irrigated to remove clots, necrotic tissue & foreign materials, excision of affected parts in EGG. 2.Antibiotics: Metronidazole given intravenously before surgery & repeated 8 hourly for 24 hrs. Broad spectrum antibiotics in combinations (like metronidazole+gentamycin+amoxicillin)are effective. 3.Antitoxins: Passive immunization with three doses 29
- 30. Other Clostridia associated with GG 1.C.septicum also called as Vibrion septique Produces 4 distinct toxins; α-toxin: hemolytic & dermonecrotic β-toxin: leucotoxic γ-toxin: hyaluronidase δ-toxin: hemolysin It also produces fibrinolysin 2.C.novyi: 4 types recognized(A-D),Type A causes GG 3.C.histolyticum: Produces 5 distinct toxins Infrequently associated with GG 30