10-Radial and ulnar nerves anatomy course description
- 1. Radial and Ulnar Nerves Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/ Extra Editing File
- 2. Objectives Describe the anatomy of the radial & ulnar nerves regarding: origin, course & distribution. List the branches of the nerves. Describe the causes and manifestations of nerve injury.
- 3. Radial Nerve Origin: Posterior cord of the brachial plexus in the axilla (the largest branch of nerves in the upper limb) Supplies: All muscles of the posterior compartment of the arm (triceps) & forearm (3 groups)
- 4. Radial Nerve Course & Distribution In the Arm It winds()فلت around the back of the arm in the Spiral Groove(radial groove) on the back of the humerus between the heads of the triceps. In the spiral groove, the nerve is accompanied by(with) the Profunda Vessels, and it lies directly in contact with the shaft of the humerus (Dangerous Position). Any fracture of humerus specifically the spiral groove leads to injury of the radial nerve Extr a Posterior view of upper arm
- 5. Radial Nerve Course In the Forearm It pierces the Lateral Intermuscular septum. (the nerve is behind the humerus ج . ي ناشع ، ق ت خ ي ما د ق the intermuscular septum ) Descends in front of the Lateral Epicondyle. Passes forward into the Cubital Fossa Divides into Superficial & Deep branches. Extr a Cubital Fossa Extra
- 6. I. Arising in the Axilla Cutaneous to: 1.Posterior cutaneous nerve of arm Muscular to: 1. Long & Medial heads of Triceps Radial Nerve Branches II. Arising in the Spiral Groove Cutaneous to: 1.Lower lateral cutaneous nerve of arm 2.Posterior cutaneous nerve of forearm Muscular to: 1. Lateral & Medial heads of Triceps 2. Anconeus III. Arising close to lateral epicondyle: Muscular to: 1.Brachioradialis 2.Extensor carpi radialis longus 3.Brachialis Articular to: 1. Elbow joint Note the medial head of triceps is innervated twice Extra
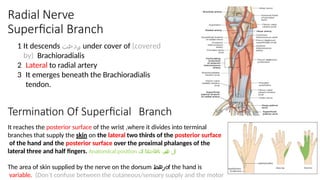
- 7. 1 It descends رد ن ح ت under cover of (covered by) Brachioradialis 2 Lateral to radial artery 3 It emerges beneath the Brachioradialis tendon. Termination Of Superficial Branch It reaches the posterior surface of the wrist ,where it divides into terminal branches that supply the skin on the lateral two thirds of the posterior surface of the hand and the posterior surface over the proximal phalanges of the lateral three and half fingers. Anatomical position لل ب ن س ب ه تاهاجتالا لك The area of skin supplied by the nerve on the dorsum رهظof the hand is variable. (Don’t confuse between the cutaneous/sensory supply and the motor Radial Nerve Superficial Branch
- 8. It winds around the neck of the radius, within the supinator muscle, and enters the posterior compartment of the forearm. It supplies : 1.Extensor carpi radialis brevis. 2.Extensor carpi ulnaris. 3.Supinator. 4.Abductor pollicis longus. 5.Extensor pollicis brevis. 6.Extensor pollicis longus. 7.Extensor indicis. 8.Extensor digitorum. 9.Extensor digiti minimi. Note: All muscles of the posterior/extensor compartment except ABE Radial Nerve Deep Branch The superficial branch is sensory whereas the deep branch is motor
- 9. The nerve can be injured by a drunkard falling asleep with one arm over the back of a chair (they call it saturday night paralysis), also by fractures and dislocations of the proximal end of the humerus. ن ة ك ي س ب ب ة ص ا إ و أ ي ر ا ن ل ط ل ق ض ر ع ت ا ح د و ا ل ث م أ و The triceps, the anconeus, and the long extensors of the wrist are paralyzed. The patient is unable to extend the elbow & the wrist joints, and the fingers flexed always (Wrist Drop) *Amazing video https://www.youtube.co m /watch?v=_Cu6ttAhe8Y *Important note : When the radial nerve injured at the axilla for any reason all the muscles and skin supplied by it will be Injury or fracture of the spiral groove of the humerus, the patient is unable to extend the wrist and the fingers (Wrist Drop). *the next slide All the branches from this point will be affected, while the branches from axilla (posterior of the forearm, long and medial head of triceps) are intact. The 2 heads of triceps are working therefor patient can extend the elbow joint . Keep in mind! The difference between injury to the radial nerve in the axilla and spiral groove is that in the spiral groove injury the patient can extend the elbow joint. Injuries to Radial Nerve In the Axilla In the Spiral Groove (in the arm) In the forearm
- 10. Injuries to the Deep Branch of the Radial Nerve •The deep branch of the radial nerve is PURELY Motor (It supplies the extensor muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm ex. Extensor carpi ulnaris). •It can be damaged in fractures of the proximal end of the radius or during dislocation of the radial head. •The nerve that supply the supinator and the extensor carpi radialis longus will be undamaged (they are supplied by radial nerve itself before it got branched), and because the latter muscle is powerful, it will keep the wrist joint extended with lateral deviation because the extensor carpi ulnaris cannot work (supplied by deep branch) Injuries to the Superficial Branch of the Radial Nerve •since patient can extend the wrist (No wrist Drop) Patient can do extension for elbow joint, skin that is supplied by radial nerve arising from the spiral groove region is intact ( No loss of Superficial radial nerve is Sensory nerve. Injury like a stab wound, results in a variable small area of anesthesia over the dorsum of the hand and lateral three and half fingers up to the base of their distal phalanges. (or distal interphalangeal joint) Injuries to Radial Nerve In the Axilla In the Spiral Groove (in the arm) In the forearm
- 11. Origin : Medial cord of brachial plexus Course : In the axilla & arm • Descends along the medial side of the following arteries: Axillary & Brachial (Axillary artery continues as the brachial artery) • Pierces the medial intramuscular septum . • Passes behind the medial epicondyle of humerus. (that’s why when you hit the medial back of your elbow you feel ك ه ر ب ه) Ulnar Nerve
- 12. In forearm : •Enters the anterior compartment of forearm through the flexor carpi ulnaris. Ulnar nerve pasess between 2 heads of flexor carpi ulnaris and supplies them . • Descends behind the flexor carpi ulnaris. • medial to ulnar artery . At the wrist : • Passes anterior (superficial) to flexor retinaculum • Lateral to pisiform bone. • Medial to ulnar artery. • Divides into : superficial and deep branches . Ulnar Nerve Course (cont)
- 13. Ulnar Nerve Branches It has no branches in the arm or axilla
- 14. Branches of Superficial Terminal Branch: 1. Muscular: • Palmaris Brevis. 2. Cutaneous: • Skin over the Palmar aspect of the medial 1+ ½ fingers (including nail beds). Branches of Deep Terminal Branch: 1. Muscular: • Hypothenar Eminence. • All Interossei (Palmar & Dorsal). • 3rd & 4th Lumbricals. • Adductor pollicis. 2. Articular: • Carpal joints. Ulnar Nerve Branches
- 15. At the Elbow: • Atrophy of Ulnar (medial) side of forearm. • Flexion of the wrist with Abduction*. • Claw hand. • Wasting of Hypothenar Eminence. At the Wrist: • Claw Hand. • Wasting of Hypothenar Eminence. Ulnar Nerve Injury *There will be flexion with radial deviation since the flexor carpi radialis is working while the flexor carpi ulnaris is not
- 16. Atrophy of the Forearm (Ulnar side) and Hypothenar muscles Wasting of Hypothenar Eminance Claw hand Ulnar Nerve Injury These pictures are extra
- 17. Summary of branches of Ulnar Nerve: Summary of branches of Radial Nerve:
- 18. Only on the boys’ slides
- 19. Its important to know the different deformities and the nerves related To remember: DR CUMAB DR = Wrist Drop > Radial Nerve CU = Claw Hand > Ulnar Nerve MAB = Median Nerve > Ape Hand > Hand of Benediction
- 20. 6- Injury to the radial nerve at which area causes wrist drop? A) Axilla B) Arm C) Forearm D)A & B 7- Which branch of the radial nerve supplies the following area? A) Superficial B) Deep C) Medial D) Lateral 8- The ulnar descends along the brachial and axillary artery. E) Anteriorly F) Posteriorly G) Medially H) Laterally 9- A patient presented with injury to the superficial branch of the ulnar nerve. Which muscle is affected? A) Palmaris Brevis B) Palmrais Longus C) Palmaris Superficialis D) Palmaris Profundus Questions 1- Which one is the largest nerve in the upper limb: A) ulnar B) radial C) axillary D) medial 2- Where does the radial nerve divide: A)spiral groove B)lateral epicndyle C)cubital fossa D)wrist 3- Superficial branch of radial nerve descends under cover of? E) Brachioradialis F) Brachialis G)Corachobrachialis 4- What are the roots of the radial nerve? H)C5, C6 I) C5, C6, C7 C) C5, C6, C7, C8 D) C5, C6, C7, C8, T1 5- The radial nerve supplies all muscles of the anterior compartment of the arm. J) True K) False Answers: 1 B 2 C 3 A 4 D 5 B 6 D 7 A 8 C 9 A
- 21. A. Ape hand. B. Claw hand. C. Wrist drop. Mohammed, A 28-year-old man, was horseback riding with his partner when the horse he was riding stumbled, throwing him from the saddle. In order to break his fall, Mohammed stretched out his right hand, he felt severe pain in his arm. At the emergency room, the doctor examined the arm,patient is unable to extend the wrist. The doctor ordered X-Ray for the arm. The radiologist ,who examined the X-rays, found fracture in the upper part of humerus. According to this case, please answer the following questions: 1) Which of the following is LEAST likely to happen in this case: A. Loss of sensation in the lateral side of dorsum of the hand. B. Extension of the medial fingers. C. Loss of ability of abduction of the pollicis. D. Extension of the elbow joint. 2) The name of injured region of the humerus : A. Intertubercular groove B. Bicipital groove C. Spiral groove D. Surgical neck 3) this deformity of mandatory flexion of the wrist is known as : Answe rs: 1 B 2 C Answers: 10- 1. Extensor carpi radialis brevis. 2.Extensor carpi ulnaris. 3.Supinator. 4.Abductor pollicis longus. 5.Extensor pollicis brevis. 11 1. Flexion of the wrist with Abduction. 2. Claw hand. 3. Wasting of Hypothenar Eminence. 10List 4 muscles supplied by the deep branch of radial nerve. 11A little girl injured her wrist while playing. Upon clinical examination it was determined that the ulnar nerve was injured. List 3 characteristics the physician could have seen while examining the patient. Questions
- 22. Leaders: Nawaf AlKhudairy Jawaher Abanumy Ghada Almazrou anatomyteam436@gmail.com @anatomy436 Members: Alanoud Alsaikhan Danyah Saja Deena AlNowiser Maha Alissa Minyal Bawazier Lara Alsaleem