02 hibernateintroduction
- 1. Professional Open Source™ Hibernate Introduction Hello World and the Hibernate APIs © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 07/17/04 1
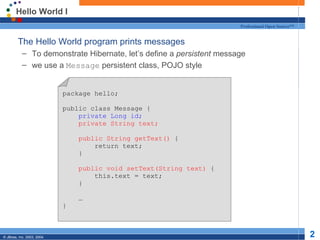
- 2. Hello World I Professional Open Source™ The Hello World program prints messages – To demonstrate Hibernate, let’s define a persistent message – we use a Message persistent class, POJO style package hello; public class Message { private Long id; private String text; public String getText() { return text; } public void setText(String text) { this.text = text; } … } © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 2
- 3. Hello World II Professional Open Source™ Messages don't have to be persistent! – we can use our persistent classes “outside” of Hibernate – Hibernate is able to “manage” persistent instances – but POJO persistent classes don't depend on Hibernate Message message = new Message("Hello World"); System.out.println( message.getText() ); © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 3
- 4. Hello World VI Professional Open Source™ XML mapping metadata: <?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD//EN" "http://hibernate.sf.net/hibernate-mapping-2.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="hello.Message" table="MESSAGES"> <id>...</id> <property name="text" column="MESSAGE_TEXT"/> </class> </hibernate-mapping> © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 4
- 5. Using C3P0 with hibernate.properties Professional Open Source™ Let's configure Hibernate to use C3P0 connection pooling Hibernate automatically loads hibernate.properties from a root directory of the classpath hibernate.connection.driver_class = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver hibernate.connection.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost/helloworld hibernate.connection.username = root hibernate.connection.password = root hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.mySQLDialect hibernate.c3p0.min_size = 5 hibernate.c3p0.max_size = 20 hibernate.c3p0.timeout = 1800 hibernate.c3p0.max_statements = 50 Hibernate.c3p0.validate = true Don't forget to set the SQL dialect! © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 5
- 6. Starting Hibernate Professional Open Source™ We create a SessionFactory using a Configuration – download and install JDBC driver in classpath – copy Hibernate and the required 3rd party libraries – chose a JDBC connection pool, customize properties – add mapping files to the Configuration – build the SessionFactory (immutable!) SessionFactory sessionFactory = new Configuration() .addResource("hello/Message.hbm.xml") .buildSessionFactory(); © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 6
- 7. Configuring hibernate.cfg.xml Professional Open Source™ Let's configure Hibernate using hibernate.cfg.xml <hibernate-configuration> <!-- a SessionFactory instance listed as /jndi/name --> <session-factory> <!-- properties --> <property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLInnoDBDialect</property> <property name="show_sql">true</property> <property name="use_outer_join">false</property> <property name="connection.username">root</property> <property name="connection.password">root</property> <property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> <property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost/helloworld</property> <property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">insert</property> <!-- mapping files --> <property name="cache.provider_class"> org.hibernate.cache.NoCacheProvider</property> <!-- mapping files --> <mapping resource="hello/Message.hbm.xml"/> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration> © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 7
- 8. Starting Hibernate Professional Open Source™ We create a SessionFactory using a Configuration – download and install JDBC driver in classpath – copy Hibernate and the required 3rd party libraries – chose a JDBC connection pool, customize properties – add mapping files to the Configuration – build the SessionFactory (immutable!) SessionFactory sessionFactory = new Configuration() .configure().buildSessionFactory(); © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 8
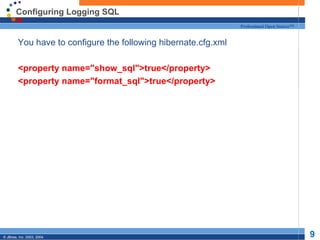
- 9. Configuring Logging SQL Professional Open Source™ You have to configure the following hibernate.cfg.xml <property name="show_sql">true</property> <property name="format_sql">true</property> © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 9
- 10. Hello World III Professional Open Source™ Let's persist a message with Session and Transaction: Session session = getSessionFactory().openSession(); Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction(); Message message = new Message("Hello World"); session.save(message); tx.commit(); session.close(); Hibernate executes this SQL: insert into MESSAGES (MESSAGE_ID, MESSAGE_TEXT) values (1, 'Hello World') © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 10
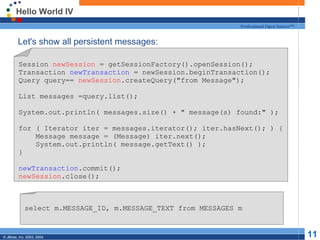
- 11. Hello World IV Professional Open Source™ Let's show all persistent messages: Session newSession = getSessionFactory().openSession(); Transaction newTransaction = newSession.beginTransaction(); Query query== newSession.createQuery("from Message"); List messages =query.list(); System.out.println( messages.size() + " message(s) found:" ); for ( Iterator iter = messages.iterator(); iter.hasNext(); ) { Message message = (Message) iter.next(); System.out.println( message.getText() ); } newTransaction.commit(); newSession.close(); select m.MESSAGE_ID, m.MESSAGE_TEXT from MESSAGES m © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 11
- 12. Hello World V Professional Open Source™ Let's update a message: Session session = getSessionFactory().openSession(); Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction(); // 1 is the generated id of the first message Message message = session.load( Message.class, new Long(1) ); message.setText("Greetings Earthling"); tx.commit(); session.close(); select m.MESSAGE_TEXT from MESSAGES m where m.MESSAGE_ID = 1 update MESSAGES set MESSAGE_TEXT = ‘Greetings Earthling' Notice that we did not explicitly call any update() method - automatic dirty checking gives us more flexibility when organizing data access code! © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 12
- 13. Other configuration options Professional Open Source™ Instead of using a hibernate.properties file, we may also – pass an instance of Properties to Configuration programmatically – set System properties using java -Dproperty=value – use a hibernate.cfg.xml file in the classpath The XML-based configuration is almost equivalent to the properties, it has some more features (cache tuning). The XML file overrides the hibernate.properties options. We usually prefer the XML configuration file, especially in managed environments. © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 13
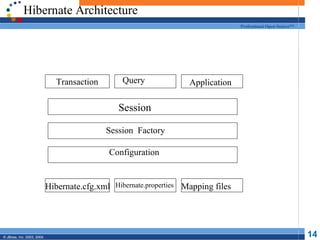
- 14. Hibernate Architecture Hibernate Architecture Professional Open Source™ Transaction Query Application Session Session Factory Configuration Hibernate.cfg.xml Hibernate.properties Mapping files © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 14
- 15. Hibernate Architecture Hibernate Architecture Professional Open Source™ © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 15
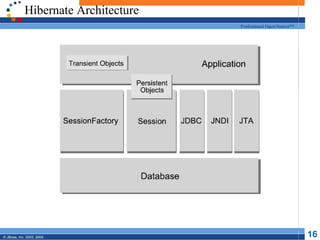
- 16. Hibernate Architecture Professional Open Source™ © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 16
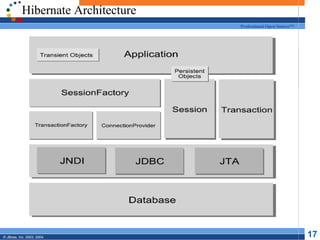
- 17. Hibernate Architecture Professional Open Source™ © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 17
- 18. SessionFactory Professional Open Source™ SessionFactory (org.hibernate.SessionFactory) A thread safe (immutable) cache of compiled mappings for a single database. A factory for Session and a client of Connection Provider. Might hold an optional (second-level) cache of data that is reusable between transactions, at a process- or cluster-level. © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 18
- 19. Session Professional Open Source™ Session (org.hibernate.Session) A single-threaded, short-lived object representing a conversation between the application and the persistent store Wraps a JDBC connection. Factory for Transaction. Holds a mandatory (first-level) cache of persistent objects, used when navigating the object graph or looking up objects by identifier. © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 19
- 20. Persistent Objects and Collections Professional Open Source™ Persistent objects and collections Short-lived, single threaded objects containing persistent state and business function. These might be ordinary JavaBeans/POJOs, the only special thing about them is that they are currently associated with (exactly one) Session. As soon as the Session is closed, they will be detached and free to use in any application layer (e.g. directly as data transfer objects to and from presentation). © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 20
- 21. Transient and detached objects and collections Professional Open Source™ Transient and detached objects and collections Instances of persistent classes that are not currently associated with a Session. They may have been instantiated by the application and not (yet) persisted or they may have been instantiated by a closed Session. . © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 21
- 22. Transaction Professional Open Source™ Transaction (org.hibernate.Transaction) (Optional) A single-threaded, short-lived object used by the application to specify atomic units of work. Abstracts application from underlying JDBC, JTA or CORBA transaction. A Session might span several Transactions in some cases. However, transaction demarcation, either using the underlying API or Transaction, is never optional! . © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 22
- 23. ConnectionProvider Professional Open Source™ ConnectionProvider (org.hibernate.connection.ConnectionProvider) (Optional) A factory for (and pool of) JDBC connections. Abstracts application from underlying Datasource or DriverManager. Not exposed to application, but can be extended/implemented by the developer. © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 23
- 24. TransactionFactory Professional Open Source™ TransactionFactory (org.hibernate.TransactionFactory) (Optional) A factory for Transaction instances. Not exposed to the application, but can be extended/implemented by the developer. © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 24
- 25. Extension Interfaces Professional Open Source™ Extension Interfaces Hibernate offers many optional extension interfaces you can implement to customize the behavior of your persistence layer.(Ex. Primary key generation,SQL Dialet , Caching,JDBC connection, Proxy creationetc., Given a "lite" architecture, the application bypasses the Transaction/TransactionFactory and/or ConnectionProvider APIs to talk to JTA or JDBC directly. © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 25
- 26. Instance States Professional Open Source™ Instance states An instance of a persistent classes may be in one of three different states, which are defined with respect to a persistence context. © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 26
- 27. Instance States Professional Open Source™ Instance states An instance of a persistent classes may be in one of three different states, which are defined with respect to a persistence context. © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 27
- 28. Instance States Professional Open Source™ Transient The instance is not, and has never been associated with any persistence context. It has no persistent identity (primary key value). © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 28
- 29. Instance States Professional Open Source™ Persistent The instance is currently associated with a persistence context. It has a persistent identity (primary key value) and, perhaps, a corresponding row in the database. For a particular persistence context, Hibernate guarantees that persistent identity is equivalent to Java identity (in-memory location of the object). © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 29
- 30. Instance States Professional Open Source™ Detached The instance was once associated with a persistence context, but that context was closed, or the instance was serialized to another process. It has a persistent identity and, perhaps, a corresponding row in the database. For detached instances, Hibernate makes no guarantees about the relationship between persistent identity and Java identity. © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 30
- 31. Managed environments Professional Open Source™ Hibernate can be used in an application server: Managed environment Application Hibernate Transaction EJB Session Manager EJB Transaction Resource EJB Query Manager Each database has it's own SessionFactory! © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 31
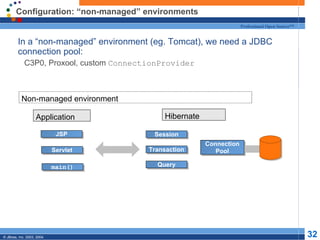
- 32. Configuration: “non-managed” environments Professional Open Source™ In a “non-managed” environment (eg. Tomcat), we need a JDBC connection pool: C3P0, Proxool, custom ConnectionProvider Non-managed environment Application Hibernate JSP Session Connection Servlet Transaction Pool main() Query © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 32
- 33. Managed environment with XML configuration file Professional Open Source™ <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory name="java:hibernate/SessionFactory"> <property name="show_sql">true</property> <property name="connection.datasource"> java:/comp/env/jdbc/HelloDB </property> <property name="transaction.factory_class"> net.sf.hibernate.transaction.JTATransactionFactory </property> <property name="transaction.manager_lookup_class"> net.sf.hibernate.transaction.JBossTransactionManagerLookup </property> <property name="dialect"> net.sf.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect </property> <mapping resource="hello/Message.hbm.xml"/> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration> © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 33
- 34. Session Cache Professional Open Source™ To improve the performance within the Hibernate service, as well as your application, is to cache objects. By caching objects in memory, Hibernate avoids the overhead of retrieving them from the database each time. Other than saving overhead when retrieving objects, the Session cache also impacts saving and updating objects. The session interface supports a simple instance cache for each object that is loaded or saved during the lifetime of a given Session. © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 34
- 35. Session Cache Professional Open Source™ Code watch : Session session = factory.openSession(); Event e = (Event) session.load(Event.class, myEventId); e.setName(“Hibernate training”); session.saveOrUpdate(e); // later, with the same Session instance Event e = (Event) session.load(Event.class, myEventId); e.setDuration(180); session.saveOrUpdate(e); session.flush(); © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 35
- 36. The Session Cache – Common problem Professional Open Source™ Don’t associate two instances of the same object with the same Session instance, resulting in a NonUniqueObjectException. Session session = factory.openSession(); Event firstEvent = (Event) session.load(Event.class, myEventId); //peform some operation on firstEvent Event secondEvent = new Event(); secondEvent.setId(myEventId); Session.save(secondEvent); This code opens the Session instance, loads an Event instance with a given ID, creates a second Event instance with the same Id, and then attempts to save the second Event instance, resulting in the NonUniqueObjectException. © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 36
- 37. The Session Cache – Object Information Professional Open Source™ To see whether an object is contained in the cache Session.contains() Objects can be evicted from the cache by calling Session.evict() To clear all the objects from Session cache Session.clear() © JBoss, Inc. 2003, 2004. 37