An approach to non convex/concave bi-level programming problems integrating Goal Programming with Satisfaction Function
- 1. An approach to non convex/concave bi-level programming problems integrating Goal Programming with Satisfaction Function Nicolò Paternoster - Sergejs Pugacs
- 2. Outline
- 3. Outline Introduction: multi-level programming State of the art Goal Programming Satisfaction Function Roghanian approach Model proposal Numerical examples Results Conclusions
- 4. Bi-level Programming (BLP) “bilevel optimization problems are mathematical programs which have a sub-set of their variables constrained to be an optimal solution of other programs parameterized by their remaining variables” By definition the bilevel programming problem is defined as
- 5. Bi-level Programming (BLP) “bilevel optimization problems are mathematical programs which have a sub-set of their variables constrained to be an optimal solution of other programs parameterized by their remaining variables” By definition the bilevel programming problem is defined as LEADER
- 6. Bi-level Programming (BLP) “bilevel optimization problems are mathematical programs which have a sub-set of their variables constrained to be an optimal solution of other programs parameterized by their remaining variables” By definition the bilevel programming problem is defined as LEADER where y, for each value of x, is the solution of the lower level problem: FOLLOWER
- 7. Goal Programming - 1 This model allows to take into account simultaneously several objectives in a problem for choosing the most satisfactory solution within a set of feasible solutions. When dealing with a multi criteria optimization problem the decision maker can choose a goal he wants to achieve for for each objective function OBJECTIVE FUNCTIONS
- 8. Goal Programming - 1 This model allows to take into account simultaneously several objectives in a problem for choosing the most satisfactory solution within a set of feasible solutions. When dealing with a multi criteria optimization problem the decision maker can choose a goal he wants to achieve for for each objective function OBJECTIVE FUNCTIONS GOALS
- 9. Goal Programming - 2 Using the GP Model formulation the problem becomes Instead of minimizing the objective function, using this approach we try to minimize the deviations between goals and the achieved level.
- 10. Satisfaction Function - 1 Through the satisfaction functions, the DM can explicitly express his preferences for any deviation of the achievement from the aspiration level of each objective An general shape of SF can be
- 11. Satisfaction Function - 2 After defining the analytical expression for a general satisfaction function F we can write the model where we try to maximize the satisfaction level for each goal : OSS: there could be a different SF for each goal
- 12. Roghanian Approach S. S. E. Roghanian, M.B. Aryanezhad, Integrating goal programming, khun-tucker conditions, and penalty function approaches to solve linear bi-level programming problems, Applied Mathematics and Computa- tion, 2008. An approach to solve linear Bilevel Problems They proposed to replace the follower's problem with its (KKT) conditions and append the resulting system to the leaders problem as a constraint . They point out that the optimal values of the Leader and Follower relaxed problem are the lower bounds for the optimal values of F(x,y),f(x,y) ,respectively
- 13. Model proposal - 1 We propose an approach that can be extended to non-convex/concave functions We replace the BLP with the multi-criteria single level problem and we use GP to solve the multi-criteria problem.
- 14. Model proposal-2 Strategies for finding goals We propose two different strategies which can help the DM in finding the goals for the Leader and the Follower.
- 15. Model proposal-2 Strategies for finding goals We propose two different strategies which can help the DM in finding the goals for the Leader and the Follower. First Strategy g1 g2
- 16. Model proposal-2 Strategies for finding goals We propose two different strategies which can help the DM in finding the goals for the Leader and the Follower. First Strategy Second Strategy g1 g1 fix x treating it as a parameter and then solve g2 g2(x)
- 17. Model proposal - 3 Introducing Satisfaction Function In order to refine results we can introduce the satisfaction function S in our model
- 18. Numerical Example - 1 Non-convex/concave follower’s function
- 19. Numerical Example - 2 This example is more complex as the goal for the follower problem depends on x
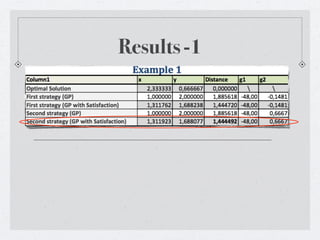
- 20. Results -1
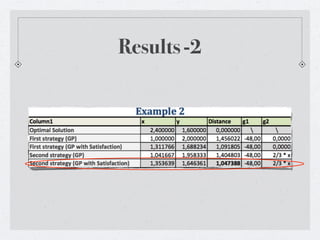
- 22. Results -2
- 23. THE END
Editor's Notes
- #2: \n
- #3: \n
- #4: \n
- #5: \n
- #6: \n
- #7: \n
- #8: \n
- #9: \n
- #10: \n
- #11: \n
- #12: \n
- #13: \n
- #14: \n
- #15: \n
- #16: \n
- #17: \n
- #18: \n
- #19: \n
- #20: \n
- #21: \n
- #22: \n
- #23: \n
- #24: \n
- #25: \n
- #26: \n
- #27: \n
- #28: \n
- #29: \n
- #30: \n
- #31: \n
- #32: \n
- #33: \n
- #34: \n
- #35: \n
- #36: \n
- #37: \n
- #38: \n
- #39: \n
- #40: \n
- #41: \n
- #42: \n
- #43: \n
- #44: \n
- #45: \n
- #46: \n
- #47: \n
- #48: \n
- #49: \n
- #50: \n
- #51: \n
- #52: \n
- #53: \n