Brackets in ortho final
- 2. • A bracket is a device that projects horizontally to provide support. • Orthodontic brackets bonded/banded to enamel acts like an handle which provides the means to transfer the force applied by the activated arch-wire to the tooth. • The term is used only when referring to those devices that are open in one side -vertical or horizontal • The term bracket came to be in use in orthodontics when Dr. Angle introduced the ribbon arch appliance www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 3. Dr NIPUN T JOHN 2nd MDS Meenakshi Ammal Dental College www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 4. EVOLUTION OF BRACKETSEVOLUTION OF BRACKETS Bandelette plates-by Pierre Fauchard.. They are crude metal plates that were ligated to the teeth with brass or silver ligature wire. • In the late 1900’s, found out if a rigid framework is tied to teeth, the arch could be expanded as dictated by the appliance www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 5. THE E-ARCH APPLIANCETHE E-ARCH APPLIANCE (1900)(1900) The first fixed appliance designed byThe first fixed appliance designed by AngleAngle Used for tipping teeth into new alignedUsed for tipping teeth into new aligned positionposition Used stationary anchorageUsed stationary anchorage Expanded the arch-traction screwExpanded the arch-traction screw No individual tooth controlNo individual tooth control possiblepossible www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 6. PIN AND TUBE APPLIANCEPIN AND TUBE APPLIANCE (1910)(1910) E.H.ANGLEE.H.ANGLE • Most of the teeth were banded . • Vertical tubes were soldered to the bands with their long axis parallel to the long axis of the crown. • Rotational movements were difficult to obtain . www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 7. RIBBON ARCH APPLIANCERIBBON ARCH APPLIANCE (1915)(1915) • The first bracket devised in 1915 by angle • Big step in evolution of brackets • Rotational movements • Bucco-lingual and inciso-gingival movements Distal Tipping Of Buccal Segment not possible Mesiodistal axial movement not possible Arch wire did’nt provide stabilization www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 8. • Final bracket design by angle Based on his “Line of occlusion” concept • Bracket with rectangular slot • 0.022”x0.028” • Orientation of wire at 90 ◦ along the edge of the rectangular wire, horizontally. Hence the name. • Movement in all 3 planes of space • Twist and torque has to be shaped in the archform • Disadvantages- time consuming » Artificial smile EDGEWISE APPLIANCE(1925) www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 9. Tweed-Merrifield edgewise applianceTweed-Merrifield edgewise appliance • Neutral 0.022” edgewise slot. • Double width brackets on anteriors • Intermediate single/double width brackets on premolars • Heavy edgewise 0.022” tubes on molars • To correct rotations – Lingual hooks on molars – Lingual cleats on premolars • Brackets & tubes are placed 90o to long axis of teeth. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 10. Straight-wire applianceStraight-wire appliance (ormco)(ormco) Lawrence F Andrews- mid 1970’sLawrence F Andrews- mid 1970’s • No sophisticated wire bending • Less chair-side time. • But results were disappointing- • Due to heavy forces. • Canines tip into extraction spaces. • In late 1970’s – – Extraction or translation series. – Increased torque to the incisor brackets. – Anti-tip and antirotation other brackets. • Disadvantages Undesirable force vectors Inbuilt Overcorrection is not required when using light forces Increased need for band & bracket inventory r www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 11. • Roth -1975 Roth ovation series. • Wick Alexander- 1978, “Vari- Simplex” prescription • Mc Laughlin, Bennett and Trevisi -3rd generation PEA brackets-MBT series. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 12. BRACKETBRACKET Wings-tie wings and wings for rotational control. Base-which is attached to the tooth surface. Stem-base and lingual half of the slot. Slot-space for archwire and for auxillaries horizontal and vertical Hook ,power arm for engagement of elastics. Identification system –distogingival raised dot or numerical system. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 14. What is in-out?What is in-out? • A horizontal change relative to the line of occlusion( first order movements) • Facio-lingual relationship of the crown to line of occlusion • ie, the labial surface of the crown can be placed labially or lingually. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
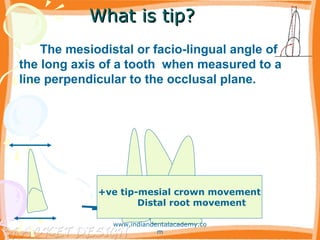
- 15. What is tip?What is tip? +ve tip-mesial crown movement Distal root movement The mesiodistal or facio-lingual angle of the long axis of a tooth when measured to a line perpendicular to the occlusal plane. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 16. What is torque?What is torque? Torque is defined as relation of crown and root inclination perpendicular to the line of occlusion. G&V Torsional or inclination changes or third order movements- angle +ve torque-labial crown movement palatal root movement www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 17. Torque in base v/s. Torque in faceTorque in base v/s. Torque in face JCO 1991 ALBERT H. OWENJCO 1991 ALBERT H. OWEN Straight-Wire Appliance bracket slots are at same height from anterior to posterior (dashed line = center of clinical crown). Edgewise bracket slots are not coordinated with bases, and therefore must be placed at different heights to line up slots. TORQUE IN FACE TORQUE IN BASE www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 18. Bracket baseBracket base Ovation seriesVictory series micro etched to increase retention Powdered coated Laser structured www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 19. Sintered base etched base Single mould bracket www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 20. Allure Ceramaflex Intrigue Transcend Dyna-Bond Ceramic bracket bases www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 21. BRACKET TYPESBRACKET TYPES WIDTH AND SIZE TYPE OF ROTATION CONTROL WINGS MODE OF LIGATION BRACKET MATERIALS BRACKETS FOR SPECIAL TECHNIQUES. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 22. Width of the bracketWidth of the bracket • Single brackets-narrow width/single brackets and wide width posterior brackets. • Twin brackets [dual, double or siamese brackets]- mini twin, intermediate twin, standard twin, extra wide twin. • Triple brackets. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 23. Single width bracketsSingle width brackets • These were angle’s original edgewise bracket design • Bracket width was 0.050” • Rotational movements were difficult • To overcome this limitation angle soldered eyelets onto bands • These eyelets were tied with ligatures to allow rotation – Repeated adjustment of ligatures – Relapse if ties not continued • Increases interbracket span. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 24. TWIN BRACKETSTWIN BRACKETS Siamese twin brackets”- swainSiamese twin brackets”- swain 2 brackets on a common base2 brackets on a common base distance between the 2 bracketsdistance between the 2 brackets -0.050”-0.050” Excellent rotational control.Excellent rotational control. Positive control on the tooth with mesio distalPositive control on the tooth with mesio distal inclination.inclination. Prevents rotation of unrotated tooth during retraction.Prevents rotation of unrotated tooth during retraction. Decreased interbracket span-thus decrease resiliency ofDecreased interbracket span-thus decrease resiliency of the wire.the wire. Difficulty in closing loops and 2nd order bends,Difficulty in closing loops and 2nd order bends, Difficulty in obtaining final 10% of desired rotationDifficulty in obtaining final 10% of desired rotation correction.correction. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 25. Rotational control wingsRotational control wings • They are added to the edgewise brackets to maintain the single width ,they offer a lever arm to deflect the arch wire and rotate the teeth. • desired tooth rotation is obtained . • its also possible to overcorrect the tooth position by bending the rigid wings. • slight errors made in placement of bracket on teeth can be corrected by selective bending of wings • Rotational control wings • Flat wings • Upset wings • Curved wings • Rigid or flexible wings • Long or short wings. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 26. • Lewis rotation bracket is a overpiece bracket with integral rotation wings,it is rigid and have flat upset wings and or curved wings. • Lang brackets have flat rotational control wings. • Steiner brackets have flexible rotational arms so it does not entirely rely on the resiliency of archwire for rotation correction. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 27. LigationLigation Stainless steel Elastomeric Conventional ligating brackets Active passive Self ligating brackets www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 28. BASED ON MATERIALSBASED ON MATERIALS • A) METAL BRACKETS • 1) Stainless steel brackets • 2) Gold-coated brackets • 3) Platinum-coated brackets • 4) Titanium brackets • B) PLASTIC BRACKETS • 1) Polycarbonate brackets • 2) Polyurethane-composite brackets • 3) Thermoplastic-polyurethane brackets • C) CERAMIC BRACKETS • 1) Monocrystalline alumina • 2) Polycrystalline alumina • 3) Polycrystalline Zirconia www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 29. TITANIUM BRACKETSTITANIUM BRACKETSGOLD-COATED BRACKETSGOLD-COATED BRACKETS STAINLESS STEEL BRACKETSSTAINLESS STEEL BRACKETS PLATINUM COATED BRACKETS Austenitic AISI 303, 304, 316, and 317 •24 karat gold plating • plated with 300 micro inches of gold •esthetic 3M UNITEK) (AMERICAN ORTHODONTICS ORMCO Five times the abrasion resistance of gold. A smoother, harder surface than stainless steel For reduced friction and improved sliding mechanics is achieved. Corrosion resistant Low thermal conductivity Increased retention –rough surface Single piece- no soldering joints- nickel free www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 30. NICKEL-FREE BRACKETSNICKEL-FREE BRACKETS • Made of Cobalt chromium (CoCr) dental alloy • One-piece construction (without solder) by metal injection molding technique • Used in nickel sensitive patients • Laser structured bracket base for retention Nu Edge nickel free TP ortho www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 31. PLASTIC BRACKETSPLASTIC BRACKETS Cohen and Silverman (IPB brackets) manufactured by GAC in 1963. The first plastic brackets were manufactured from unfilled polycarbonate and esthetics was its main advantage. Pure plastic brackets lack strength to resist distortion and breakage, wire slot wear, uptake of water, discoloration and the need for compatible resins.www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 32. DISADVANTAGES OF POLYCARBONATE BRACKETS Polycarbonate brackets undergo creep deformation when transferring torque loads generated by arch wires to teeth. Discoloration of first generation unfilled polycarbonate brackets during clinical aging. They absorb water to a slight extent and tend to weaken in the course of about one year. Various reinforced polycarbonate brackets were, •Polymer fiber reinforced •Fiberglass reinforced •Ceramic reinforced •Metal slot reinforced •Metal slot and ceramic reinforced www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 33. some commercially available plastic brackets…. Polycarbonate-Composite •DB fibre •Elan Polyurethane-Composite - Envision Thermoplastic-polyurethane Value Line POLYCARBONATE BRACKETS ElationTM (GAC) Polycarbonate-glass fibers •Aesthetic Line •Image FIBER-REINFORCED POLYCARBONATE BRACKETS www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 34. CERAMIC BRACKETSCERAMIC BRACKETS TYPES OF CERAMIC BRACKETS • Monocrystalline (Sapphire) • Polycrystalline Alumina • Polycrystalline Zirconia-Yttrium oxide • Partially Stabilised Zirconia www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 35. MONOCRYSTALLINE CERAMIC BRACKETMONOCRYSTALLINE CERAMIC BRACKET Inspire Starfire POLYCRYSTALLINE ALUMINA CERAMIC BRACKETS www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 36. Metal-Reinforced Ceramic BracketsMetal-Reinforced Ceramic Brackets Clarity™ www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 37. Brackets for special purposesBrackets for special purposes Lewis and Lang brackets for Vari-simplex discipline Bracket for bio-progressive therapy Broussard brackets by Garford Broussard used in the Broussard technique is also a combination bracket . its a modification of edgewise with a 0.0185”x0.046” vertical slot to accept a double 0.018” auxiliary wire. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 38. • PRE-ADJUSTED EDGEWISE BRACKETS • TIPEDGE • CERAMIC BRACKETS • LINGUAL BRACKETS • SELF LIGATING BRACKETS So where are we now????? www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 40. • Roth started Rx with andrew’s bracket and altering the values and bracket positions. • Bracket identification marks. – Dot - disto-gingival wing of upper. – Dash- disto-gingival wing of lower. – Groove - second bicuspid. • Auxiliary attachments were added to the brackets, such as…. – double and triple tubes for headgears, lip bumpers and rectangular auxiliary tubes for Burstone or Bioprogressive mechanics. – Additional hooks on each bracket evolved for the use of short Class II or Class III elastics. ROTH (ovation brackets) (1975)ROTH (ovation brackets) (1975) www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 41. Overcorrection in rothOvercorrection in roth TORQUE central lateral canine 1st PM 2nd PM 1st M 2nd M SW Upper 7 3 -7 -7 -7 -9 -9 ROTH Upper 12 8 -2 -7 -7 -14 -14 ROTH Lower -1 -1 -11 -17 -22 -30 -30 SW lower -1 -1 -11 -17 -22 -30 -35 There is a "Super Torque" set of maxillary anteriors For cases like Class II, division 2, where an extreme amount of torque may be needed. SUPER TORQUE central lateral canine 1st PM 2nd PM 1st M 2nd M tip 5 9 9 2 0 0 0 torque 17 10 3 -7 -7 -14 -14 rotation 0 0 4M 2D 2D 0 0 NOT MUCH OVER CORRECTION IN LOWER TO AVOID CUSPAL INTERFERENCE www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 42. TIP central lateral canine 1st PM 2nd PM 1st M 2nd M SW Upper 5 9 11 0/2 0/2 5 5 ROTH Upper 5 9 13 0 0 0 0 ROTH Lower 2/0 2/0 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 SW lower 2 2 5 2 2 2 2 ROTATION central lateral canine 1st PM 2nd PM 1st M 2nd M ROTH Upper 0 0 4 2 2 14 14 ROTH Lower 0 0 2 4 4 4 4 The upper buccal segments are distally uprighted to 0The upper buccal segments are distally uprighted to 0 lower segments has given an 3*additional distal tiplower segments has given an 3*additional distal tip www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 43. This system evolved around five factors related to brackets bracket selection bracket height bracket angulation bracket torque bracket in-out The Vari-Simplex Discipline JCO 1983 JUN R.G. ALEXANDER www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 44. bracket selection LANG BRACKETS LEWIS BRACKETS CONVERATBLE SHEATH OCCLUSALLY PLACED HEADGEAR TUBE bracket height BRACKET HEIGHT Maxillary Arch Centrals X Laterals X – 0.5mm Cuspids X + 0.5mm Bicuspids X 1st Molars X – 0.5mm 2nd Molars X – 1.0mm Mandibular Arch Centrals X – 0.5mm Laterals X – 0.5mm Cuspids X + 0.5mm Bicuspids X 1st Molars X – 0.5mm www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 45. BRACKET ANGULATIONS Maxillary Arch Centrals 5° Laterals 8° Cuspids 10° Bicuspids and Molars 0° Mandibular Arch Centrals 2° Laterals 2° Cuspids 6° Bicuspids 0° 1st Molars – 6° 2nd Molars 0° BRACKET TORQUES Maxillary Arch Centrals 14° Laterals 7° Cuspids –3° Bicuspids – 7° Molars – 10° Mandibular Arch Incisors – 5° Cuspids – 7° 1st Bicuspids – 11° 2nd Bicuspids – 17° 1st Molars – 22° 2nd Molars 0° or – 27° bracket angulation bracket torque BRACKET IN-OUT Maxillary Arch IST MOLAR +15 SECOND MOLAR +12 Mandibular Arch IST MOLAR +5 SECOND MOLAR +6 bracket in-out www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 47. • Mc LAUGHLIN & BENNET 1975-1993 – Used SWA brackets with sliding mechanics and brackets positioned at centre of the crown. – Only one arch form- ovoid • 1993-97 with TREVESI – redesigned the bracket to MBT TM – Dots and dashes changed into laser numbering – Rectangular shape replaced by rhomboidal shape. – Revised bracket positioning to improve vertical accuracy. – Brackets available in – standard metal –when control is required – midsized –small sized teeth, poor oral hygiene – Clear (ClarityTM )- older patients www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 48. • 1997-2001- new range of MBT TM Versatile+ brackets • Brackets positioned with gauges • 3 arch-forms • Updated Light force and sliding mechanics. • MBT bracket is recommended as a modern version of PEA bracket for use with continuous forces, lace backs and bend backs. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 49. MBT-Bracket designMBT-Bracket design • Laser numbering • Rhomboidal shape-reduces bulk – Allows reference lines in both horizontal and vertical planes-accurate bracket positioning. • Milled in CAD-CAM-Torque in base. – In mid sized brackets-combi-torque in base and face www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 50. In outIn out • In –out of MBT is expressed well – arch-wire fits snugly in the slot. • 2nd PM bracket-0.5mm thicker for small teeth www.indiandentalacademy.co m
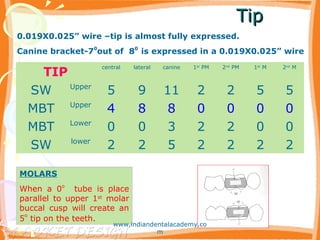
- 51. TipTip TIP central lateral canine 1st PM 2nd PM 1st M 2nd M SW Upper 5 9 11 2 2 5 5 MBT Upper 4 8 8 0 0 0 0 MBT Lower 0 0 3 2 2 0 0 SW lower 2 2 5 2 2 2 2 MOLARS When a 0o tube is place parallel to upper 1st molar buccal cusp will create an 5 o tip on the teeth. 0.019X0.025” wire –tip is almost fully expressed. Canine bracket-70 out of 80 is expressed in a 0.019X0.025” wire www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 52. TorqueTorque • Torque is not effectively expressed – Small area of torque expression. – 19x25 wire on 0.022 slot- 10o play – Radiusing of the wire • So extra torque is build up on the bracket -reduces the amount of wire bending at later stages www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 53. TORQUE central lateral canine 1st PM 2nd PM 1st M 2nd M SW Upper 7 3 -7 -7 -7 -9 -9 MBT Upper 17 10 -7 0 +7 -7 -7 -14 -14 MBT Lower -6 -6 -6 0 +6 -12 -17 -20 -10 SW lower -1 -1 -11 -17 -22 -30 -35 INCISOR TORQUE Upper-Palatal root torque Lower-labial root torque Indicated in Class II cases with class II elastics Class I cases where torque helps correct anterior tooth fit Calss III-where correct torque compensted for class III bases CANINE -7 is satisfactory to keep the canine roots in a prominent position canine roots by remodelling in cancellous bone offers less resistance during retraction. +7 and o –prominent canine roots or narrow maxillary bone UPPER POSTERIORS Premolars- continued with same Molars- increased lingual crown torque- reduces palatal cusp interferences 10* offset in -1st and 2nd molar tube LOWER POSTERIORS Reduced torque in posteriors to avoid lingual rolling In premolars by 5 degree In 1st molar by 10 degree In 2nd molar by 25 degree No offset www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 54. Versatility of MBTVersatility of MBTTMTM Versatile+Versatile+ 1. Palataly placed upper lateral incisor torque option -10o . 2. 3 torque option for upper canine. 3. 3 torque option for lower canine. 4. Inter-changable lower incisor brackets. 5. Inter-changable upper PM brackets. 6. Use of upper 2M tubes on 1M non HG cases. 7. Use of lower 2M bracket on opposite side 1M when finishing on class II. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 55. Additional benefitsAdditional benefits • Thicker brackets for small premolars • Self ligating second molar tubes • Lower 1st molar non convertible tubes • Lower 1st molar double tube and upper 1st molar triple tube. • Bondable 2nd molar mini tubes www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 56. Uni-Twin™ BracketsUni-Twin™ Brackets • Interbracket span of a single bracket with the rotation control of a twin bracket. • The Uni-Twin system is a twin bracket frame with a centered, single bracket archwire slot. Together, these features of the Uni-Twin brackets provide approximately 50% more interbracket distance than ordinary twin brackets. This enables to start patients in larger archwires and then progress to full- sized archwire faster, increasing patient comfort. • The innovative mesh bonding base is designed to match precisely to the curvature of the tooth for maximum contact and strong, consistent bonding. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 58. Low profile Uni twin design Smooth and contured labial surface Tooth shaped design www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 60. TRIANGULAR BIOEFFICIENTTRIANGULAR BIOEFFICIENT BRACKETSBRACKETS • The large inter-bracket distance between the slots of the triangular brackets allows engagement of super-elastic square wire from the onset of treatment. The arch-wire slot is elevated so that the wire, once inserted, will come in contact with the side elbow extension in misaligned teeth and start uprighting the root from the beginning of treatment. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 61. • The single slot (X-1) bracket allows for a large inter-slot distance for the maximum arch wire flexibility during it's insertion. The arch-wire slot is elevated so that the wire may come in contact with the side elbow extension only during movement, thus allowing the bracket slot to become a wide twin slot (X-2), to upright the root from the beginning of treatment. Hence, the bracket is a single and twin bracket that allows the clinician to move teeth in one stage (crown and root) with only one wire, in about a year. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 62. The Crown SystemThe Crown System low profile - maximum patient comfort. all four sides of the Crown Bracket’s base can be used to position the bracket. increases accuracy in aligning and positioning brackets reduces chair-side time one-piece construction. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 63. BUTTERFLY SYSTEMBUTTERFLY SYSTEM HYBRID 3RD GENERATION BRACKETBOWMAN AND CARANO JCO MAY 2004 Reduced profile Miniature twin wing design Rounded tie wings No standard hooks Versatile vertical slot Progressive posterior torque Reversible 2ND premolar brackets Progressive mandibular anterior tip Angulated first molar attachment Conservative anterior torque Improvement in overjet Bonding pad enhancement www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 64. VERSATILE VERTICAL SLOT • ELIMINATES BALL HOOKS • SIMPLE HOOK PIN OR A ‘T’ PIN • VERTICAL SLING TIES • U TURN ROTATION SPRING • COMPLIANCE SPRING • BEGG UPRIGHTING SPRING • POWER ARM PROGRESSIVE POSTERIOR TORQUE • OVERCOMES THE LINGUAL ROLLING EFFECT OF LOWER MOLARS AND BUCCAL CROWN TORQUE OF UPPER MOLARS RESULTS IN BAD INTERCUSPATION • BUTTERFLY- UPPER-INCREASED TORQUE -14* • LOWER- DECREASED TORQUE -10* www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 65. • REVEREBILE SECOND PREMOLAR BRACKET www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 66. • PROGRESSIVE MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR TIP • ANGULATED FIRST MOLAR ATTACHMENTS • -6o TIP IS PLACED IN MOLAR TUBE ATTACHMENTS • When the bands are fitted evenly in mesial and distal marginal ridges, the bracket slots will be level. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 67. • PREVENTIVE MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR TORQUE – LINGUAL CROWN TORQUE -5 / -10* – PREVENTS ANTEIOR FLARING WITH USE OF CLASS II ELASTICS OR HERBST APPLIANCE. • BONDING PAD ENHANCEMENT - PHOTOETCHED POCKETS – OPTIONAL OFFSET BASES IN THE PREMOLAR BRACKET BASES www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 68. TORQUE TIP ROTATION MAXILLARY CI +14 +5 LI +8 +9 C 0 +9 1 PM -7 0 2PM -8 +3 MANDIBULAR CI -5 / -10 +2 LI -5 /-10 +5 C -3 +6 3 DO 1 PM -7 0 2PM -9 +3www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 69. Bracket with variable ligationBracket with variable ligation JCO 1995JCO 1995 rounded slot wall- low arch wire binding variable ligation reduced friction-when module placed in center wing www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 70. Friction free bracketsFriction free brackets Development of Friction-Free Edgewise bracket,Development of Friction-Free Edgewise bracket, Jap. Orthod. Soc. 51:298, 1992Jap. Orthod. Soc. 51:298, 1992.. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 73. • minimizes the normal forces caused by ligation decreases the resistance to sliding • Minimizes chair side time. • Precise control of tooth translation. • Greater interbracket span of archwire available without binding of ligature wires and elastics. • Hygienic, wingless, easy to clean. • Esthetic and comfortable to patient. • Ligation stability retains original form throughout treatment. • Some self ligating bracket designs permit significant miniaturization of bracket size. Advantages…… . www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 74. Active vs. Passive BracketsActive vs. Passive Brackets - action of the locking slide or clip on the wire • Active-SPEED, Sigma, and Time brackets • Passive-Damon SL, EdgeLok, and Wildman TwinLock • The aim of active ligation is to seat the arch wire against the back of the bracket slot for rotation and torque control. • When the slide is closed, the lumen of the slot is full- size • Rotations are expressed by using high-tech flexible wires to nearly fill the slot in a labiolingual direction • In active self-ligation, the energy to control rotations is primarily derived from the clip; in passive self-ligation, the energy is stored and expressed in the high-tech wires. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
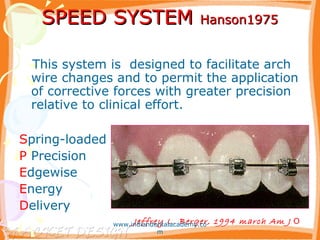
- 75. SPEED SYSTEMSPEED SYSTEM HanSon 1975HanSon 1975 www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 76. SPEED SYSTEMSPEED SYSTEM Hanson1975Hanson1975 This system is designed to facilitate arch wire changes and to permit the application of corrective forces with greater precision relative to clinical effort. Spring-loaded P Precision Edgewise Energy Delivery Jeffrey L. Berger, 1994 march Am J Owww.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 78. Bracket bodyBracket body • Narrow, single bracket body • Mushroom-shaped hook that projects from the distogingival of each bracket body. • Multislotted in design (3 slots) • A pretorqued arch wire slot, 0.018 x 0.025 inch or 0.022 x 0.028 inch • An auxiliary slot, 0.016” square for preformed hooks for use with elastics Alternatively, a ligature tie or elastomeric thread may be fed through the auxiliary slot and then tied to the arch wire. For lingually displaced teeth, this approach tends to minimize overstressing of the arch wire or periodontium. • A spring retainer slot. to house the recurved tip of the spring clip. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 79. • Roll-shaped, flexible, highly resilient spring clip. • opens and closes in a vertical manner to permit arch wire removal and insertion • Its shape eliminates any possibility of accidental arch wire release through the incorporation of a recurved tip. • This escape-proof spring design also readily permits the engagement and retention of elastic thread or steel ligature ties. This feature is particularly useful in situations where a tooth is greatly displaced from the arch and arch wire engagement would result in the permanent deformation of the arch wire or exceed the bond strength of the attachment . The spring clipThe spring clip www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 80. This highly resilient spring clip is primarily responsible for controlling tooth movement in all three planes of space through rotation, tip, and torque. Its unique method of delivery ensures a more continuous delivery of force, as well as a reduced level of frictional drag. • If the spring is damaged it can be replaced with a micro utility plier.www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 81. • THE IN-OUT ADAPTOR SPEED adaptor features both an angular and a translational dimension. This unique characteristic ensures the creation of an exceptionally smooth arch form that is achieved through a progressive “ ramp- like” effect of the in-out adaptors • THE MESH PAD • a foil mesh with complex asymmetric curvatures. • the recent change in size of the brazed foil mesh from a fine 100 gauge to a more coarse 60 gauge has further enhanced the bond strength of the SPEED attachment. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 82. Opening and closingOpening and closing • Opening with a sickle scaler or SPEED opening instrument. • The instrument tip is centrally positioned on the gingival aspect of the bracket against the indent in the spring clip. A light force of approximately 300 gm applied in an occlusal direction will displace the spring clip into its "slot open" resting position. • Closure of the SPEED appliance is achieved simply by applying a gingivally directed force to the spring clip with a gloved finger or thumb. A fine ligature directory should be used to simultaneously seat the arch wire while the closure force is applied. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 83. 1998 NOV JCO1998 NOV JCO www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 84. Passive Low friction self-ligating twin bracket • The Damon bracket was designed to satisfy the following major criteria: • Andrews Straight-Wire Appliance concept • Twin configuration • Slide forming a complete tube • Passive slide on outside face of bracket • Brackets opening inferiorly in both arches www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 86. greater control. Improves patient comfort Shortens treatment time for most cases. Aligns teeth faster. Saves time with sliding mechanics. Requires less time for finishing. Shortens chair side time for each visit. Expands treatment planning options. Simplifies treatment mechanics. Makes it easier to keep appliances clean. Improves practice efficiency and profitability. advantages www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 87. • Stainless steel 17-4 metal-injection molded (MIM) construction for exceptional strength and durability • Four solid walls for fast, low-friction tooth movement and superior control • Remarkably easy-to-use slide mechanism with deep funnel and backstop for quick wire changes • Smooth slot corners for reduced binding • Vertical slot for removable drop-in hooks and other auxiliaries • Contoured base design and Optimesh® pads for optimal bond retention • Ultra-smooth contours and rounded edges for maximum patient comfort www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 88. Frictional Resistance of the Damon SLFrictional Resistance of the Damon SL BracketBracket JCO august 1998JCO august 1998 Results- self-ligating brackets not only make arch-wire placement more convenient and secure, but also have lower kinetic frictional forces than conventional brackets. These features can be substantial advantages for orthodontists who use sliding mechanics. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 89. THE EDGELOK BRACKET Dr. Alexander J. Wildman JCO 1998 www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 90. Edgelok is a slot surrounded on four sides by contoured metal surfaces. Smooth, round, button shaped surface- patient comfort The absence of ties is an obvious additional benefit. Low profile. Edgelok's button shape allows it to be large where needed for strength, but small in the critical areas. The occlusal boss can be reduced as much as necessary to accommodate the occlusion. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 91. Auxillary slot-0.014”-used to thread elastic thread instead of “figure eighting” Complete control in all planes of space. Ligature ties can be tied into saddle horn -severely malpostioned teeth www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 92. BRACKET OPENING AND CLOSING TOOLSBRACKET OPENING AND CLOSING TOOLS • There is a special tool for opening the Edgelok bracket and another for holding the wire in the slot and closing the lock. • A scaler or ligature cutter can be used to open the bracket and a utility plier can close it. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 93. The wire is retained by a resilient clip that rotates into a retaining groove gingival to the arch wire, positioning two straps labial to the wire and creating a bracket that is very similar mechanically to a molar tube with twin channel caps. Vertical slots behind the arch wire channel. Brackets for the anterior teeth have gingival and occlusal tabs to assist orientation relative to the facial axis of the clinical crown. The brackets are also available pre-welded to bands. ACTIVA BRACKETS Irwin Pletcher 1986 www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 94. advantages • 1. Low friction between bracket and arch wire. • 2. More certain full arch wire engagement. • 3. Less chair-side assistance. • 4. A vertical slot for hooks and auxiliaries. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 95. TIME BRACKETSTIME BRACKETS 1998 JCO1998 JCO The first one-piece self-ligating system, was developed using CAD/CAM technology. Microetched undercuts on the bases Reduced profile Reduction in in out thickness of 0.14 in bicuspid and 0.5 in incisors The outline of the bracket pad follows the mesial and distal margins and the contour lines of the bracket pad are parallel to the gingival line and the incisal edges. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 96. System R( In-Ovation series)System R( In-Ovation series) 20012001 • Only self-ligating twin bracket with an active clip. • Two sizes- – Standard (1999) – Reduced width (2001) • Failure of clip is seldom-if failed modules can be used. • Standard bracket has additional slot for aligning displaced or ectopic teeth. • Don’t use this in patients with calculus forming tendency. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 97. 1. Rhomboid-Shaped Base 2. Metal Injection Molding 3. Torque-In-Base 4. CNC milled for precision and smoothness 5. A Compound Contoured Base for a more anatomical fit 6. Center of Slot ID Marker for better placement and orientation 1. True Twin "Four Tie Wing" design offers rotational control and versatile use of ligatures 2. Co-Cr "Active" Clip provides full slot coverage to gently seat the arch wire 3. A Horizontal Auxiliary Slot for sectionals, uprighting springs, and rotation springs 4. Smooth Rounded 'Mini' Posts 5. A Slot Blocker for preventing the arch wire from escaping the bracket slotwww.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 99. • The SmartClip Self-Ligating Appliance System design shares the MBT philosophy: – maximum versatility, – mid-sized twin brackets, – bracket prescription – the use of light force. • The SmartClip consists of two Nitinol clips that open and close through elastic deformation of the material when the arch wire exerts a force on the clip. The bracket contains no moving door or latch. • eliminates problems such as sticking, spontaneous opening, plaque build-up, etc., that are associated with other types of self-ligating brackets. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 100. • These are true self-ligating brackets, because the clip automatically closes and secures the arch wire in the wire slot. • simplifies the process of arch wire engagement and disengagement. Because of the true twin design, the clinician has the option of selectively engaging the arch wire in only one clip when teeth are severely malalignied • additional tie wing design allows ligature ties also. Nitinol Clip Design • Designed with finite element analysis. Ensures proper arch wire engagement and disengagement Forces Stress-strain distributions for fatigue resistance. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 103. • In early 1970s Dr Craven Cruz devolped true lingual appliance. – Plastic lee Fischer brackets on the anteriors and metal brackets on the posterior • In mid 1970s he smoothened the surfaces. • 1976 Ormco together with miller craig kruz devolped lingual appliances with inclined planes- intrusive force & reduced bond failure • 1979- brackets came into market www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 104. Generation of lingual bracketsGeneration of lingual brackets GENERATION I-1976 ORMCO-FIRST KRUZ LINGUAL APPLIANCE FLAT OCCLUSAL PLANES IN ANTERIORS LOW PROFILE & ROUND BRACKETS ON LOWER INCISOR AND PREMOLAR NO HOOKS www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 105. GENERATION II-1980 Canine hooks Hooks on premolars and anterior First molar- internal hook Second molar- terminal recess GENERATION III-1981 www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 106. GENERATION IV-1982-84 Low profile Anterior inclined plane Hooks-optional GENERATION V-1985-86 Max anteriors- pronounced inclined plane Increased labial torque Canine- Bibevelled and inclined plane TPA attachment Torque: +68 Angulation:+5 Slot size:0.018 Pad: special design Torque +55 angulation +120 in-out . 010 .018 slot www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 107. GENERATION VI-1987-90 Inclined – more square Elongated hooks on anteriors and premolars Optional TPA attachments Hinge cap GENERATION VII-1990… Heart shaped inclined plane Premolar brackets widened and hooks shortened Molar bands – terminal sheath or hinge capwww.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 108. • Modular construction- each components are fabricated and positioned independently. • Low profile ,exact fit • Made of gold alloy with CAD-CAM software. • Individualized bracket design. • Bracket production and positioning are carried out at single step. • Improved patient comfort. • Optimal finishing. • Ease of direct rebonding. • More torque is expressed, due to the reduced thickness of the bracket. Lingual care - 2001 Wiechmann www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 109. manufacturingmanufacturing • Impression in polyvinyl siloxane. • 3D scanning • Digital bracket base is created on digital model. • The bracket body is created with pro lingual software. • Digital library will help technician to select the size of bracket. • Placed on the base. • The virtual model is crested into a wax pattern. • Casted and fabricated • Checked with a 0.018 fine precision gauge • Polished with Al2O3 and coated with Rocatec plus www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 112. • Flower, Heart, Star, Soccer-ball and Football brackets • Wild Smiles brackets are patented designs • They are crafted in the US to Roth prescription. • Torque in base • 80 grade mesh bonding base • Axial Placement Technology (vertical stripe line along the tip angle through the center of each bracket) • metal injection molding • Compound contoured surfaces • No sharp corners provide easy bonding clean-up • Cuspids and premolars have hooks • Tooth number is on mesial gingival tie wing • Maxillary distal gingival tie wing has a "dash" www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 113. cc oo nn cc ll uu ss ii oo nn cc oo nn cc ll uu ss ii oo nn cc oo nn cc ll uu ss ii oo nn cc oo nn cc ll uu ss ii oo nn cc oo nn cc ll uu ss ii oo nn cc oo nn cc ll uu ss ii oo nn cc oo nn cc ll uu ss ii oo nn cc oo nn cc ll uu ss ii oo nn cc oo nn cc ll uu ss ii oo nn The recent advancement in the bracket design with various prescriptions has made it possible to chose the right pre programmed bracket for a particular patient and various forms of base has led to good bonding features. The choice of right bracket design therefore helps in achieving the best results for an orthodontic patient www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 118. Kesling, modified the basic edgewise bracket by removing the diagonally opposed corners from the conventional edgewise slot to permit free mesial or distal tipping The tip-edge bracket takes advantage of the slot and permits differential tooth movement with straight arch- wires, And therefore, called as “Differential Straight ArchDifferential Straight Arch TechniqueTechnique” APPLIANCE DESIGN Available in single, twin, ceramic versions. Molar tubes-2 slots Gingival round slot-longer-for initial alignment Rectangular-occlusal-shorter-same level of premolar slot-final stages. Add g v 15-7 www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 119. Tipping surfaces. Up righting surfaces. Central Ridges. Rotation control. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 120. A. Slot dimension is 0.022 inch when uprighting surfaces are parallel with the arch wire. B, Slot can increase to 0.027 inch when distal tipping of canine occurs. This permits changing from 0.016 to 0.022-inch arch wires with no deflection. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 121. • Differential tooth movement plus predetermined degrees of final crown tip and torque. • Chamfered edges minimizes the anchorage strain and permits the desired distal crown tipping required for differential tooth movement. • Pre adjusted in three dimensions • The slot is designed so that initial second order changes, mesio-distal crown tipping, can be accomplished in the presence of a straight, round arch wire and powered by a light intra oral forces, elastic or coil springs. Forces for subsequent root up righting, tip and/or torque are generated by auxiliaries, not by flexing the arch wires advantages www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 122. • Not only do the arch wire slots permits initial crown tipping but also they are pre-adjusted to provide the desired final degrees crown tip and torque. • Anchorage problems associated with previous straight wire brackets should be completely eliminated as spaces can be closed with relatively light forces and minimal arch wire deflection.This results in diminished anchorage demands and increased vertical control. With differential tooth movement anchor molars are not subjected to forces great enough to initiate their movement until spaces are closed www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 123. • In final stages of treatment, only single point contacts/ no contact between bracket and wire. Hence effective IBW is from molar to molar. • The in/out compensation built in to Tip-edge brackets eliminates the need for molar offsets normally required when using ribbon arch type bracket • Horizontally facing arch wire slots facilitate initial arch wire engagement especially on rotated teeth. Elastomeric ties provide a degree of flexibility or “cushion” that doesn't exist when using ribbon arch type brackets and lock pins. This enhances patient comfort and reduces the chances for bond failures. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 125. a) Standard Tip-Edge bracket. b) "Deep Groove" version for maxillary incisors, featuring conventional edgewise slot that is filled with special cap to keep arch wire in outer slot during Stages I and II. c) Cap is removed for Stage III and deep groove used to engage nickel titanium torquing auxiliary under main arch wire. www.indiandentalacademy.co m
- 126. Single width brackets with wings. Double width bracket. Ceramic bracket.www.indiandentalacademy.co m





















![Width of the bracketWidth of the bracket
• Single brackets-narrow width/single
brackets and wide width posterior
brackets.
• Twin brackets [dual, double or siamese brackets]-
mini twin, intermediate twin, standard
twin, extra wide twin.
• Triple brackets.
www.indiandentalacademy.co
m](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bracketsinorthofinal-160506113956/85/Brackets-in-ortho-final-22-320.jpg)