3GPP LTE.ppt
- 1. An Introduction of 3GPP Long Term Evolution (LTE) Mujib Tamboli
- 2. 2 Reference http://www.tcs.com “LTE-Advanced: Future of Mobile Broadband,” TATA Consultancy Services Takehiro Nakamura ,“Proposal for Candidate Radio Interface Technol ogies for IMT‐Advanced Bas d on LTE Release 10 and Beyond,” 3GPP TSG‐RAN Chairman “3GPP LTE Channels and MAC Layer,” EventHelix.com Inc. 2009 Ahmed Hamza, Network Systems Laboratory Simon Fraser University, “Long Term Evolution (LTE) - A Tutorial,” October 13, 2009 Jim Zyren, “Overview of the 3GPP Long Term Evolution Physical Layer,” Document Number: 3GPP EVOLUTIONWP Rev0 07/2007 David Astély, Erik Dahlman, Anders Furuskär, Ylva Jading, Magnus Lindström, and Stefan Parkvall, Ericsson Research, “LTE: The Evolution of Mobile Broadband” , IEEE Communications Magazine, April 2009
- 3. 3 Outline History of 3GPP LTE Basic Concepts of LTE Introduction of LTE Protocol Compare with LTE and LTE-Advanced Conclusion
- 4. 4 What is LTE ? In Nov. 2004, 3GPP began a project to define the long-term evolution (LTE) of Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) cellular technology Higher performance Backwards compatible Wide application
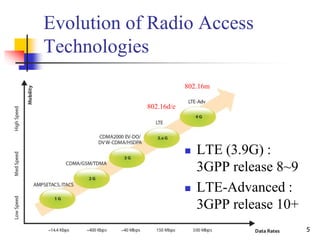
- 5. 5 Evolution of Radio Access Technologies LTE (3.9G) : 3GPP release 8~9 LTE-Advanced : 3GPP release 10+ 802.16d/e 802.16m
- 6. 6 LTE Basic Concepts LTE employs Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) for downlink data transmission and Single Carrier FDMA (SC-FDMA) for uplink transmission
- 7. 7 Multipath-Induced Time Delays Result in Inter-Symbol Interference (ISI) ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( t n m t S t S t y y(t) : output signal S(t) : input signal S(t-m) : delayed m time input signal n(t) : noise y(t) βS(t-m) S(t)
- 8. 8 Equalizers in Receiver Against Frequency Selective Fading Channel transform function Hc(f) Equalizers transform function Heq(f) (Receiver) fm j c e f H 2 1 ) ( fm j c c e f H f H 2 1 1 ) ( 1 ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( m t S t S t y
- 9. 9 Frequency Selective Fading the coherence bandwidth of the channel is smaller than the bandwidth of the signal It may be useless for increasing transmission power Frequency Correlation > 0.9 Bc = 1 / 50α α is r.m.s. delay spread
- 11. 11 FDM vs. OFDM
- 12. 12 LTE-Downlink (OFDM) Improved spectral efficiency Reduce ISI effect by multipath Against frequency selective fading
- 13. 13 LTE Uplink (SC-FDMA) SC-FDMA is a new single carrier multiple access technique which has similar structure and performance to OFDMA A salient advantage of SC- FDMA over OFDM is low to Peak to Average Power Ratio (PAPR) : Increasing battery life
- 15. 15 Generic Frame Structure Allocation of physical resource blocks (PRBs) is handled by a scheduling function at the 3GPP base station (eNodeB) Frame 0 and frame 5 (always downlink)
- 16. 16 Resource Grid One frame is 10ms 10 subframes One subframe is 1ms 2 slots One slot is 0.5ms N resource blocks [ 6 < N < 110] One resource block is 0.5ms and contains 12 subcarriers from each OFDM symbol
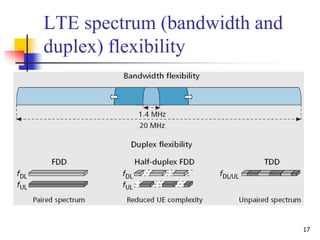
- 17. 17 LTE spectrum (bandwidth and duplex) flexibility
- 18. 18 LTE Downlink Channels Paging Channel Paging Control Channel Physical Downlink Shared Channel
- 19. 19 LTE Uplink Channels Random Access Channel Physical Radio Access Channel Physical Uplink Shared Channel CQI report
- 20. 20 LTE Release 8 Key Features (1/2) High spectral efficiency OFDM in Downlink Single‐Carrier FDMA in Uplink Very low latency Short setup time & Short transfer delay Short hand over latency and interruption time Support of variable bandwidth 1.4, 3, 5, 10, 15 and 20 MHz
- 21. 21 LTE Release 8 Key Features (2/2) Compatibility and interworking with earlier 3GPP Releases FDD and TDD within a single radio access technology Efficient Multicast/Broadcast
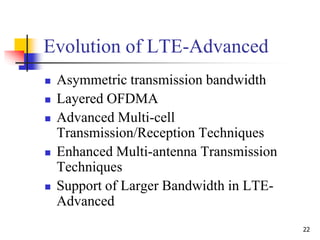
- 22. 22 Evolution of LTE-Advanced Asymmetric transmission bandwidth Layered OFDMA Advanced Multi-cell Transmission/Reception Techniques Enhanced Multi-antenna Transmission Techniques Support of Larger Bandwidth in LTE- Advanced
- 23. 23 Asymmetric transmission bandwidth Symmetric transmission voice transmission : UE to UE Asymmetric transmission streaming video : the server to the UE (the downlink)
- 24. 24 Layered OFDMA The bandwidth of basic frequency block is, 15–20 MHz Layered OFDMA radio access scheme in LTE-A will have layered transmission bandwidth, support of layered environments and control signal formats
- 25. 25 Advanced Multi-cell Transmission/Reception Techniques In LTE-A, the advanced multi-cell transmission/reception processes helps in increasing frequency efficiency and cell edge user throughput Estimation unit Calculation unit Determination unit Feedback unit
- 26. 26 Enhanced Multi-antenna Transmission Techniques In LTE-A, the MIMO scheme has to be further improved in the area of spectrum efficiency, average cell throughput and cell edge performances In LTE-A the antenna configurations of 8x8 in DL and 4x4 in UL are planned
- 27. 27 Enhanced Techniques to Extend Coverage Area Remote Radio Requirements (RREs) using optical fiber should be used in LTE-A as effective technique to extend cell coverage
- 28. 28 Support of Larger Bandwidth in LTE-Advanced Peak data rates up to 1Gbps are expected from bandwidths of 100MHz. OFDM adds additional sub-carrier to increase bandwidth
- 30. 30 Conclusion LTE-A helps in integrating the existing networks, new networks, services and terminals to suit the escalating user demands LTE-Advanced will be standardized in the 3GPP specification Release 10 (LTE-A) and will be designed to meet the 4G requirements as defined by ITU
- 31. 31 Backup
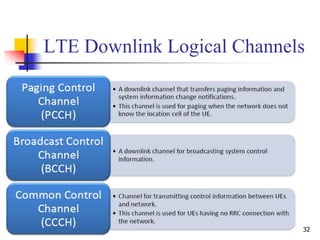
- 32. 32 LTE Downlink Logical Channels
- 33. 33 LTE Downlink Logical Channels
- 34. 34 LTE Downlink Transport Channel
- 35. 35 LTE Downlink Transport Channel
- 36. 36 LTE Downlink Physical Channels
- 37. 37 LTE Downlink Physical Channels
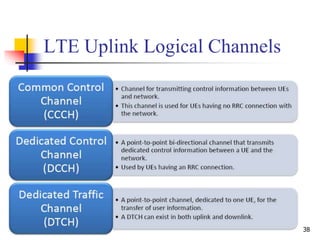
- 38. 38 LTE Uplink Logical Channels
- 39. 39 LTE Uplink Transport Channel
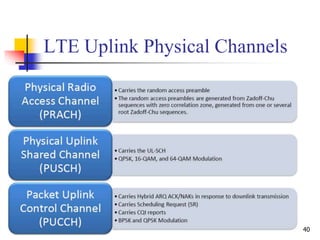
- 40. 40 LTE Uplink Physical Channels














![16
Resource Grid
One frame is 10ms
10 subframes
One subframe is 1ms
2 slots
One slot is 0.5ms
N resource blocks
[ 6 < N < 110]
One resource block is 0.5ms
and contains 12 subcarriers
from each OFDM symbol](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3gpplte-231005050142-e174592b/85/3GPP-LTE-ppt-16-320.jpg)