Are Mega Menus Really Heroic? 20160317
- 1. 25 1st St., Suite 104, Cambridge, MA 02141 | www.BioRAFT.com Are Mega Menus Really Heroic? Designing Your Site NavigaIon Heather Bauer Drupal Nights Thursday, March 17, 2016 – 7:00
- 2. About Me: Heather Bauer • UX Product Specialist at BioRAFT • M.S. in Human Factors in InformaIon Design at Bentley University • Co-‐Organizer of Boston Service Jam 2014 • Expert in Residence for GA UXD course summer 2014 drupal.org/u/hezzieb twi]er.com/hezzieb524 linkedin.com/in/heathersbauer IntroducIon
- 3. About BioRAFT • Enterprise safety, compliance & training so`ware for lab scienIsts and those that work with them built with Drupal • SaaS, mulI-‐site applicaIon. • WE’RE HIRING! BioRAFT.com DrupalNights.org IntroducIon
- 5. Agenda • IntroducIon • What is InformaIon Architecture? • How to Research • NavigaIon Overview • NavigaIon Design • Things to Keep in Mind IntroducIon
- 6. 25 1st St., Suite 104, Cambridge, MA 02141 | www.BioRAFT.com InformaIon Architecture
- 7. InformaIon Architecture InformaIon Architecture
- 8. InformaIon Architecture • Creates intuiIve ways to navigate data • Makes informaIon easy to find • Schemes must be: – Concise – DescripIve – Mutually exclusive – Possess informaIon scent InformaIon Architecture
- 9. InformaIon Scent? InformaIon Architecture
- 10. InformaIon Scent • Cues that indicate what you’re looking for is down a parIcular path • Informs decisions • Allows informaIon that doesn’t seem relevant to be discarded or ignored InformaIon Architecture
- 11. InformaIon Scent InformaIon Architecture
- 12. What Users Need to Know • Am I in the right place? • Does the site have what I’m looking for? • Is there anything be]er? • What now? InformaIon Architecture
- 13. What Users Need to Know • Am I in the right place? – Make sure they can tell what your site is for – Every page is your home page • Does the site have what I’m looking for? • Is there anything be]er? • What now? InformaIon Architecture
- 14. What Users Need to Know • Am I in the right place? • Does the site have what I’m looking for? – Use organizaIon systems that make sense (e.g. alphabeIcal, by Ime, locaIon, etc.) – Obvious labels – NavigaIon should look like navigaIon – You are here and you were there indicators • Is there anything be]er? • What now? InformaIon Architecture
- 15. What Users Need to Know • Am I in the right place? • Does the site have what I’m looking for? • Is there anything be]er? – Hierarchy should be obvious – Breadcrumbs – “See also” opIons • What now? InformaIon Architecture
- 16. What Users Need to Know • Am I in the right place? • Does the site have what I’m looking for? • Is there anything be]er? • What now? – Next steps should be obvious – Don’t hide the last step to success InformaIon Architecture
- 17. Why Users Visit Your Site • Searching for something • Task to accomplish • Killing Ime • Not always mutually exclusive InformaIon Architecture
- 18. 25 1st St., Suite 104, Cambridge, MA 02141 | www.BioRAFT.com Research
- 19. How to Do OrganizaIon • Observe people • Study the compeIIon • Look at the search logs – what are people looking for and not finding? Research
- 20. Doing Your Research • Card Sort • Sitepath diagramming • Task analysis • Journey mapping • Sitemap Research
- 22. Card SorIng • Early stage technique • 2 types: – Open Card Sort: Can make as many groups as appropriate – Closed Card Sort: Groups pre-‐determined • Can be done with users or stakeholders Research
- 23. Card SorIng Tools • SIcky Notes • OpImalSort • UserZoom • UserTesIng.com • Many more: www.measuringuserexperience.com/ CardSorIng/index.htm Research
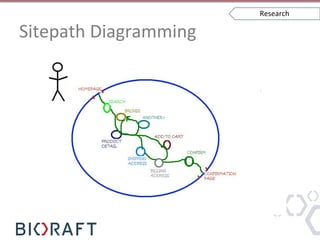
- 25. Sitepath Diagramming • Sketching system – determine users and their acIviIes • Good for deciding site flow, early UI design, and workflow • Can show a process that you can design for one user and reuse Research
- 26. Sitepath Diagramming Tools • Something to draw on • Lots of colored drawing implements • Draw people (sIck figures A-‐OK) • Personas (OpIonal) Research
- 27. Sitepath Diagramming How To • Draw a circle represenIng your system • Put types of people around the edge (obvious people in upper le`) • Ways people might come to the site (lower le`) • People using the site very differently (right) • Draw the scenarios within the circle Research
- 29. Task Analysis • Much more detailed than Sitepath Diagramming • A way to fill in the li]le pieces the scenarios may gloss over • Helps figure out design quesIons to be answered • Captures subtleIes of each step in the process Research
- 30. Task Analysis How To • Determine task goal • Pull pieces of the scenario that relate directly • Determine subtasks • Determine sub-‐subtasks • Add system interacIon Research
- 32. Sitemapping 4 Types • Tree Map – great for hierarchy • Comb Map – uses space be]er • Star Map – hierarchy isn’t strict • Tab Map – grouped by similariIes instead of hierarchy Research
- 33. Sitemap consideraIons • Big or small? • Shallow or deep? • How important is the hierarchy? • Are there mulIple ways to get to one page? NOTE: No right or wrong answers! Research
- 35. Journey Mapping • IdenIfies problem areas with workflows • Focuses on users’ emoIonal state at a given step • CombinaIon of Sitepath Diagramming/Task Analysis/Sitemap and Personas Research
- 37. Forces at Play • Business • Users • Technology Research
- 38. Roadblocks • SomeImes you can put them in users’ way • SomeImes they cause more harm than good Research
- 39. 25 1st St., Suite 104, Cambridge, MA 02141 | www.BioRAFT.com NavigaIon
- 40. Types of NavigaIon • Structural NavigaIon: Hierarchy including global and local • AssociaIve NavigaIon: Similar items that help with exploratory seeking • UIlity NavigaIon: Sign in, user info, etc. NavigaIon
- 41. Types of NavigaIon • Global NavigaIon – Your big categories – Visible from every page – Gives a rough feel for what the site is about • Local NavigaIon – Page specific – Gets to the finer details – Allows for more specific browsing NavigaIon
- 42. NavigaIon Access PogosIcking • Have to go to a parent category before a new sub category • Usually for large, varied collecIons of content • Requires very clear and clickable sense of place • Hiding top level categories – easier to focus • Allows for space saving methods NavigaIon
- 43. NavigaIon Access Crabwalking • Can move between categories at the same depth • Easier error recovery • Requires everything of the same level to be visible at the same Ime NavigaIon
- 44. Faceted ClassificaIon • Good if you have items that can be classified by many characterisIcs • Considers the quesIon of how else someone would search for this • Becoming increasingly common NavigaIon
- 45. 25 1st St., Suite 104, Cambridge, MA 02141 | www.BioRAFT.com NavigaIon Design
- 46. NavigaIon LocaIon Top • All navigaIon visible at once • Full width of the screen is available to content below navigaIon • Good if you have a few big categories • Gets messy if you have more than about 5 NavigaIon Design
- 47. NavigaIon LocaIon Le` • More flexible with the number of categories • VerIcal space conInues infinitely • Leaves less space for local navigaIon and content NavigaIon Design
- 48. NavigaIon LocaIon Right • Don’t do it • Least effecIve with users NavigaIon Design
- 49. NavigaIon UI Mega Menu NavigaIon Design
- 50. NavigaIon UI Mega Menu • Jakob Nielsen endorsed Mega Menus in 2009 • Allow you to see mulIple levels of navigaIon • Requires less drill down • Allows for recogniIon over recall • PotenIally overwhelming • Can be used at any level of navigaIon • Take up a large porIon of the screen • Not mobile friendly NavigaIon Design
- 51. NavigaIon UI Breadcrumbs • Provide a trail of hierarchy • Useful for pogosIcking • Expert users get the most use of breadcrumbs • Use > instead of : to indicate hierarchy • Should live right under page Itle • Jury is sIll out on whether they decrease task compleIon Ime or increase success rate NavigaIon Design
- 52. Sub NavigaIon Best LocaIon • Start le` OR top • 2nd and 3rd selecIons should be from the same place but 1st selecIon can be separated • Top-‐le`-‐le` and le`-‐le`-‐le` were the best NavigaIon Design
- 53. Top-‐Le`-‐Le` NavigaIon NavigaIon Design
- 54. Le`-‐Le`-‐Le` NavigaIon NavigaIon Design
- 55. Hover = Bad Usability • People think hover is faster than click • The problems: – Accidental menu triggering/un-‐triggering – Unnatural cursor movements NavigaIon Design
- 56. Absent NavigaIon • When it is crucial for users to take a specified path • Wizards • IniIal setup NavigaIon Design
- 57. How Users Search • Known-‐item search • Exploratory seeking • Don’t know what I need to know • Re-‐finding NavigaIon Design
- 58. NavigaIon for Wayfinding NavigaIon Design
- 59. NavigaIon for Wayfinding • Landmarks are the only way to navigate • Users need to know: – Where they are – Where’s the thing they need – How did they get there? – Where have they already looked? • Be consistent with organizaIon • Provide detours for errors NavigaIon Design
- 60. 25 1st St., Suite 104, Cambridge, MA 02141 | www.BioRAFT.com Keep in Mind
- 61. When Organizing Content • Users perform be]er with deep (3 levels) rather than wide (2 levels) navigaIon • Good navigaIonal structure doesn’t make up for junk labels • Organize products/features together with a focus on what they have in common instead of organizing by goal Keep in Mind
- 62. Novices • Only novice for a short Ime • Many plateau at intermediate • Don’t be in the way Keep in Mind
- 63. Sustainable Structures • Allow room for growth (within a secIon and whole new secIons) • Avoid making structures too narrow or deep Keep in Mind
- 64. What’s Different with Mobile? • Space is more limited • Fat Finger Syndrome – targets need to be large enough • NavigaIon may be hidden • Hover is not an opIon • Relevant content may be different Keep in Mind
- 65. 25 1st St., Suite 104, Cambridge, MA 02141 | www.BioRAFT.com QuesIons?
- 66. Shameless Plug Encore presentaIon at UXPA Boston on 4/29 @ 1pm h]ps://uxpabostonconference2016.sched.org/ event/6GeO/are-‐mega-‐menus-‐really-‐all-‐that-‐ heroic
- 67. Photo Credits • h]p://downthenaturetrail.blogspot.com/2013/05/architecture-‐ design-‐wallpaper.html • h]ps://www.interacIon-‐design.org/ux-‐daily/194/web-‐user-‐ behaviour-‐directed-‐by-‐informaIon-‐scent • h]ps://www.newfangled.com/an-‐offline-‐informaIon-‐architecture-‐ exercise/ • h]p://itcourses.cs.unh.edu/assets/docs/502/tutorials/fall09-‐tut/ asr25/page2.html • h]p://kaylaashley345.blogspot.com/2013/12/task-‐analysis.html • h]p://imgbuddy.com/pogo-‐sIck-‐clip-‐art.asp • h]ps://www.flickr.com/photos/peterkaminski/47922080 • h]p://www.creaIvebloq.com/navigaIon/design-‐be]er-‐faceted-‐ navigaIon-‐your-‐websites-‐41411437
- 68. Resources • h]p://www.usabilityfirst.com/about-‐usability/informaIon-‐architecture • h]p://www.usabilityfirst.com/glossary/informaIon-‐scent • h]ps://www.interacIon-‐design.org/ux-‐daily/194/web-‐user-‐behaviour-‐directed-‐ by-‐informaIon-‐scent • Wodtke, C., & Govella, A. (2009). Informa=on Architecture: Blueprints for the Web. Pearson EducaIon. • h]p://theuxreview.co.uk/user-‐journeys-‐beginners-‐guide/ • h]p://www.creaIvebloq.com/navigaIon/design-‐be]er-‐faceted-‐navigaIon-‐your-‐ websites-‐41411437 • h]p://www.usability.gov/get-‐involved/blog/2006/11/breadcrumb-‐navigaIon.html • h]p://www.usability.gov/get-‐involved/blog/2006/04/le`-‐navigaIon-‐is-‐best.html • h]p://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v3/n4/full/nn0400_404.html • h]p://www.usability.gov/how-‐to-‐and-‐tools/methods/organizaIon-‐structures.html
- 69. 25 1st St., Suite 104, Cambridge, MA 02141 | www.BioRAFT.com Are Mega Menus Really Heroic? drupal.org/u/hezzieb twi]er.com/hezzieb524 linkedin.com/in/heathersbauer Slides will be available on drupalnights.org/library Heather Bauer Drupal Nights Thursday, March 17, 2016 – 7:00


![About
Me:
Heather
Bauer
• UX
Product
Specialist
at
BioRAFT
• M.S.
in
Human
Factors
in
InformaIon
Design
at
Bentley
University
• Co-‐Organizer
of
Boston
Service
Jam
2014
• Expert
in
Residence
for
GA
UXD
course
summer
2014
drupal.org/u/hezzieb
twi]er.com/hezzieb524
linkedin.com/in/heathersbauer
IntroducIon](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/megamenusreallyheroic20160317-160615134226/85/Are-Mega-Menus-Really-Heroic-20160317-2-320.jpg)









![What
Users
Need
to
Know
• Am
I
in
the
right
place?
• Does
the
site
have
what
I’m
looking
for?
• Is
there
anything
be]er?
• What
now?
InformaIon
Architecture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/megamenusreallyheroic20160317-160615134226/85/Are-Mega-Menus-Really-Heroic-20160317-12-320.jpg)
![What
Users
Need
to
Know
• Am
I
in
the
right
place?
– Make
sure
they
can
tell
what
your
site
is
for
– Every
page
is
your
home
page
• Does
the
site
have
what
I’m
looking
for?
• Is
there
anything
be]er?
• What
now?
InformaIon
Architecture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/megamenusreallyheroic20160317-160615134226/85/Are-Mega-Menus-Really-Heroic-20160317-13-320.jpg)
![What
Users
Need
to
Know
• Am
I
in
the
right
place?
• Does
the
site
have
what
I’m
looking
for?
– Use
organizaIon
systems
that
make
sense
(e.g.
alphabeIcal,
by
Ime,
locaIon,
etc.)
– Obvious
labels
– NavigaIon
should
look
like
navigaIon
– You
are
here
and
you
were
there
indicators
• Is
there
anything
be]er?
• What
now?
InformaIon
Architecture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/megamenusreallyheroic20160317-160615134226/85/Are-Mega-Menus-Really-Heroic-20160317-14-320.jpg)
![What
Users
Need
to
Know
• Am
I
in
the
right
place?
• Does
the
site
have
what
I’m
looking
for?
• Is
there
anything
be]er?
– Hierarchy
should
be
obvious
– Breadcrumbs
– “See
also”
opIons
• What
now?
InformaIon
Architecture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/megamenusreallyheroic20160317-160615134226/85/Are-Mega-Menus-Really-Heroic-20160317-15-320.jpg)
![What
Users
Need
to
Know
• Am
I
in
the
right
place?
• Does
the
site
have
what
I’m
looking
for?
• Is
there
anything
be]er?
• What
now?
– Next
steps
should
be
obvious
– Don’t
hide
the
last
step
to
success
InformaIon
Architecture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/megamenusreallyheroic20160317-160615134226/85/Are-Mega-Menus-Really-Heroic-20160317-16-320.jpg)











![Task
Analysis
• Much
more
detailed
than
Sitepath
Diagramming
• A
way
to
fill
in
the
li]le
pieces
the
scenarios
may
gloss
over
• Helps
figure
out
design
quesIons
to
be
answered
• Captures
subtleIes
of
each
step
in
the
process
Research](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/megamenusreallyheroic20160317-160615134226/85/Are-Mega-Menus-Really-Heroic-20160317-29-320.jpg)


![Sitemapping
4
Types
• Tree
Map
–
great
for
hierarchy
• Comb
Map
–
uses
space
be]er
• Star
Map
–
hierarchy
isn’t
strict
• Tab
Map
–
grouped
by
similariIes
instead
of
hierarchy
Research](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/megamenusreallyheroic20160317-160615134226/85/Are-Mega-Menus-Really-Heroic-20160317-32-320.jpg)




























![When
Organizing
Content
• Users
perform
be]er
with
deep
(3
levels)
rather
than
wide
(2
levels)
navigaIon
• Good
navigaIonal
structure
doesn’t
make
up
for
junk
labels
• Organize
products/features
together
with
a
focus
on
what
they
have
in
common
instead
of
organizing
by
goal
Keep
in
Mind](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/megamenusreallyheroic20160317-160615134226/85/Are-Mega-Menus-Really-Heroic-20160317-61-320.jpg)




![Shameless
Plug
Encore
presentaIon
at
UXPA
Boston
on
4/29
@
1pm
h]ps://uxpabostonconference2016.sched.org/
event/6GeO/are-‐mega-‐menus-‐really-‐all-‐that-‐
heroic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/megamenusreallyheroic20160317-160615134226/85/Are-Mega-Menus-Really-Heroic-20160317-66-320.jpg)
![Photo
Credits
• h]p://downthenaturetrail.blogspot.com/2013/05/architecture-‐
design-‐wallpaper.html
• h]ps://www.interacIon-‐design.org/ux-‐daily/194/web-‐user-‐
behaviour-‐directed-‐by-‐informaIon-‐scent
• h]ps://www.newfangled.com/an-‐offline-‐informaIon-‐architecture-‐
exercise/
• h]p://itcourses.cs.unh.edu/assets/docs/502/tutorials/fall09-‐tut/
asr25/page2.html
• h]p://kaylaashley345.blogspot.com/2013/12/task-‐analysis.html
• h]p://imgbuddy.com/pogo-‐sIck-‐clip-‐art.asp
• h]ps://www.flickr.com/photos/peterkaminski/47922080
• h]p://www.creaIvebloq.com/navigaIon/design-‐be]er-‐faceted-‐
navigaIon-‐your-‐websites-‐41411437](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/megamenusreallyheroic20160317-160615134226/85/Are-Mega-Menus-Really-Heroic-20160317-67-320.jpg)
![Resources
• h]p://www.usabilityfirst.com/about-‐usability/informaIon-‐architecture
• h]p://www.usabilityfirst.com/glossary/informaIon-‐scent
• h]ps://www.interacIon-‐design.org/ux-‐daily/194/web-‐user-‐behaviour-‐directed-‐
by-‐informaIon-‐scent
• Wodtke,
C.,
&
Govella,
A.
(2009).
Informa=on
Architecture:
Blueprints
for
the
Web.
Pearson
EducaIon.
• h]p://theuxreview.co.uk/user-‐journeys-‐beginners-‐guide/
• h]p://www.creaIvebloq.com/navigaIon/design-‐be]er-‐faceted-‐navigaIon-‐your-‐
websites-‐41411437
• h]p://www.usability.gov/get-‐involved/blog/2006/11/breadcrumb-‐navigaIon.html
• h]p://www.usability.gov/get-‐involved/blog/2006/04/le`-‐navigaIon-‐is-‐best.html
• h]p://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v3/n4/full/nn0400_404.html
• h]p://www.usability.gov/how-‐to-‐and-‐tools/methods/organizaIon-‐structures.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/megamenusreallyheroic20160317-160615134226/85/Are-Mega-Menus-Really-Heroic-20160317-68-320.jpg)
![25
1st
St.,
Suite
104,
Cambridge,
MA
02141
|
www.BioRAFT.com
Are
Mega
Menus
Really
Heroic?
drupal.org/u/hezzieb
twi]er.com/hezzieb524
linkedin.com/in/heathersbauer
Slides
will
be
available
on
drupalnights.org/library
Heather
Bauer
Drupal
Nights
Thursday,
March
17,
2016
–
7:00](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/megamenusreallyheroic20160317-160615134226/85/Are-Mega-Menus-Really-Heroic-20160317-69-320.jpg)