C programming Tutorial Session 2
- 2. OBJECTIVES • Discuss variables •Differentiate between variables and constants •List the different data types and make use of them in C programs • Discuss arithmetic operators Presented by: Muhammad Ehtisham Siddiqui (BSCS) 2
- 3. VARIABLE Presented by: Muhammad Ehtisham Siddiqui (BSCS) 3
- 4. VARIABLE EXAMPLE • BEGIN • DISPlAY ‘Enter 2 numbers’ • INPUT A, B • C = A + B • DISPLAY C • END A, B and C are variables in the pseudocode BEGIN DISPlAY ‘Enter 2 numbers’ INPUT A, B C = A + B DISPLAY C END Variable names takes away the need for a programmer to access memory locations using their address The operating system takes care of allocating space for the variables Presented by: Muhammad Ehtisham Siddiqui (BSCS) 4
- 5. CONSTANT • A constant is a value whose worth never changes. • Example: • 5 numeric / integer constant • 5.3 numeric / float constant • ‘Black’ string constant • ‘C’ Character constant • Variable holds constant values • Int a=5; • Char a=‘C’ Presented by: Muhammad Ehtisham Siddiqui (BSCS) 5
- 6. IDENTIFIERS • The names of variables, functions, labels, and various other user defined objects are called identifiers • Some correct identifier names • arena • s_count • marks40 • class_one • Some In correct identifier names • 1sttest • oh!god • start...end Presented by: Muhammad Ehtisham Siddiqui (BSCS) 6
- 7. IDENTIFIERS • Identifiers can be of any convenient length, but the number of characters in a variable that are recognized by a compiler varies from compiler to compiler • Identifiers in C are case sensitive Presented by: Muhammad Ehtisham Siddiqui (BSCS) 7
- 8. KEYWORD All languages reserve certain words for their internal use Keywords hold a special meaning within the context of the particular language No problem of conflict as long as the keyword and the variable name can be distinguished. For example, having integer as a variable name is perfectly valid even though it contains the keyword int Presented by: Muhammad Ehtisham Siddiqui (BSCS) 8
- 9. DATA TYPES Presented by: Muhammad Ehtisham Siddiqui (BSCS) 9 o data type or simply type is a classification of data which tells the compiler or interpreter how the programmer intends to use the data. o A data type provides a set of values from which an expression (i.e. variable, function...) may take its values.
- 10. INT DATA TYPE • Stores numeric data • int num; • Cannot then store any other type of data like “Alan” or “abc” • 16 bits (2 bytes) • Integers in the range -32768 to 32767 • • Examples: • 12322, • 0, • -232 Presented by: Muhammad Ehtisham Siddiqui (BSCS) 10 #include<stdio.h> void main() { Int i=98; Int j=-67; }
- 11. FLOAT Stores values containing decimal places float num; Precision of upto 6 digits 32 bits (4 bytes) of memory Examples: 23.05, 56.5, 32 Presented by: Muhammad Ehtisham Siddiqui (BSCS) 11 #include<stdio.h> void main() { Float var= 28.00006; }
- 12. DOUBLE • Stores values containing decimal places • double num; • Precision of upto 10 digits • 64 bits (8 bytes) of memory • Examples: ‘a’, ‘m’, ‘$’ ‘%’ , ‘1’, ’5’ Presented by: Muhammad Ehtisham Siddiqui (BSCS) 12 #include<stdio.h> void main() { DOUBLE var= ’28%’; }
- 13. CHAR • Stores a single character of information • char gender; gender='M'; • 8 bits (1 byte) of memory • Examples: ‘a’, ‘m’, ‘$’ ‘%’ , ‘1’, ’5’ Presented by: Muhammad Ehtisham Siddiqui (BSCS) 13 #include<stdio.h> void main() { Char var= ’X’; }
- 14. VOID • Stores nothing • Indicates the compiler that there is nothing to expect Presented by: Muhammad Ehtisham Siddiqui (BSCS) 14
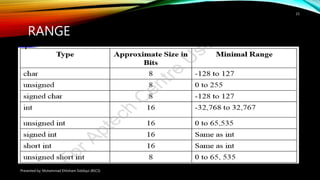
- 15. RANGE Presented by: Muhammad Ehtisham Siddiqui (BSCS) 15
- 16. DECLARING VARIABLE main () { char abc; /*abc of type character */ int xyz; /*xyz of type integer */ float length; /*length of type float */ double area; /*area of type double */ long liteyrs; /*liteyrs of type long int */ short arm; /*arm of type short integer*/ } Presented by: Muhammad Ehtisham Siddiqui (BSCS) 16
- 17. Presented by: Muhammad Ehtisham Siddiqui (BSCS) 17