Apache Helix presentation at Vmware
- 1. Building distributed systems using Helix h?p://helix.incubator.apache.org Apache IncubaGon Oct, 2012 @apachehelix Kishore Gopalakrishna, @kishoreg1980 h?p://www.linkedin.com/in/kgopalak 1
- 2. Outline • Introduc)on • Architecture • How to use Helix • Tools • Helix usage 2
- 3. Examples of distributed data systems 3
- 4. Lifecycle Cluster Fault Expansion tolerance • Thro?le data movement MulG • Re-‐distribuGon • ReplicaGon node • Fault detecGon • Recovery Single Node • ParGGoning • Discovery • Co-‐locaGon 4
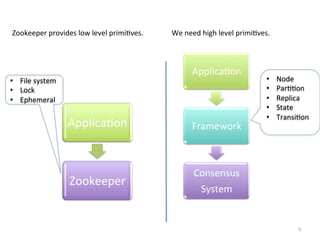
- 5. Zookeeper provides low level primiGves. We need high level primiGves. ApplicaGon • File system • Node • Lock • ParGGon • Ephemeral • Replica • State • TransiGon ApplicaGon Framework Consensus Zookeeper System 5
- 6. 6
- 7. Outline • IntroducGon • Architecture • How to use Helix • Tools • Helix usage 7
- 8. Terminologies Node A single machine Cluster Set of Nodes Resource A logical en/ty e.g. database, index, task ParGGon Subset of the resource. Replica Copy of a parGGon State Status of a parGGon replica, e.g Master, Slave TransiGon AcGon that lets replicas change status e.g Slave -‐> Master 8
- 9. Core concept -‐ state machine • Set of legal states – S1, S2, S3 • Set of legal state transiGons – S1àS2 – S2àS1 – S2àS3 – S3àS2 9
- 10. Core concept -‐ constraints • Minimum and maximum number of replicas that should be in a given state – S3àmax=1, S2àmin=2 • Maximum concurrent transiGons – Per node – Per resource – Across cluster 10
- 11. Core concept: objecGves • ParGGon placement – Even distribuGon of replicas in state S1,S2 across cluster • Failure/Expansion semanGcs – Create new replicas and assign state – Change state of exisGng replicas – Even distribuGon of replicas 11
- 12. Augmented finite state machine State Machine Constraints ObjecGves • States • States • ParGGon Placement • S1,S2,S3 • S1à max=1, S2=min=2 • Failure semanGcs • TransiGon • TransiGons • S1àS2, S2àS1, S2àS3, • Concurrent(S1-‐>S2) S3àS1 across cluster < 5 12
- 13. Message consumer group -‐ problem ASSIGNMENT SCALING FAULT TOLERANCE PARTITIONED QUEUE CONSUMER ParGGon management ElasGcity Fault tolerance • One consumer per • Re-‐distribute queues • Re-‐distribute queue among consumers • Minimize movement • Even distribuGon • Minimize movement • Limit max queue per consumer 13
- 14. Message consumer group: soluGon ONLINE OFFLINE STATE MODEL MAX 10 queues per consumer Start consumpGon MAX=1 per par))on Offline Online Stop consumpGon 14
- 15. Distributed data store P.1 P.2 P.3 P.5 P.6 P.7 P.9 P.10 P.11 P.4 P.5 P.6 P.8 P.1 P.2 P.12 P.3 P.4 P.1 P.9 P.10 P.11 P.12 P.7 P.8 SLAVE MASTER Node 1 Node 2 Node 3 ParGGon Fault tolerance ElasGcity management • MulGple replicas • Fault detecGon • Minimize • 1 designated • Promote slave downGme master to master • Minimize data • Even • Even movement distribuGon distribuGon • Thro?le data • No SPOF movement
- 16. Distributed data store: soluGon MASTER SLAVE STATE MODEL COUNT=2 minimize(maxnj∈N S(nj) ) t1≤5 S t1 t2 t3 t4 O M COUNT=1 minimize(maxnj∈N M(nj) ) 16
- 17. Distributed search service INDEX SHARD P.1 P.2 P.5 P.6 P.3 P.4 P.3 P.4 P.1 P.2 P.5 P.6 REPLICA Node 1 Node 2 Node 3 ParGGon Fault tolerance ElasGcity management • MulGple replicas • Fault detecGon • re-‐distribute • Even • Auto create parGGons distribuGon replicas • Minimize • Rack aware • Controlled movement placement creaGon of • Thro?le data replicas movement
- 18. Distributed search service: soluGon MAX per node=5 MAX=3 (number of replicas) 18
- 19. Internals 19
- 20. IDEALSTATE P1 P2 P3 ConfiguraGon Constraints • 3 nodes • 1 Master • 3 parGGons • 2 replicas • 1 Slave • Even N1:M N2:M N3:M • StateMachine distribuGon Replica placement N2:S N3:S N1:S Replica State 20
- 21. CURRENT STATE N1 • P1:OFFLINE • P3:OFFLINE N2 • P2:MASTER • P1:MASTER N3 • P3:MASTER • P2:SLAVE 21
- 22. EXTERNAL VIEW P1 P2 P3 N1:O N2:M N3:M N2:M N3:S N1:O 22
- 23. Helix Based System Roles PARTICIPANT IDEAL STATE SPECTATOR Controller Parition routing logic CURRENT STATE RESPONSE COMMAND P.1 P.2 P.3 P.5 P.6 P.7 P.9 P.10 P.11 P.4 P.5 P.6 P.8 P.1 P.2 P.12 P.3 P.4 P.1 P.9 P.10 P.11 P.12 P.7 P.8 Node 1 Node 2 Node 3 23
- 24. Logical deployment 24
- 25. Outline • IntroducGon • Architecture • How to use Helix • Tools • Helix usage 25
- 26. Helix based soluGon 1. Define 2. Configure 3. Run 26
- 27. Define: State model definiGon • States • e.g. MasterSlave – All possible states – Priority • TransiGons – Legal transiGons S – Priority • Applicable to each O M parGGon of a resource 27
- 28. Define: state model Builder = new StateModelDefinition.Builder(“MASTERSLAVE”);! // Add states and their rank to indicate priority. ! builder.addState(MASTER, 1);! builder.addState(SLAVE, 2);! builder.addState(OFFLINE);! ! //Set the initial state when the node starts! builder.initialState(OFFLINE); //Add transitions between the states.! builder.addTransition(OFFLINE, SLAVE);! builder.addTransition(SLAVE, OFFLINE);! builder.addTransition(SLAVE, MASTER);! builder.addTransition(MASTER, SLAVE);! ! 28
- 29. Define: constraints State Transi)on ParGGon Y Y Resource -‐ Y Node Y Y COUNT=2 Cluster -‐ Y S COUNT=1 State Transi)on O M ParGGon M=1,S=2 -‐ 29
- 30. Define:constraints // static constraint! builder.upperBound(MASTER, 1);! ! ! // dynamic constraint! builder.dynamicUpperBound(SLAVE, "R");! ! ! ! // Unconstrained ! builder.upperBound(OFFLINE, -1; 30
- 31. Define: parGcipant plug-‐in code 31
- 32. Step 2: configure helix-‐admin –zkSvr <zkAddress> CREATE CLUSTER -‐-‐addCluster <clusterName> ADD NODE -‐-‐addNode <clusterName instanceId(host:port)> CONFIGURE RESOURCE -‐-‐addResource <clusterName resourceName par;;ons statemodel> REBALANCE èSET IDEALSTATE -‐-‐rebalance <clusterName resourceName replicas> 32
- 33. zookeeper view IDEALSTATE 33
- 34. Step 3: Run START CONTROLLER run-‐helix-‐controller -‐zkSvr localhost:2181 –cluster MyCluster START PARTICIPANT 34
- 35. zookeeper view 35
- 36. Znode content CURRENT STATE EXTERNAL VIEW 36
- 37. Spectator Plug-‐in code 37
- 38. Helix ExecuGon modes 38
- 39. IDEALSTATE P1 P2 P3 ConfiguraGon Constraints N1:M N2:M N3:M • 3 nodes • 1 Master • 3 parGGons • 1 Slave • 2 replicas • Even • StateMachine distribuGon N2:S N3:S N1:S Replica Replica placement State 39
- 40. ExecuGon modes • Who controls what AUTO AUTO CUSTOM REBALANCE Replica Helix App App placement Replica Helix Helix App State 40
- 41. Auto rebalance v/s Auto AUTO REBALANCE AUTO 41
- 42. In acGon Auto rebalance Auto MasterSlave p=3 r=2 N=3 MasterSlave p=3 r=2 N=3 Node1 Node2 Node3 Node 1 Node 2 Node 3 P1:M P2:M P3:M P1:M P2:M P3:M P2:S P3:S P1:S P2:S P3:S P1:S On failure: Auto create replica On failure: Only change states to saGsfy and assign state constraint Node 1 Node 2 Node 3 Node 1 Node 2 Node 3 P1:O P2:M P3:M P1:M P2:M P3:M P2:O P3:S P1:S P2:S P3:S P1:M P1:M P2:S 42
- 43. Custom mode: example 43
- 44. Custom mode: handling failure ™ Custom code invoker ™ Code that lives on all nodes, but acGve in one place ™ Invoked when node joins/leaves the cluster ™ Computes new idealstate ™ Helix controller fires the transiGon without viola)ng constraints P1 P2 P3 P1 P2 P3 Transi)ons 1 N1 MàS 2 N2 Sà M N1:M N2:M N3:M N1:S N2:M N3:M 1 & 2 in parallel violate single master constraint N2:S N3:S N1:S N2:M N3:S N1:S Helix sends 2 aqer 1 is finished 44
- 45. Controller deployment Embedded Separate • Embedded controller within • At least 2 separate each parGcipant controllers process to • Only one controller acGve avoid SPOF • No extra process to manage • Only one controller acGve • Suitable for small size cluster. • Extra process to manage • Upgrading controller is costly • Recommended for large • ParGcipant health impacts size clusters controller • Upgrading controller is easy 45
- 46. Controller fault tolerance Zookeeper Controller Controller Controller 1 2 3 LEADER STANDBY STANDBY Zookeeper ephemeral based leader elecGon for deciding controller leader 46
- 47. Controller fault tolerance Zookeeper Controller Controller Controller 1 2 3 OFFLINE LEADER STANDBY When leader fails, another controller becomes the new leader 47
- 48. Managing the controllers 48
- 49. Scaling the controller: Leader Standby Model STANDBY Cluster S Cluster Controller O L Cluster OFFLINE LEADER Controller Cluster Cluster Controller Cluster 49
- 50. Scaling the controller: Failure STANDBY S Cluster Cluster Controller O L Cluster OFFLINE LEADER Controller Cluster Cluster Controller Cluster 50
- 51. Outline • IntroducGon • Architecture • How to use Helix • Tools • Helix usage 51
- 52. Tools • Chaos monkey • Data driven tesGng and debugging • Rolling upgrade • On demand task scheduling and intra-‐cluster messaging • Health monitoring and alerts 52
- 53. Data driven tesGng • Instrument – • Zookeeper, controller, parGcipant logs • Simulate – Chaos monkey • Analyze – Invariants are • Respect state transiGon constraints • Respect state count constraints • And so on • Debugging made easy • Reproduce exact sequence of events 53
- 54. Structured Log File -‐ sample timestamp partition instanceName sessionId state 1323312236368 TestDB_123 express1-md_16918 ef172fe9-09ca-4d77b05e-15a414478ccc OFFLINE 1323312236426 TestDB_123 express1-md_16918 ef172fe9-09ca-4d77b05e-15a414478ccc OFFLINE 1323312236530 TestDB_123 express1-md_16918 ef172fe9-09ca-4d77b05e-15a414478ccc OFFLINE 1323312236530 TestDB_91 express1-md_16918 ef172fe9-09ca-4d77b05e-15a414478ccc OFFLINE 1323312236561 TestDB_123 express1-md_16918 ef172fe9-09ca-4d77b05e-15a414478ccc SLAVE 1323312236561 TestDB_91 express1-md_16918 ef172fe9-09ca-4d77b05e-15a414478ccc OFFLINE 1323312236685 TestDB_123 express1-md_16918 ef172fe9-09ca-4d77b05e-15a414478ccc SLAVE 1323312236685 TestDB_91 express1-md_16918 ef172fe9-09ca-4d77b05e-15a414478ccc OFFLINE 1323312236685 TestDB_60 express1-md_16918 ef172fe9-09ca-4d77b05e-15a414478ccc OFFLINE 1323312236719 TestDB_123 express1-md_16918 ef172fe9-09ca-4d77b05e-15a414478ccc SLAVE 1323312236719 TestDB_91 express1-md_16918 ef172fe9-09ca-4d77b05e-15a414478ccc SLAVE 1323312236719 TestDB_60 express1-md_16918 ef172fe9-09ca-4d77b05e-15a414478ccc OFFLINE 1323312236814 TestDB_123 express1-md_16918 ef172fe9-09ca-4d77b05e-15a414478ccc SLAVE
- 55. No more than R=2 slaves Time State Number Slaves Instance 42632 OFFLINE 0 10.117.58.247_12918 42796 SLAVE 1 10.117.58.247_12918 43124 OFFLINE 1 10.202.187.155_12918 43131 OFFLINE 1 10.220.225.153_12918 43275 SLAVE 2 10.220.225.153_12918 43323 SLAVE 3 10.202.187.155_12918 85795 MASTER 2 10.220.225.153_12918
- 56. How long was it out of whack? Number of Slaves Time Percentage 0 1082319 0.5 1 35578388 16.46 2 179417802 82.99 3 118863 0.05 83% of the Gme, there were 2 slaves to a parGGon 93% of the Gme, there was 1 master to a parGGon Number of Masters Time Percentage 0 15490456 7.164960359 1 200706916 92.83503964
- 57. Invariant 2: State TransiGons FROM TO COUNT MASTER SLAVE 55 OFFLINE DROPPED 0 OFFLINE SLAVE 298 SLAVE MASTER 155 SLAVE OFFLINE 0
- 58. Outline • IntroducGon • Architecture • How to use Helix • Tools • Helix usage 58
- 59. Helix usage at LinkedIn Espresso 59
- 60. In flight • Apache S4 – ParGGoning, co-‐locaGon – Dynamic cluster expansion • Archiva – ParGGoned replicated file store – Rsync based replicaGon • Others in evaluaGon – Bigtop 60
- 61. Auto scaling soqware deployment tool • States Offline < 100 • Download, Configure, Start Download • AcGve, Standby Configure • Constraint for each state Start • Download < 100 • AcGve 1000 Active 1000 • Standby 100 Standby 100 61
- 62. Summary • Helix: A Generic framework for building distributed systems • Modifying/enhancing system behavior is easy – AbstracGon and modularity is key • Simple programming model: declaraGve state machine 62
- 63. Roadmap • Features • Span mulGple data centers • AutomaGc Load balancing • Distributed health monitoring • YARN Generic ApplicaGon master for real Gme Apps • Stand alone Helix agent
- 64. website h?p://helix.incubator.apache.org user user@helix.incubator.apache.org dev dev@helix.incubator.apache.org twi?er @apachehelix, @kishoreg1980 64
Editor's Notes
- #5: Moving from single node to scalable, fault tolerant distributed mode is non trivial and slow, even though core functionality remains the same.
- #6: You must define correct behavior of your system. How do you partition? What is the replication factor? Are replicas the same or are there different roles such as master/slave replicas? How should the system behave when nodes fail, new nodes are added etc. This differs from system to system.2. Once you have defined how the system must behave, you have to implement that behavior in code, maybe on top of ZK or otherwise. That implementation is non-trivial, hard to debug, hard to test. Worse, in response to requirements, if the behavior of the system were to change even slightly, the entire process has to repeat.MOVING FROM ONE SHARD PER NODE to MULTIPLE SHARD PER NODEInstead, wouldn't it be nice if all you had to do was step 1 i.e. simply define the correct behavior of your distributed system and step 2 was somehow taken care of?
- #8: Core helix concepts What makes it generic
- #10: With each replica associated with a state
- #11: With each replica associated with a state
- #12: With each replica associated with a state
- #13: In this slide, we will look at the problem from a different perspective and possibly re-define the cluster management problem.So re-cap to solve dds we need to define number of partitions and replicas, and for each replicas we need to different roles like master/slave etcOne of the well proven way to express such behavior is use a state machine
- #15: Dynamically change number of replicasAdd new resources, add nodesChange behavior easilyChange what runs whereelasticity
- #18: Limit the number of partitions on a single node,
- #19: Dynamically change number of replicasAdd new resources, add nodesChange behavior easilyChange what runs whereelasticity
- #25: Design choicesCommunicationZK optimizationsMultiple deployment optionsNo SPOF
- #33: Mention configuration etc
- #43: Auto rebalance: Applicable to message consumer group, searchAutoDistributed data store
- #53: Allows one to come up with common toolsThink of maven plugins
- #60: Used in production and manage the core infrastructure components in the companyOperation is easy and easy for dev ops to operate multiple systems
- #61: S4 Apps and processing tasks, each have different state modelMultitenancy multiple resources
- #62: Define statesHow many you want in each stateState modelHelix provides MasterSlaveOnlineOfflineLeaderStandbyTwo master systemAutomatic replica creation
- #63: Provides the right combination of abstraction and flexibilityCode is stable and deployed in productionIntegration between multiple systems co-locatingGood thing helps think more about your design putting in right level of abstraction and modularity
- #65: contribution