A Report on Routers
- 2. Explanation Router is Internetworking device that forwards data packets toward their destinations through a process known as routing. A router is a device that forwards data packets between computer network creating an overlay internetwork. A router is connected to two or more data lines from different networks. When a data packet comes in one of the lines, the router reads the address information in the packet to determine its ultimate destination.
- 3. Explanation Then, using information in its routing table or routing policy, it directs the packet to the next network on its journey. Routers perform the "traffic directing" functions on the internet. A data packet is typically forwarded from one router to another through the networks that constitute the internetwork until it reaches its destination node
- 4. Routers Complex networks usually require routers instead of bridges because routers provide filtering and network traffic control. Routers have the ability to connect multiple segments and multiple networks. Networks connected by multiple routers are called internetworks. Routers operate at the Network layer of the OSI model. Routers use the logical address of the OSI Network layer. Routers do not forward broadcast traffic and therefore define broadcast domains.
- 5. Group of Routers… There are two major groups of router interfaces: LAN Interfaces WAN Interfaces
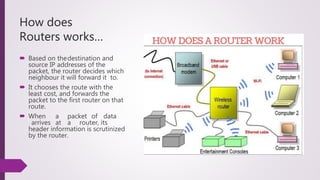
- 6. How a Router Works… When data packets are transmitted over a network (say the Internet), they move through many routers (because they pass through many networks) in their journey from the source machine to the destinationmachine. Routers work with IP packets, meaning that it works at the level of the IP protocol.
- 7. How does Routers works… Based on thedestination and source IP addresses of the packet, the router decides which neighbour it will forward it to. It chooses the route with the least cost, and forwards the packet to the first router on that route. When a packet of data arrives at a router, its header information is scrutinized by the router.
- 8. TYPES OF ROUTERS: There are several types of routers in the market. Broadband Routers Wireless Routers Core Routers Edge Router
- 10. Wireless Routers Wireless routers create a wireless signal in your home or office. So, any computer within range of Wireless routers can connect it and use Internet. It works much like a wired router but replaces wires with wireless radio signals to communicate within and to external network environments. It enables you to run a computer or gaming system from anywhere in the house without having to run cables through the walls In order to secure your Wireless routers, you simply need to come secure it with password or get your IP address. Then, you'll log on into your router with the user ID and passwords will that come with your router Example:-Netgear (Nighthawk X4S)
- 11. Core Router A core router is a router designed to operate in the Internet backbone, or core. To full fill this role, a router must be able to support multiple telecommunications interfaces of the highest speed in use in the core Internet and must be able to forward IP packets at full speed on all of them. It must also support the routing protocols being used in the core. Example:- Cisco Systems (CRS, NCS series)
- 12. Edge Router Edge devices are that which provide entry points into enterprise or service provider core networks. Examples include routers, routing switches, integrated access devices (IAD), multiplexers, and a variety of metropolitan area network (MAN) and wide area network (WAN) access devices. Edge devices also provide connections into carrier and service provider networks. Example:- Ubiquiti EdgeRouter X (ER-X), EdgeRoute
- 13. Routing Protocols A routing protocol specifies how routers communicate with each other, disseminating information that enables them to select routes between any two nodes on a computer network. Routing algorithms determine the specific choice of route. Each router has a priori knowledge only of networks attached to it directly. A routing protocol shares this information first among immediate neighbors, and then throughout the network. This way, routers gain knowledge of the topology of the network.
- 14. Types of routing protocols Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP)
- 15. Advantages While switches are the device of choice for improving performance on a network, routers are used to segment large networks into internetworks made up of smaller networks. Routers and switches are often used in combination. •Routers can connect different network architectures, such as Ethernet and Token Ring. Routers can choose the best path across the network using dynamic routing techniques. Routers can reduce network traffic because they do not retransmit network broadcast traffic.
- 16. Disadvantages Routers work only with routable network protocols; not all protocols are routable. •Routers are more expensive than bridges or repeaters. Dynamic router communications (inter-router communication) causes additional network traffic. Routers are slower than bridges or repeaters because they must analyze a data transmission from the Physical to the Network layer.