Auckland Programming Algorithms and Performance Meetup about Stacks & LeetCode Problems
- 1. Stacks Rodrigo Villarreal && Paulo Almeida Auckland Data Structures and Algorithms
- 2. Agenda ● Introduction to Stacks ○ Design ○ Real-world applications ● Practice ○ Examples ○ Let’s get our hands dirty! ● What’s next?
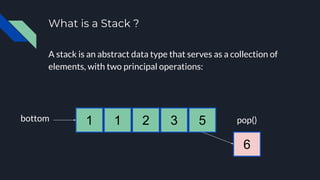
- 3. What is a Stack ? A stack is an abstract data type that serves as a collection of elements, with two principal operations: 1 1 2 3 5 6bottom top
- 4. What is a Stack ? A stack is an abstract data type that serves as a collection of elements, with two principal operations: 1 1 2 3 5 6 pop()bottom
- 5. What is a Stack ? A stack is an abstract data type that serves as a collection of elements, with two principal operations: 1 1 2 3 5 8 push(x) bottom
- 6. What is a Stack ? A stack is an abstract data type that serves as a collection of elements, with two principal operations: 1 1 2 3 5 8 Both operations change the top of the stack. bottom top
- 7. What is a Stack ? This behaviour is sometimes referred as LIFO (Last in, First out).
- 8. What is a Stack ? This behaviour is sometimes referred to as LIFO (Last in, First out). 1 push(x) bottom top
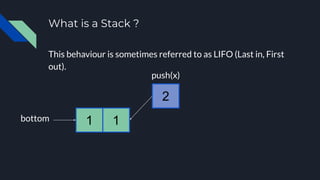
- 9. What is a Stack ? This behaviour is sometimes referred to as LIFO (Last in, First out). 1 push(x) 1 bottom
- 10. What is a Stack ? This behaviour is sometimes referred to as LIFO (Last in, First out). 1 push(x) 2 1bottom
- 11. What is a Stack ? This behaviour is sometimes referred to as LIFO (Last in, First out). 1 push(x) 3 1 2bottom
- 12. What is a Stack ? This behaviour is sometimes referred to as LIFO (Last in, First out). 1 31 2bottom top
- 13. What is a Stack ? This behaviour is sometimes referred to as LIFO (Last in, First out). 1 pop() 3 1 2bottom
- 14. What is a Stack ? This behaviour is sometimes referred to as LIFO (Last in, First out). 1 pop() 2 1bottom
- 15. What is a Stack ? This behaviour is sometimes referred to as LIFO (Last in, First out). 1 pop() 1 bottom
- 16. What is a Stack ? This behaviour is sometimes referred to as LIFO (Last in, First out). 1 pop() bottom top
- 17. What is a Stack ? Like in a stack of books. One can only add or remove from the top of the stack. …. (Or push/pop respectively)
- 18. Big O Time Complexity (Avg/Worst) Search: O(n) Access: O(n) Insertion: O(1) Deletion: O(1) Space Complexity (Worst): O(n)
- 19. Where would I use Stacks in the real world ? I’m glad you asked :)
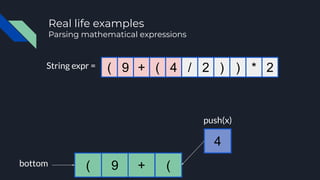
- 20. Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions String expr = ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2
- 21. Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions String expr = ( push(x) bottom top ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2
- 22. String expr = (bottom top ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 23. String expr = (bottom push(x) 9 ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 24. String expr = (bottom 9 ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
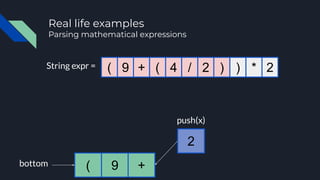
- 25. String expr = (bottom 9 push(x) + ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 26. String expr = (bottom 9 + ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 27. String expr = (bottom 9 + push(x) ( ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 28. String expr = (bottom 9 + ( ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 29. String expr = (bottom 9 + ( push(x) 4 ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 30. String expr = (bottom 9 + ( 4 ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
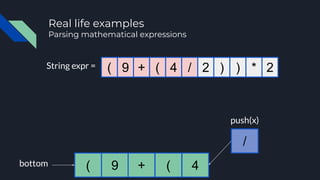
- 31. String expr = (bottom 9 + ( 4 ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 push(x) / Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 32. String expr = (bottom 9 + ( 4 ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 / Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 33. String expr = (bottom 9 + ( 4 ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 / push(x) 2 Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 34. String expr = (bottom 9 + ( 4 ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 / 2 Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 35. String expr = (bottom 9 + ( 4 ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 / 2 pop()pop()pop()pop() Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 36. String expr = (bottom 9 + ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 push(x) 2 Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 37. String expr = (bottom 9 + ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 2 Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 38. String expr = (bottom 9 + ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 2 pop()pop()pop()pop() Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 39. String expr = bottom ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 11 push(x) top Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 40. String expr = bottom ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 11 top Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 41. String expr = bottom ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 11 push(x) * Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 42. String expr = bottom ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 11 * Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 43. String expr = bottom ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 11 * push(x) 2 Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 44. String expr = bottom ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 11 * 2 Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 45. String expr = bottom ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 11 * 2 pop()pop()pop() Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 46. String expr = ( 9 + ( 4 / 2 ) ) * 2 bottom 22 push(x) top Real life examples Parsing mathematical expressions
- 47. Using Stacks in Java Declare stack: Stack<Type> stack = new Stack<>(); Push element: stack.push(element); Pop element: stack.pop();
- 48. Valid Parentheses (L #20) Given a string containing just the characters determine if the input string is valid. An input string is valid if: ● Open brackets must be closed by the same type of brackets. ● Open brackets must be closed in the correct order. ( ) { } [ ]
- 49. Valid Parentheses (L #20) Test cases Example Output “()” true “()[]{}” true “(]” false “([)]” false “{[]}” true
- 50. DIVISORIA
- 51. DIVISORIA
- 52. Valid Parentheses (L #20) Time Complexity = O(n) Space Complexity = O(n)
- 53. Still not convinced… where else would I use stacks? Can you relate to this example?
- 54. Real life examples Back / Forward Browser Button Back Stack Forward Stack
- 55. Real life examples Back / Forward Browser Button Back Stack Forward Stack www.google.comcurrent
- 56. Real life examples Back / Forward Browser Button Back Stack Forward Stack www.google.com www.facebook.comcurrent
- 57. Real life examples Back / Forward Browser Button Back Stack Forward Stack www.google.com www.facebook.com current www.twitter.com
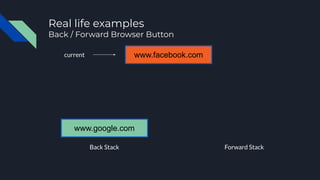
- 58. Real life examples Back / Forward Browser Button Back Stack Forward Stack www.google.com www.facebook.com current www.twitter.com www.meetup.com
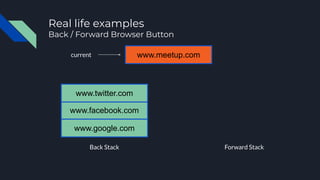
- 59. Real life examples Back / Forward Browser Button Back Stack Forward Stack www.google.com www.facebook.com current www.twitter.com www.meetup.com www.linkedin.com
- 60. Real life examples Back / Forward Browser Button Back Stack Forward Stack www.google.com www.facebook.com current www.twitter.com www.meetup.com www.linkedin.com
- 61. Real life examples Back / Forward Browser Button Back Stack Forward Stack www.google.com www.facebook.com current www.twitter.com www.meetup.com www.linkedin.com
- 62. Real life examples Back / Forward Browser Button
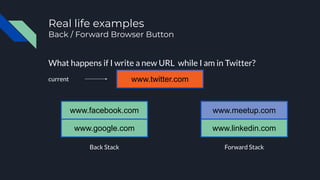
- 63. Real life examples Back / Forward Browser Button What happens if I write a new URL while I am in Twitter? Back Stack Forward Stack www.google.com www.facebook.com current www.twitter.com www.meetup.com www.linkedin.com
- 64. Real life examples Back / Forward Browser Button Forward Stack gets cleared Back Stack Forward Stack www.google.com www.facebook.com current www.twitter.com www.gmail.com
- 65. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) Given a string S of lowercase letters, a duplicate removal consists of choosing two adjacent and equal letters, and removing them. We repeatedly make duplicate removals on S until we no longer can. Return the final string after all such duplicate removals have been made. It is guaranteed the answer is unique. Input: "abbaca" Output: "ca" Explanation: For example, in "abbaca" we could remove "bb" since the letters are adjacent and equal, and this is the only possible move. The result of this move is that the string is "aaca", of which only "aa" is possible, so the final string is "ca".
- 66. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) Test cases Input: "abbaca" Output: "ca" Input: "abcdeedcba" Output: "" Input: "abcdefg" Output: "abcdefg"
- 67. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) Approach #1 Iterate the string and remove the adjacents. If we find a pair, we set a flag to true indicating we need to iterate again (since we have created a new string) Input: "abcdeedcba" Iteration #1: "abcddcba" Iteration #5: "abba" Iteration #2: "abccba" Iteration #6: "aa" Iteration #3: "abccba" Iteration #7 : "" Iteration #4: "abccba"
- 68. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) Approach #1 Time Complexity = O(n^2) Space Complexity = O(n)
- 69. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) Approach #2 We’ll use a stack this time as our support tool to solve this problem. We’ll iterate the string and we’ll check if the stack has elements and if top of the stack (the previous char) is equal to the element we’re currently checking. If the previous statement is false, add the char to the stack If the previous statement is true, pop the previous char and don’t add the current to the stack
- 70. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) a b b a c a Input Stack
- 71. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) a b b a c a Input Stack
- 72. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) a b b a c a Input Stack a
- 73. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) a b b a c a Input Stack a
- 74. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) a b b a c a Input Stack a b
- 75. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) a b b a c a Input Stack a b
- 76. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) a b b a c a Input Stack a
- 77. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) a b b a c a Input Stack a
- 78. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) a b b a c a Input Stack
- 79. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) a b b a c a Input Stack
- 80. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) a b b a c a Input Stack c
- 81. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) a b b a c a Input Stack c
- 82. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) a b b a c a Input Stack c a
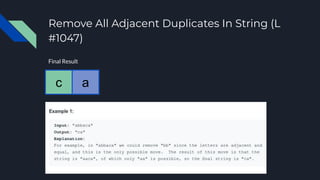
- 83. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) Final Result c a
- 84. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) Approach #1 Time Complexity = O(n^2) Space Complexity = O(n) Approach #2 Time Complexity = O(n) Space Complexity = O(n)
- 85. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (L #1047) Approach #1 Time Complexity = O(n^2) Space Complexity = O(n) Approach #2 ← Winner! Time Complexity = O(n) Space Complexity = O(n)
- 87. Leetcode Problems Easy Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String (Leetcode #1047) Valid Parentheses (Leetcode #20) Min Stack (Leetcode #155) Decode String (Leetcode #394) Medium Design Browser History (Leetcode #1472) Remove K Digits (Leetcode #402) Online Stock Span (Leetcode #901) Hard Basic Calculator (Leetcode #224)
- 88. What next? The next session will be about Trees!











































![Valid Parentheses (L #20)
Given a string containing just the characters
determine if the input string is valid.
An input string is valid if:
● Open brackets must be closed by the same type of brackets.
● Open brackets must be closed in the correct order.
( ) { } [ ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meetup271088411stacksandleetcode-200626080724/85/Auckland-Programming-Algorithms-and-Performance-Meetup-about-Stacks-LeetCode-Problems-48-320.jpg)
![Valid Parentheses (L #20)
Test cases
Example Output
“()” true
“()[]{}” true
“(]” false
“([)]” false
“{[]}” true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meetup271088411stacksandleetcode-200626080724/85/Auckland-Programming-Algorithms-and-Performance-Meetup-about-Stacks-LeetCode-Problems-49-320.jpg)