9380673.ppt
- 1. The Chemistry of Coordination Compounds Chapter 20 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
- 2. What is a transition metal? Transition metals have incompletely filled d subshells or produce ions with incompletely filled d subshells. This is responsible for many of the properties of transition metals including color, catalytic activity, formation of paramagnetic compounds, and the tendency to form complex ions.
- 4. Is zinc a transition metal? Explain your answer. Write out the electronic structure of Zn and of Zn2+
- 5. 20.1 Electron Configurations and Other Properties of the First-Row Transition Metals
- 6. 20.1 Physical Properties of Elements K to Zn
- 7. Oxidation States of the 1st Row Transition Metals 20.1
- 8. 20.1 Ionization Energies for the 1st Row Transition Metals
- 9. General Properties of Transition Metals Small atomic radii and close packing—strong metallic bonds Transition metals have… • Higher ________________________ • Higher ________________________ • Higher ________________________ • Higher ________________________ • Higher ________________________ …than _________________________ p.650
- 10. Coordination Compounds A ________________________ typically consists of a complex ion and a counter ion. A ________________________ contains a central metal cation bonded to one or more molecules or ions. The molecules or ions that surround the metal in a complex ion are called _______. A ligand has ______________ unshared pair of valence electrons H O H •• H N H H •• • • Cl •• • • - • • C O • • 20.3 pp.653ff
- 11. Coordination Compounds 20.3 The atom in a ligand that is bound directly to the metal atom is the _________________________. H O H •• H N H H The number of donor atoms surrounding the central metal atom in a complex ion is the _______________________. Ligands with: one donor atom _____________ two donor atoms three or more donor atoms H2O, NH3, Cl- ethylenediamine EDTA _____________ _____________
- 12. Coordination Compounds 20.3 H2N CH2 CH2 NH2 •• •• ____________ ligand ____________ ligand (EDTA) Bidentate and polydentate ligands are called ______________
- 14. What are the oxidation numbers of the metals in K[Au(OH)4] and of [Cr(NH3)6](NO3)3 ? OH- has charge of ___ K+ has charge of ___ ? Au + __ + (__x-__) = 0 Au = +___ NO3 - has charge of __ NH3 has no charge ? Cr + (__x__) + (__x-__) = 0 Cr = ___ 20.3 Ex. 20.1, p.655
- 15. Naming Coordination Compounds 20.3 • The cation is named before the anion. • Within a complex ion, the ligands are named first in ________________ order and the metal atom is named last. • The names of anionic ligands end with the letter o. Neutral ligands are usually called by the name of the molecule. The exceptions are H2O (aquo), CO (carbonyl), and NH3 (amine). • When several ligands of a particular kind are present, the Greek prefixes di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, and hexa- are used to indicate the number. If the ligand contains a Greek prefix, use the prefixes bis, tris, and tetras to indicate the number. • The oxidation number of the metal is written in Roman numerals following the name of the metal. • If the complex is an ion, its name ends in –ate.
- 16. 20.3 Names of Common Ligands in Coordination Compounds
- 17. 20.3 What is the systematic name of [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl ? ________________________________ Write the formula of tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(II) sulfate Names of Anions Containing Metal Atoms ________________________________
- 18. Structure of Coordination Compounds 20.4 Coordination number Structure 2 4 6 Linear Tetrahedral or Square planar Octahedral
- 19. Structure of Coordination Compounds 20.4 ___________________ are compounds that are made up of the same types and numbers of atoms bonded together in the same sequence but with different spatial arrangements. ___________________ are stereoisomers that cannot be interconverted without breaking a chemical bond. cis-[Pt(NH3)2Cl2] trans-[Pt(NH3)2Cl2]
- 20. Structure of Coordination Compounds 20.4 cis-[Co(NH3)4Cl2] trans-[Co(NH3)4Cl2] Are these additional geometric isomers of [Co(NH3)4Cl2]?
- 21. Structure of Coordination Compounds 20.4 _________________ are non-superimposable mirror images. cis-[Co(en)2Cl2] trans-[Co(en)2Cl2] _________________ ____________ _________________ ____________
- 22. Structure of Coordination Compounds 20.4 _______________________ are optically active.
- 23. _________________________ – rotates plane polarized light to the right _________________________ – rotates plane polarized light to the left _________________________ rotate plane polarized light by the same amount, but in opposite directions _________________________ – an equimolar mixture of enantiomers
- 24. Coordination compounds are used in: ___________ – extracting gold and silver, purifying nickel ___________ – treating lead poisoning and cancer ___________ – identification of certain chemicals ___________ – largely banned from modern detergents because the phosphates caused eutrophication of lakes
- 25. _________ _________ _________ explains the bonding of complex ions in terms of two electrostatic forces 1. _________ between the positive metal ion and the negatively charged ligand or the negatively charged end of a polar ligand 2. _________ between the electron lone pairs on the ligands and the d orbitals of the metals pp.659ff
- 26. Bonding in Coordination Compounds 20.5 All equal in energy in the absence of _____________ !
- 27. Bonding in Coordination Compounds 20.5 Isolated transition metal atom Bonded transition metal atom As a result of these two metal-ligand electrostatic interactions, the 5 d orbitals in an octahedral complex are split between two sets of energy levels: a higher level with two orbitals and a lower level with three levels. Crystal field splitting (D) . p.659
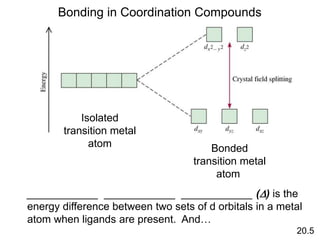
- 28. Bonding in Coordination Compounds 20.5 Isolated transition metal atom Bonded transition metal atom ____________ ____________ ____________ (D) is the energy difference between two sets of d orbitals in a metal atom when ligands are present. And…
- 29. Bonding in Coordination Compounds 20.5 D = hn
- 30. The absorption maximum for the complex ion [Co(NH3)6]3+ occurs at 470 nm. What is the color of the complex and what is the crystal field splitting in kJ/mol? Absorbs blue, will appear orange. D = hn hc l = (6.63 x 10-34 J s) x (3 x 108 m s-1) 470 x 10-9 m = = __________ J D (kJ/mol) = 4.23 x 10-19 J/atom x 6.022 x 1023 atoms/mol = ___________ kJ/mol 20.5
- 31. Bonding in Coordination Compounds 20.5 I- < Br- < Cl- < OH- < F- < H2O < NH3 < en < CN- < CO Spectrochemical Series Strong field ligands _____________ D Weak field ligands _____________ D
- 32. Bonding in Coordination Compounds 20.5
- 33. Reactions of coordination compounds Coordination compounds typically undergo ligand exchange (a/k/a ligand substitution) in solution













![What are the oxidation numbers of the metals in
K[Au(OH)4] and of [Cr(NH3)6](NO3)3 ?
OH- has charge of ___
K+ has charge of ___
? Au + __ + (__x-__) = 0
Au = +___
NO3
- has charge of __
NH3 has no charge
? Cr + (__x__) + (__x-__) = 0
Cr = ___
20.3
Ex. 20.1, p.655](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9380673-230126023309-5cf672a6/85/9380673-ppt-14-320.jpg)


![20.3
What is the systematic name of
[Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl ?
________________________________
Write the formula of
tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(II) sulfate
Names of Anions
Containing Metal Atoms
________________________________](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9380673-230126023309-5cf672a6/85/9380673-ppt-17-320.jpg)

![Structure of Coordination Compounds
20.4
___________________ are compounds that are made up of
the same types and numbers of atoms bonded together in the
same sequence but with different spatial arrangements.
___________________ are stereoisomers that cannot be
interconverted without breaking a chemical bond.
cis-[Pt(NH3)2Cl2] trans-[Pt(NH3)2Cl2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9380673-230126023309-5cf672a6/85/9380673-ppt-19-320.jpg)
![Structure of Coordination Compounds
20.4
cis-[Co(NH3)4Cl2] trans-[Co(NH3)4Cl2]
Are these
additional
geometric
isomers of
[Co(NH3)4Cl2]?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9380673-230126023309-5cf672a6/85/9380673-ppt-20-320.jpg)
![Structure of Coordination Compounds
20.4
_________________ are non-superimposable mirror images.
cis-[Co(en)2Cl2] trans-[Co(en)2Cl2]
_________________
____________
_________________
____________](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9380673-230126023309-5cf672a6/85/9380673-ppt-21-320.jpg)







![The absorption maximum for the complex ion [Co(NH3)6]3+
occurs at 470 nm. What is the color of the complex and
what is the crystal field splitting in kJ/mol?
Absorbs blue, will appear orange.
D = hn
hc
l
=
(6.63 x 10-34 J s) x (3 x 108 m s-1)
470 x 10-9 m
= = __________ J
D (kJ/mol) = 4.23 x 10-19 J/atom x 6.022 x 1023 atoms/mol
= ___________ kJ/mol
20.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9380673-230126023309-5cf672a6/85/9380673-ppt-30-320.jpg)


