Agents in Artificial intelligence
- 1. The Structure of Agents • There are two parts in agents 1. Architecture: Hardware with sensors and actuators. 2. Program: Convert percepts into actions. Agents are classified into 5 classes, based on their agent programs. Lets us discuss them
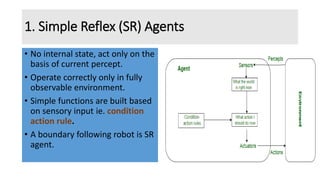
- 2. 1. Simple Reflex (SR) Agents • No internal state, act only on the basis of current percept. • Operate correctly only in fully observable environment. • Simple functions are built based on sensory input ie. condition action rule. • A boundary following robot is SR agent.
- 3. Simple Reflex (SR) Agents Limitations • Very limited intelligence. • Usually too big to generate and store. • Not flexible, need to update the rules if any change occurs in environment.
- 4. 2. Model Based Agents • Find a rule whose condition matches the current situation. • Handle partially observable environments by using model. • The agent has internal state, adjusted by each percept and that depends on the percept history. • Current state stored inside the agents, describing the part of the world which cannot be seen. • Updating the state requires information about : • how the world evolves in-dependently from the agent, and • how the agent actions affects the world.
- 5. Model Based Reflex Agents
- 6. 3. Goal Based Agents • Extension of model based agents. • Take decision based on how far they are currently from their goal. • Every action is intended to reduce its distance from the goal. • Agent choose a way among multiple possibilities, selecting the one which reaches a goal state. • Searching and planning. • Agent needs some sort of looking into future.
- 8. 4. Utility Based Agents • Main focus on utility not goal. • Used when there are multiple possible alternatives • Actions based on preference ( Utility). • Utility describes how happy the agent is. • Agent chooses the action that maximize utility.
- 9. 5. Learning Agent • Learn from past experiences • It start with knowledge then able to act and adapt automatically. • It has 4 components 1. Learning element: It is responsible for making improvements by learning from the environment 2. Critic: Learning element takes feedback from critic which describes how well the agent is doing with respect to a fixed performance standard.
- 10. Learning Agent 3. Performance element: Responsible for selecting external action, based on percept and feedback from learning element . 4. Problem Generator: Suggest actions that will lead to new and informative experiences.
- 11. Different forms of learning • Rote learning or memorization. • Least amount of inferencing. • Knowledge is copied in knowledge base. • Learning through instructions • Learning by analogy • Development of new concepts through already known similar concepts • Learning by induction • Conclusion drawn based on large number of examples.
- 12. Different forms of learning • Learning by deduction • Irrefutable form of reasoning. • Concepts drawn always already correct, if given facts are correct. • Learning based on feedback • Supervised • Unsupervised • Reinforcement learning