2_5diabetes.pptx ccbcbcbcbcbcbcbcbcbcbcbc
- 1. Diabetes mellitus and clinical pharmacology: now and forever George Anikin Associate professor Department of Clinical Pharmacology and Propaedeutic of Internal Diseases
- 2. CLASSIFICATION 1. Type 1 diabetes (due to autoimmune b-cell destruction, usually leading to absolute insulin deficiency) 2. Type 2 diabetes (due to a progressive loss of b-cell insulin secretion frequently on the background of insulin resistance) 3. Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) (diabetes diagnosed in the second or third trimester of pregnancy that was not clearly overt diabetes prior to gestation) 4. Specific types of diabetes due to other causes, e.g., monogenic diabetes syndromes (such as neonatal diabetes and maturity-onset diabetes of the young [MODY]), diseases of the exocrine pancreas (such as cystic fibrosis), and drug- or chemical-induced diabetes (such as with glucocorticoid use, in the treatment of HIV/AIDS, or after organ transplantation)
- 3. Prediabetes • Impaired fasting glucose. • Impaired glucose tolerance. Capillary BS Venous BS fasting < 6,1 mmol/L < 7,0 mmol/L 2 hours after GTT ≥ 7,8 и < 11,1 mmol/L ≥7,8 и < 11,1 mmol/L Capillary BS Venous BS fasting ≥ 5,6 и < 6,1 mmol/L ≥ 6,1 и < 7,0 mmol/L 2 hours after GTT < 7,8 mmol/L < 7,8
- 5. Main classes of hypoglycemic drugs Biguanides TZDs DPP-4 inhibitor Insulins* SGLT-2 GLP-1 receptor agonists Sulfonylureas Metformin Pioglitazone Rosiglitazone Glyburide Glipizide Glimepirid Sitagliptin Saxagliptin Linagliptin Alogliptin α-Glucosidase inhibitors Liraglutide Albiglutide Lixisenatide Dulaglutide Canagliflozin Dapagliflozin Empagliflozin Acarbose Miglitol Meglitinides Repaglinide Nateglinide
- 6. Drugs, improving insulin sensitivity Metformin, Thiazolidinediones
- 7. Metformin
- 8. Metformin mechanism of action • Decreases hepatic glucose production • Improves insulin sensitivity of muscle and fat tissues • HbA1с– 1-2%
- 9. Extensive experience Rare hypoglycemia ↓ CVD events (UKPDS) Relatively higher A1C efficacy Low price Metformin advanteges
- 10. Gastrointestinal side effects (diarrhea, abdominal cramping, nausea) Vitamin B12 deficiency Contraindications: eGFR 45 mL/min/1.73 m2, acidosis, hypoxia, dehydration, etc. Lactic acidosis risk (rare) Metformin disadvanteges
- 12. Contraindications Met • Severe renal impairment (eGFR below 45 mL/min/1.73 m2) • Known hypersensitivity to Metformin hydrochloride. • Acute or chronic metabolic acidosis, including diabetic ketoacidosis, with or without coma. Diabetic ketoacidosis should be treated with insulin.
- 14. TZD mechanism of action • Decreases hepatic glucose production • Improves insulin insulin sensitivity of muscle and fat tissues • HbA1с– 0,5–1,4 %
- 15. Rare hypoglycemia Relatively higher A1C efficacy Durability ↓ Triglycerides (pioglitazone) ↓ CVD events (PROactive, pioglitazone) ↓ Risk of stroke and MI in patients without diabetes and with insulin resistance and history of recent stroke or TIA (pioglitazone) Advantages TZD
- 16. ↑ Weight Edema/heart failure Bone fractures ↑ LDL-C (rosiglitazone) Disadvantages TZD
- 17. TZD CONTRAINDICATIONS • Initiation in patients with established NYHA Class III or IV heart failure • Use in patients with known hypersensitivity to pioglitazone or any other component of pioglitazone hydrochloride • Pregnancy and lactation.
- 18. Drugs, stimulated insulin secretion • Sulfonylureas 2nd generation – Glyburide – Glipizide – Glimepiride
- 20. SU mechanism of action ↑ Insulin secretion – HbA1с– 1–2 %
- 21. Extensive experience ↓ Microvascular risk (UKPDS) Relatively higher A1C efficacy SU Advantages
- 23. SU Contraindications ABSOLUTE • Hypersensitivity to sulfa drugs or other sulfonylureas • History of adverse hematologic response to the sulfonylurea • Pregnancy and lactation. RELATIVE • Insufficient pancreatic tissue (lack of insulin secretory capacity) • Glyburide if history of glyburide-induced hepatitis • Chlorpropamide if history of chlorpropamide-induced cholestatic jaundice • History of sulfonylurea-induced porphyria • History of photoxicity associated with sulfonylurea therapy • History of SIADH while taking chlorpropamide or tolbutamide.
- 24. Drugs with incretinlike activity • DPP-4 Inhibitors • GLP-1 receptor agonists DPP-4 Inhibitors DPP-4 inactivate incretins Incretins: GLP-1, GIP ↑ Insulin secretion ↓ Glucagon secretion ↓ plasma glucose FOOD
- 26. DPP-4 inhibitors mechanism of action • ↑ Insulin secretion (glucose dependent) • ↓ Glucagon secretion (glucose dependent) • HbA1с– 0,5-1,0 %
- 27. Rare hypoglycemia Well tolerated DPP-4 Advantages
- 28. Angioedema/urticaria and other immune- mediated dermatological effects ? Acute pancreatitis ↑ Heart failure hospitalizations (saxagliptin; ? alogliptin) High price DPP-4 Disadvantages
- 29. DPP-4 Contraindications • Individuals with sensitivity to DPP-4 or any of its components • Pancreatitis
- 30. GLP-1 receptor agonists • Exenatide • Exenatide extended release • Liraglutide • Albiglutide • Lixisenatide • Dulaglutide
- 31. GLP-1 mechanism of action • ↑ Insulin secretion (glucose dependent) • ↓ Glucagon secretion (glucose dependent) • Slows gastric emptying • ↑ Satiety • HbA1с–0,8-1,8%
- 32. Rare hypoglycemia ↓ Weight ↓ Postprandial glucose excursions ↓ Some cardiovascular risk factors Associated with lower CVD event rate and mortality in patients with CVD (liraglutide) GLP-1 Advantages
- 33. Gastrointestinal side effects (nausea/vomiting/diarr hea) ↑ Heart rate ? Acute pancreatitis C-cell hyperplasia/medulla ry thyroid tumors in animals Injectable Training requirements GLP-1 Disadvantages
- 34. GLP-1 Contraindications • Severe renal and hepatic impairment • Ketoacidosis • Pregnancy and lactation.
- 35. Drugs, inhibits intestinal a-glucosidase – Acarbose – Miglitol
- 36. Acarbose mechanism of action HbA1с0,5–0,8 %
- 37. Rare hypoglycemia ↓ Postprandial glucose excursions ? ↓ CVD events in prediabetes (STOP-NIDDM) Nonsystemic Acarbose Advantages
- 38. Generally modest A1C efficacy Gastrointestinal side effects (flatulence, diarrhea) Frequent dosing schedule Acarbose Disadvantages
- 39. a-Glucosidase inhibitors Contraindications • Known hypersensitivity to the drug • Diabetic ketoacidosis • Cirrhosis • Inflammatory bowel disease • Intestinal obstruction • chronic intestinal diseases associated with marked disorders of digestion or absorption • Pregnancy and lactation
- 40. Drugs, that inhibit the reabsorption of glucose in kidneys SGLT2 inhibitors – Canagliflozin – Dapagliflozin‡ – Empagliflozin HbA1с - 0,8-0,9%
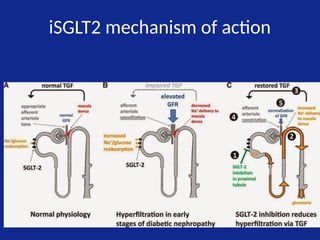
- 41. iSGLT2 mechanism of action • Blocks glucose reabsorption by the kidney, increasing glucosuria
- 42. iSGLT2 mechanism of action
- 43. Rare hypoglycemia ↓ Weigh ↓ Blood pressure Associated with lower CVD event rate and mortality in patients with CVD (empagliflozin EMPA-REG OUTCOME) iSGLT-2 Advantages
- 44. Genitourina ry infections Polyuria Volume depletion/hypotension /dizziness ↑ LDL-C ↑ Creatinine (transient) Diabetic ketoacidosis Urinary tract infections leading to urosepsis, pyelonephritis iSGLT-2 Disadvantages
- 45. Canagliflozin (Invokana) Dapagliflozin (Farxiga) Empagliflozin(Jardiance) Efficacy ↓ A1C by ~ 0.7 to 1 percentage point ↓ A1C by ~ 0.5 to 0.7 percentage points ↓ A1C by ~ 0.4 to 0.9 percentage points eGFR must be > 45 mL/min > 60 mL/min > 45 mL/min Dose 100 mg/day, before 1st meal of day; ↑ to 300 mg if needed and if eGFR > 60 5 mg/day, taken in morning, with or w/out food; ↑ to 10 mg if needed 10 mg/day, taken in morning, with or w/out food; ↑ to 25 mg if needed Advantages Low risk of hypoglycemia ↓ wgt by 2.2-3.3% (~ 5 lb) ↓ systolic BP by ~3 to 5 mm Hg ↑ HDL by ~8% Low risk of hypoglycemia ↓ wgt by ~ 5 lb ↓ systolic BP by ~3 to 5 mm Hg Low risk of hypoglycemia ↓ wgt by ~ 3 lb ↓ systolic BP by ~3 to 5 mm Hg Disadvantages ↑ LDL by ~4 to 8% ↑ LDL by 2.9% ↑ LDL by ~5-7% Common side effects Genital yeast infections (women: 10-11%; men: 4%) UTI: 4 to 6% Increased urination Dehydration Hyperkalemia Genital yeast infections (women: 7-8%; men: 3%) UTI: 4 to 6% Increased urination Dehydration Nasopharyngitis Genital yeast infections (women: 5-6%; men: 2- 3%) UTI: 8 to 9% Increased urination Dehydration Use with Caution in Patients > 65 years old (more prone to volume depletion; lower efficacy) At risk for hyperkalemia (ACEi or ARB) Prone to DKA > 65 years old (more prone to volume depletion) With h/o bladder cancer, bladder cancer risk factors, hematuria Prone to DKA > 75 years old (more prone to volume depletion & UTIs) Prone to DKA Patient Education (1) Drink plenty of fluids; (2) Talk to HCP if ↓ in kcal intake; (3) Sx of DKA; (4) Sx of UTI
- 46. iSGLT2 contraindications • Ketoacidosis • Pregnancy and lactation, • Decreased GFR < 45 ml/min/1.73 м2 (Dapagliflozin, Canagliflozin и Empagliflozin)
- 47. Insulins Rapid-acting analogs Short-acting Intermediate-acting Basal insulin analogs Lispro Aspart Glulisine Inhaled insulin Human Regular Human NPH Glargine Detemir Degludec
- 50. Thank you
Editor's Notes
- #7: Model of metformin action in the hepatocyte. Metformin enters the cell through transporters such as SLC22A1 and inhibits mitochondrial complex I. Complex I inhibition results in reduced ATP levels and an accumulation of AMP. AMP binds to the so called ‘P-site’ at the adenylate cyclase enzyme and inhibits its activity, leading to reduced generation of cAMP upon stimulation of the glucagon receptor. As a result, PKA activation and its downstream pathways are inhibited. Gluconeogenesis is suppressed as a result of reduced activity of enzymes involved in the gluconeogenic flux (for example, owing to lack of phosphorylation of PFK/FBPase 1) and reduced gene expression (owing to decreased phosphorylation of the transcription factor CREB‑1). Metformin-induced change in energy charge also activates AMPK, which suppresses fat metabolism and possibly also contributes to the reduced gluconeogenic gene expression. In addition, AMP and ATP have an independent modulatory role on these pathways. Abbreviations: AMPK, 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase; CREB‑1, cAMP response element-binding protein; CRTC2, CREB regulated transcription coactivator 2; G6Pase, glucose‑6-phosphatase; I3PR, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptors; PEPCK, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; PFK/FBPase 1, 6‑phosphofructo‑2-kinase/fructose‑2,6-bisphosphatase 1; PGC‑1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor‑γ coactivator‑1α; PKA, protein kinase A; SLC22A1, solute carrier family 22 member 1. ФЕППК Фосфоенолпирува карбоксикиназа
- #24: Глюкозозависимый инсулинотропный полипептид

![CLASSIFICATION
1. Type 1 diabetes (due to autoimmune b-cell destruction, usually
leading to absolute insulin deficiency)
2. Type 2 diabetes (due to a progressive loss of b-cell insulin secretion
frequently on the background of insulin resistance)
3. Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) (diabetes diagnosed in the
second or third trimester of pregnancy that was not clearly overt
diabetes prior to gestation)
4. Specific types of diabetes due to other causes, e.g., monogenic
diabetes syndromes (such as neonatal diabetes and maturity-onset
diabetes of the young [MODY]), diseases of the exocrine pancreas
(such as cystic fibrosis), and drug- or chemical-induced diabetes
(such as with glucocorticoid use, in the treatment of HIV/AIDS, or
after organ transplantation)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/25diabetes-241102161729-f5676aa9/85/2_5diabetes-pptx-ccbcbcbcbcbcbcbcbcbcbcbc-2-320.jpg)