Ac single phase
- 1. Characteristics of Sinusoidal Phasors Phasor Relationships for R, L and C Impedance Parallel and Series Resonance Examples for Sinusoidal Circuits Analysis Single Phase AC
- 2. Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis • Any steady state voltage or current in a linear circuit with a sinusoidal source is a sinusoid – All steady state voltages and currents have the same frequency as the source • In order to find a steady state voltage or current, all we need to know is its magnitude and its phase relative to the source (we already know its frequency) • We do not have to find this differential equation from the circuit, nor do we have to solve it • Instead, we use the concepts of phasors and complex impedances • Phasors and complex impedances convert problems involving differential equations into circuit analysis problems
- 3. Characteristics of Sinusoids Outline: 1. Time Period: T 2. Frequency: f (Hertz) 3. Angular Frequency: (rad/sec) 4. Phase angle: Φ 5. Amplitude: Vm Im
- 4. Characteristics of Sinusoids : tVv mt sin iI1 I1 I1 I1 I1 I1 R1 R1 R 5 5 + _ IS E I1 U1 + - U I iI1 I1 I1 I1 R1 R1 R 5 5 - + IS E I1 U1 + - U I v ,i tt1 t20 Both the polarity and magnitude of voltage are changing.
- 5. Radian frequency(Angular frequency): = 2f = 2/T (rad/s) Time Period: T — Time necessary to go through one cycle. (s) Frequency: f — Cycles per second. (Hz) f = 1/T Amplitude: Vm Im i = Imsint, v =Vmsint v ,i t 20 Vm , Im Characteristics of Sinusoids :
- 6. Effective Roof Mean Square (RMS) Value of a Periodic Waveform — is equal to the value of the direct current which is flowing through an R-ohm resistor. It delivers the same average power to the resistor as the periodic current does. RIRdti T T 2 0 21 Effective Value of a Periodic Waveform T eff dti T I 0 21 22 1 2 2cos1 sin 1 2 0 2 0 22 m m T m T meff IT I T dt t T I tdtI T I 2 1 0 2 m T eff V dtv T V Characteristics of Sinusoids :
- 7. Phase (angle) tIi m sin sin0 mIi Phase angle -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6 8 0 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 <0 0 Characteristics of Sinusoids :
- 8. )sin( 1 tVv m )sin( 2 tIi m Phase difference 2121 )( ttiv 021 — v(t) leads i(t) by (1 - 2), or i(t) lags v(t) by (1 - 2) 2 21 v, i t v i 21 Out of phase t v, i v i v, i t v i 021 In phase 021 — v(t) lags i(t) by (2 - 1), or i(t) leads v(t) by (2 - 1) Characteristics of Sinusoids :
- 9. Review The sinusoidal waves whose phases are compared must: 1. Be written as sine waves or cosine waves. 2. With positive amplitudes. 3. Have the same frequency. 360°—— does not change anything. 90° —— change between sin & cos. 180°—— change between + & - 2 sin cos cos 3 2 cos sin 2 Characteristics of Sinusoids :
- 10. Phase difference 30314sin22201 tv 9030314sin222030314cos22202 ttv 120314sin2220 t 1501203021 30314cos22202 tv 30314cos22202 tv 18030314cos2220 t 210314360cos2220 t 90150314sin2220 t 60314sin2220 t 30603021 Find ? 30314cos22202 tvIf Characteristics of Sinusoids :
- 11. Phase difference v, i t v i -/3 /3 • •• 3 sin tVm 3 sin tIm Characteristics of Sinusoids :
- 12. Outline: 1. Complex Numbers 2. Rotating Vector 3. Phasors A sinusoidal voltage/current at a given frequency, is characterized by only two parameters : amplitude and phase A phasor is a Complex Number which represents magnitude and phase of a sinusoid Phasors
- 13. e.g. voltage response A sinusoidal v/i Complex transform Phasor transform By knowing angular frequency ω rads/s. Time domain Frequency domain eR v t Complex form: cosmv t V t Phasor form: j t mv t V e Angular frequency ω is known in the circuit. || mVV || mVV Phasors
- 14. Rotating Vector tIti m sin)( i Im t1 i t Im t x y max cos sin sin j t m m m j t m m I e I t jI t i t I t I I e A complex coordinates number: Real value: i(t1) Imag Phasors
- 15. Rotating Vector Vm x y 0 )sin( tVv m Phasors
- 16. Complex Numbers jbaA — Rectangular Coordinates sincos jAA j eAA — Polar Coordinates j eAAjbaA conversion: 22 baA a b arctg jbaeA j cosAa sinAb a b Real axis Imaginary axis jjje j 090sin90cos90 Phasors
- 17. Complex Numbers Arithmetic With Complex Numbers Addition: A = a + jb, B = c + jd, A + B = (a + c) + j(b + d) Real Axis Imaginary Axis AB A + B Phasors
- 18. Complex Numbers Arithmetic With Complex Numbers Subtraction : A = a + jb, B = c + jd, A - B = (a - c) + j(b - d) Real Axis Imaginary Axis AB A - B Phasors
- 19. Complex Numbers Arithmetic With Complex Numbers Multiplication : A = Am A, B = Bm B A B = (Am Bm) (A + B) Division: A = Am A , B = Bm B A / B = (Am / Bm) (A - B) Phasors
- 20. Phasors A phasor is a complex number that represents the magnitude and phase of a sinusoid: tim cos mI Phasor Diagrams • A phasor diagram is just a graph of several phasors on the complex plane (using real and imaginary axes). • A phasor diagram helps to visualize the relationships between currents and voltages. Phasors
- 21. )sin()cos()( tAjtAeAAe tjtj )cos(||}Re{ tAAe tj Complex Exponentials j eAA A real-valued sinusoid is the real part of a complex exponential. Complex exponentials make solving for AC steady state an algebraic problem. Phasors
- 22. Phasor Relationships for R, L and C Outline: I-V Relationship for R, L and C, Power conversion
- 23. Phasor Relationships for R, L and C v~i relationship for a resistor _ v i R + S tIt R V R v i m m sinsin tVv m sin Relationship between RMS: R V I Wave and Phasor diagrams: v、i t v i I V R V I Resistor Suppose
- 24. Time domain Frequency domainResistor With a resistor θ﹦ϕ, v(t) and i(t) are in phase . )cos()( )cos()( wtIti wtVtv m m IRV RIV eRIeV eRIeV mm j m j m wtj m wtj m )()( Phasor Relationships for R, L and C
- 25. PowerResistor _ v i R + P 0 tItVvip mm sinsin tVI mm 2 sin t VI mm 2cos1 2 tIVIV 2cos v, i t v i P=IV T pdt T P 0 1 T VIdttVI T 0 2cos1 1 R V RIIVP 2 2 • Average Power • Transient Power Note: I and V are RMS values. Phasor Relationships for R, L and C
- 26. Resistor , R=10,Find i and Ptv 314sin311 V V V m 220 2 311 2 A R V I 22 10 220 ti 314sin222 WIVP 484022220 Phasor Relationships for R, L and C
- 27. v~i relationshipInductor dt di Lvv AB tLI dt tId L dt di Lv m m cos sin 90sin tLIm 90sin tVm t vdt L i 1 t vdt L vdt L 0 0 11 t vdt L i 0 0 1 tIi m sinSuppose Phasor Relationships for R, L and C
- 28. v~i relationshipInductor 90sin tLIm dt di Lv 90sin tVm LIV mm Relationship between RMS: LIV L V I fLLXL 2 For DC,f = 0,XL = 0. fXL v(t) leads i(t) by 90º, or i(t) lags v(t) by 90º Phasor Relationships for R, L and C
- 29. v ~ i relationshipInductor v, i t v i eL V I LXIjV Wave and Phasor diagrams: Phasor Relationships for R, L and C
- 30. PowerInductor vip tItV mm sin90sin ttIV mm sincos t IV mm 2sin 2 tVI 2sin P t v, i t v i ++ --22 max 2 1 LILIW m 2 00 2 1 LiLidividtW it Energy stored: T T tdtVI T pdt T P 0 0 02sin 11 Average Power Reactive Power L L X V XIIVQ 2 2 (Var) Phasor Relationships for R, L and C
- 31. Inductor L = 10mH,v = 100sint,Find iL when f = 50Hz and 50kHz. 14.310105022 3 fLX L Atti A X V I L L 90sin25.22 5.22 14.3 2/100 50 31401010105022 33 fLX L mAtti mA X V I L L k 90sin25.22 5.22 14.3 2/100 50 Phasor Relationships for R, L and C
- 32. v ~ i relationshipCapacitor _ v i + C dt dv C dt dq i tVv m sinSuppose: 90sincos tCVtCVi mm 90sin tIm t tt idt c vidt c idt c idt c v 0 0 0 0 1111 i(t) leads v(t) by 90º, or v(t) lags i(t) by 90º Relationship between RMS: CX V C V CVI 1 fCC XC 2 11 For DC,f = 0, XC f XC 1 mm CVI Phasor Relationships for R, L and C
- 33. _ v i + C tj m tj m eCVj dt edV C dt tdv Cti )( )( v(t) = Vm ejt Represent v(t) and i(t) as phasors: CjX V VCωjI == • The derivative in the relationship between v(t) and i(t) becomes a multiplication by in the relationship between and . • The time-domain differential equation has become the algebraic equation in the frequency-domain. • Phasors allow us to express current-voltage relationships for inductors and capacitors much like we express the current-voltage relationship for a resistor. v ~ i relationshipCapacitor V I wC j Phasor Relationships for R, L and C
- 34. v ~ i relationshipCapacitor v, i t v i I V CXIjV Wave and Phasor diagrams: Phasor Relationships for R, L and C
- 35. PowerCapacitor Average Power: P = 0 Reactive Power C C X V XIIVQ 2 2 (Var) 90sinsin tItVvip mm tVIt IV mm 2sin2sin 2 P t v, i t v i ++ -- Energy stored: t vv CvCvdvdt dt dv CvvidtW 0 0 2 0 2 1 22 max 2 1 CVCVW m Phasor Relationships for R, L and C
- 36. Capacitor Suppose C=20F,AC source v=100sint,Find XC and I for f = 50Hz, 50kHz。 159 2 11 Hz50 fCC Xf c A44.0 2 c m c X V X V I 159.0 2 11 KHz50 fCC Xf c A440 2 c m c X V X V I Phasor Relationships for R, L and C
- 37. Review (v – i Relationship) Time domain Frequency domain iRv IRV I Cj V 1 ILjV dt di LvL dt dv CiC C XC 1 LXL , , , v and i are in phase. , v leads i by 90°. , v lags i by 90°. R C L Phasor Relationships for R, L and C
- 38. Summary: R: RX R 0 L: ffLLXL 2 2 iv C: ffcc XC 1 2 11 2 iv IXV Frequency characteristics of an Ideal Inductor and Capacitor: A capacitor is an open circuit to DC currents; A Inductor is a short circuit to DC currents. Phasor Relationships for R, L and C
- 39. Impedance (Z) Outline: Complex currents and voltages. Impedance Phasor Diagrams
- 40. • AC steady-state analysis using phasors allows us to express the relationship between current and voltage using a formula that looks likes Ohm’s law: ZIV Complex voltage, Complex current, Complex Impedance vm j m VeVV v im j m IeII i ZeZe I V I V Z jj m m iv )( ‘Z’ is called impedance measured in ohms () Impedance (Z)
- 41. Complex Impedance ZeZe I V I V Z jj m m iv )( Complex impedance describes the relationship between the voltage across an element (expressed as a phasor) and the current through the element (expressed as a phasor). Impedance is a complex number and is not a phasor (why?). Impedance depends on frequency. Impedance (Z)
- 42. Complex Impedance ZR = R = 0; or ZR = R 0 Resistor——The impedance is R c j c jX C j e C Z 21 ) 2 ( iv or 90 1 C ZC Capacitor——The impedance is 1/jωC L j L jXLjLeZ 2 ) 2 ( iv or 90 LZL Inductor——The impedance is jωL Impedance (Z)
- 43. Complex Impedance Impedance in series/parallel can be combined as resistors. _ U U Z1 + Z2 Zn I n k kn ZZZZZ 1 21 ... _ US In I1 I1 I1 I1 I1 I1 R1 R1 Zn 5 5 5 5 + + _ US IS U1 + - U I Z2Z1 n k kn ZZZZZ 121 11 ... 111 21 1 2 21 2 1 ZZ Z II ZZ Z II Current divider: n k k i i Z Z VV 1 Voltage divider: Impedance (Z)
- 44. Complex Impedance _ + V I 1IZ1 Z2 Z 2121 2 2121 2 1 2 1 1 2 2 1 11 ZZZZZZ ZV I ZZZZZZ ZZV ZZ Z V I ZZ Z II Impedance (Z)
- 45. Complex Impedance Phasors and complex impedance allow us to use Ohm’s law with complex numbers to compute current from voltage and voltage from current 20kW + - 1mF10V 0 VC + - w = 377 Find VC • How do we find VC? • First compute impedances for resistor and capacitor: ZR = 20kW = 20kW 0 ZC = 1/j (377 *1mF) = 2.65kW -90 Impedance (Z)
- 46. Complex Impedance 20kW + - 1mF10V 0 VC + - w = 377 Find VC 20kW 0 + - 2.65kW - 90 10V 0 VC + - Now use the voltage divider to find VC: 46.82V31.1 54.717.20 9065.2 010VCV ) 0209065.2 9065.2 (010 kk k VVC Impedance (Z)
- 47. Impedance allows us to use the same solution techniques for AC steady state as we use for DC steady state. • All the analysis techniques we have learned for the linear circuits are applicable to compute phasors – KCL & KVL – node analysis / loop analysis – Superposition – Thevenin equivalents / Norton equivalents – source exchange • The only difference is that now complex numbers are used. Complex Impedance Impedance (Z)
- 48. Kirchhoff’s Laws KCL and KVL hold as well in phasor domain. KVL: 0 1 n k kv vk- Transient voltage of the #k branch 0 1 n k kV KCL: 0 1 n k ki 0 1 n k kI ik- Transient current of the #k branch Impedance (Z)
- 49. Admittance • I = YV, Y is called admittance, the reciprocal of impedance, measured in Siemens (S) • Resistor: – The admittance is 1/R • Inductor: – The admittance is 1/jL • Capacitor: – The admittance is jC Impedance (Z)
- 50. Phasor Diagrams • A phasor diagram is just a graph of several phasors on the complex plane (using real and imaginary axes). • A phasor diagram helps to visualize the relationships between currents and voltages. 2mA 40 – 1mF VC + – 1kW VR + + – V I = 2mA 40, VR = 2V 40 VC = 5.31V -50, V = 5.67V -29.37 Real Axis Imaginary Axis VR VC V Impedance (Z)
- 51. Parallel and Series Resonance Outline: RLC Circuit, Series Resonance Parallel Resonance
- 52. v vR vL vC CLR vvvv CLR VVVV Phasor I V LV CV RV IZ XRI XXRI IXIXIR VVVV CL CL CLR 22 22 22 22 )( )()( )( )CL XXX ( 22 XRZ 22 ) 1 ( c LR (2nd Order RLC Circuit )Series RLC Circuit Parallel and Series Resonance :
- 53. 22 XRZ 22 ) 1 ( c LR IZVVVV CLR 22 )( Z X = XL-XC R V RV CLX VVV R XX V VV CL R CL 1 1 tan - tan Phase difference: XL>XC >0,v leads i by — Inductance Circuit XL<XC <0,v lags i by — Capacitance Circuit XL=XC =0,v and i in phase — Resistors Circuit Series RLC Circuit Parallel and Series Resonance :
- 54. CLR VVVV CL XIjXIjRI ZIjXRIXXjRI CL )()](( )( CL XXjR I V Z ZjXRZ 22 )( CL XXRZ R XX CL 1 tan iv v vR vL vC Series RLC Circuit Parallel and Series Resonance :
- 55. Series Resonance (2nd Order RLC Circuit ) CLR VVVV CL XIjXIjRI R XX arctg V VV arctg CL R CL CLCL VVL C XXWhen 1 , VVR 0and —— Series Resonance Resonance condition I LV CV VVR LC for LC 2 11 00 f0 f X Cf XC 2 1 fLXL 2 Resonant frequency Parallel and Series Resonance :
- 56. Series Resonance R V Z V IRXXRZ CL 0 0 22 0 )(• Zmin;when V = constant, I = Imax= I0 RXX CL RIXIXI CL 000 VVV CL • Quality factor Q, R X R X V V V V Q CLCL CLCL VVL C XX ) 1 ( Resonance condition: When, Parallel and Series Resonance :
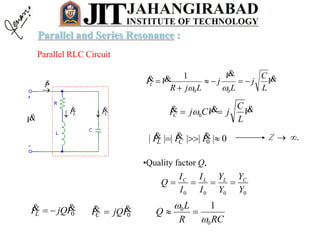
- 57. Parallel RLC Circuit V I LI CI )( 1 / 11 222222 LR L Cj LR R Cj LjRLjR LjR Cj LjRCjLjR Y Parallel Resonance Parallel Resonance frequency L CR LC 2 0 1 1 LXR In generally ) 2 1 ( 0 LC f LC 1 0 0)( 222 LR L C When 2220 LR R Y , In phase withV I V L RC C L R R V L LC R R V LR R VVYII 222 22 0 200 1 Zmax Imin: Parallel and Series Resonance :
- 58. Parallel RLC Circuit V I LI CI V L C j L V j LjR VIL 00 1 V L C jVCjIC 0 0|||||| 0 III CL Z . RCR L Q 0 0 1 0IjQIL 0IjQIC •Quality factor Q, 0000 Y Y Y Y I I I I Q CLLC Parallel and Series Resonance :
- 59. Parallel RLC Circuit Review For sinusoidal circuit, Series : 21 vvv 21 VVV 21 iii 21 III ? Two Simple Methods: Phasor Diagrams and Complex Numbers Parallel : Parallel and Series Resonance :





















































( CL XXjR
I
V
Z
ZjXRZ
22
)( CL XXRZ
R
XX CL
1
tan
iv
v
vR
vL
vC
Series RLC Circuit
Parallel and Series Resonance :](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acsinglephase-161231060524/85/Ac-single-phase-54-320.jpg)