1.4 Work with data types and variables, numeric data, string data.pptx
- 1. PYTHON PROGRAMMING WITH WEB FRAMEWORKS – CSE304 This presentation contains the concepts related to work with data types and variables, numeric data, string data
- 2. Data Types • When you develop a Python program, you work with variables that store data. • A data type defines the type of data for a value. • 3 types of basic Python data types: 2
- 3. 3
- 4. Data Types 4
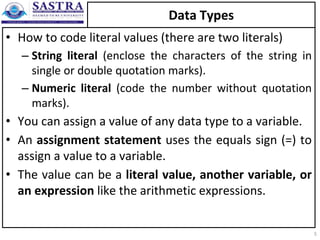
- 5. Data Types • How to code literal values (there are two literals) – String literal (enclose the characters of the string in single or double quotation marks). – Numeric literal (code the number without quotation marks). • You can assign a value of any data type to a variable. • An assignment statement uses the equals sign (=) to assign a value to a variable. • The value can be a literal value, another variable, or an expression like the arithmetic expressions. 5
- 6. Variables • A Python variable is a symbolic name that is a reference or pointer to an object. • Once an object is assigned to a variable, you can refer to the object by that name anywhere inside the program. • How to name variables ? – Give meaningful names. That means that it should be easy to tell and easy to remember. – Avoid abbreviations. – Use underscore notation. (example: tax_rate) – You may use camel case. (example: taxRate) 6
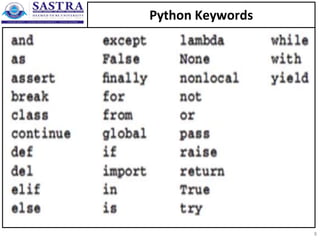
- 7. Rules for naming variables • A variable name must begin with a letter or underscore. • A variable name can't contain spaces, punctuation, or special characters other than the underscore. • A variable name can't begin with a number, but can use numbers later in the name. • A variable name can't be the same as a keyword that's reserved by Python. 7
- 9. Python 3.9.X Keywords List • 36 keywords 9
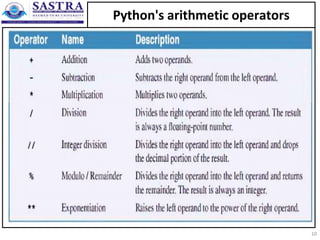
- 11. How to work with numeric data • The order of precedence for arithmetic expressions: • Examples that show the order of precedence and use of parentheses 11
- 12. How to work with numeric data • An arithmetic expression consists of one or more operands that are operated upon by arithmetic operators. • No need of spaces before and after the arithmetic operators. • When an expression mixes integer and floating-point numbers, Python converts the integers to floating- point numbers. • Use parentheses to clarify the sequence of operations (when multiple operators are used). Otherwise, Python applies its order of precedence. 12
- 13. How to work with numeric data • Compound assignment operators provide a shorthand way to code common assignment statements. • Besides the compound operators in the table. Python offers /=. //=. %=, and **=. • When working with floating-point numbers, be aware that they are approximations, not exact values. This can cause inaccurate results. 13
- 14. Other Operators • Comparison Operators: !=, ==, <, <=, >, >= • Unary Operators: Unary plus (+) Unary minus (-) • Bitwise Operators &(AND), |(OR), ^(XOR), ~(One's Compliment), << (Left Shift), >>(Right Shift) 14
- 15. Other Operators • Logical Operators: and, or, not • Assignment Operators: =, +=, -+, *=, /=, //=,... • Membership Operators: in, not in • Identity Operators: is , is not 15
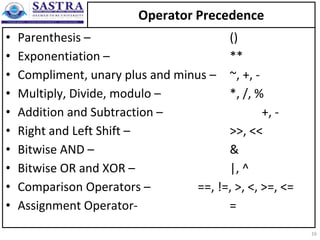
- 16. Operator Precedence • Parenthesis – () • Exponentiation – ** • Compliment, unary plus and minus – ~, +, - • Multiply, Divide, modulo – *, /, % • Addition and Subtraction – +, - • Right and Left Shift – >>, << • Bitwise AND – & • Bitwise OR and XOR – |, ^ • Comparison Operators – ==, !=, >, <, >=, <= • Assignment Operator- = 16
- 17. How to use the interactive shell for testing numeric operations • Demo 17
- 18. How to work with string data • You can also create an empty string by coding a set of quotation marks with nothing between them. • And you can assign a new value to a string variable. This works the same way it does with numeric variables. 18
- 19. How to work with string data 19
- 20. Common escape sequences • you can use escape sequences to include certain types of special characters such as new lines and tabs. • You can also use escape characters to include special characters such as quotation marks and backslashes. 20