Chapter1 modified
- 2. Figure 1-1: Basic Networking Concepts • What Is a Network? – A network is a transmission system that connects two or more applications running on different computers. Network Network 2
- 3. Figure 1-1: Basic Networking Concepts • Client/Server Applications – Most Internet applications are client/server applications – Clients receive service from servers – The client is often a browser Client Server Program Program Services Client Computer Server Computer 3
- 4. The Nine Elements of a Network Although the idea of “network” is simple, you must understand the nine elements found in most networks
- 5. Figure 1-3: Elements of a Network Client Application Server Application Message (Frame) Message (Frame) Access Switch Line 1. 1. 2 Client Networks connect Networks connect Server Computer applications on different computers. applications on different computers. Computer Switch Switch 1 Trunk Networks connect computers: 3 Networks connect computers: Line 2. Clients (fixed and mobile) and 2. Clients (fixed and mobile) and Mobile 3. Servers 3. Servers Client Outside World Wireless Access Point Router 5
- 6. Figure 1-3: Elements of a Network Client Application Server Application Message (Frame) Client Server Computer Computer Switch 4. 4. Switch Computers1 Computers (and routers) (andTrunk routers) 3 usually communicate usually communicate Line by sending messages Mobile by sending messages called frames called frames Client Outside World Wireless Access Point Router 6
- 7. Figure 1-3: Elements of a Network Client Application Server Application Client Client Message (Frame) Message (Frame) Sw2 Sends Sends Sw1 Sends Sw2 Sends Sends Sw1 Sends Frame Frame Frame Frame Frame Frame To Sw3 To Sw3 to Sw1 to Sw2 to Sw2 to Sw1 Client Switch 2 Switch 2 Server Sw3 Sends Sw3 Sends Computer Computer Frame to Frame to Switch 1 Switch 1 Server Server Switch 3 Switch 3 Trunk Line Mobile 5. 5. Client Switches Forward Switch Outside Switches Forward Frames Sequentially Frames Sequentially 4 World Wireless Access Point Router 7
- 8. Figure 1-5: Ethernet Switch Operation C3- is out Port 15 C3- is out Port 15 D4-47-55-C4-B6-F9 Switching Table Switching Table Port Switch Port Host Host 10 10 A1-44-D5-1F-AA-4C A1-44-D5-1F-AA-4C 13 2 B2-CD-13-5B-E4-65 13 B2-CD-13-5B-E4-65 15 15 15 15 C3-2D-55-3B-A9-4F C3-2D-55-3B-A9-4F C3-2D-55-3B-A9-4F C3-2D-55-3B-A9-4F 16 16 D4-47-55-C4-B6-F9 D4-47-55-C4-B6-F9 Port 15 3 Frame to C3… Frame to C3… Frame to C3… Frame to C3… 1 C3-2D-55-3B-A9-4F A1-44-D5-1F-AA-4C B2-CD-13-5B-E4-65 A1- sends a frame to C3- Switch sends frame to C3- Switch sends frame to C3- A1- sends a frame to C3- 8
- 9. Figure 1-3: Elements of a Network Client Application Server Application Message (Frame) Message (Frame) Access Switch Line 2 Client Server Computer 6. 6. Computer Switch Wireless Access Wireless Access Switch 1 Points Connect Points Connect Trunk 3 Wireless Stations Wireless Stations Line to Switches Mobile to Switches Client Switch Outside 4 World Wireless Access Point Router 9
- 10. Figure 1-3: Elements of a Network Client Application Server Application Message (Frame) Message (Frame) Access Switch Line 2 Client 7. Server Computer 7. Routers connect networks Computer Routers connect networks Switch to the outside world; Switch to the outside world; 1 Trunk Treated just like computers 3 Treated just like computers Line in single networks in single networks Mobile Client Switch Outside Yes, single networks can 4 World Wireless contain routers Access Point Router 10
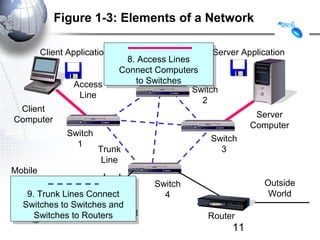
- 11. Figure 1-3: Elements of a Network Client Application Server Application 8. Access Lines 8. Access Lines Message (Frame) Message (Frame) Connect Computers Connect Computers Access to Switches to Switches Switch Line 2 Client Server Computer Computer Switch Switch 1 Trunk 3 Line Mobile Client Switch Outside 9. Trunk Lines Connect 9. Trunk Lines Connect 4 World Wireless Switches to Switches and Switches to Switches and Switches to Routers Point Access Switches to Routers Router 11
- 12. Figure 1-4: Packet Switching and Multiplexing Breaking Communications into Small Messages is Called Packet Switching, even if the Messages are Frames AC AC Client AC Server AC Computer A Computer C AC BD AC Trunk Line BD Access Line Multiplexed Packets BD BD Share Trunk Lines Mobile Client So Packet Switching Router D Computer B Reduces the Cost of Trunk Lines 12
- 13. Figure 1-8: LANs Versus WANs Characteristics Characteristics LANs LANs WANs WANs Scope Scope For transmission within For transmission within For transmission For transmission a site. Campus, a site. Campus, between sites between sites building, and SOHO building, and SOHO (Small Office or Home (Small Office or Home Office) LANs Office) LANs Building Building Campus Campus LAN LAN Wide Area LAN LAN Network Home Home LAN LAN 13
- 14. Figure 1-8: LANs Versus WANs Characteristics LANs WANs Cost per bit Transmitted Low High Unshared 100 Mbps Shared 128 kbps to to a gigabit per several megabits per Typical Speed second to each second trunk line desktop. Even faster speeds trunk line speeds. It’s simple economics. If the cost per unit is higher, the number of units demanded will be lower. Corporations cannot afford high-speed for most of their WAN transmission 14
- 15. Figure 1-8: LANs Versus WANs Characteristics LANs WANs WANs On own premises, so Must use a carrier with On own premises, so Must use a carrier with Management Management firm builds and firm builds and rights of way for rights of way for manages its own LAN transmission in public manages its own LAN transmission in public or outsources the or outsources the Area. Carrier handles Area. Carrier handles Work Work most work but most work but Charges a high price. Charges a high price. Choices Choices Unlimited Unlimited Only those offered by Only those offered by carrier carrier 15
- 16. Figure 1-9: Local Area Network (LAN) in a Large Building Wall Jack Workgroup Switch 2 Client Server Workgroup Switch 1 Wall Jack To Router Core Switch WAN Frames from the client to the server go through Workgroup Switch 2, through the Core Switch, through Workgroup Switch 1, and then to the server 16
- 17. Figure 1-11: Internets • Single LANs Versus Internets – In single networks (LANs and WANs), all devices connect to one another by switches—our focus so far. – In contrast, an internet is a group of networks connected by routers so that any application on any host on any single network can communicate with any application on any other host on any other network in the internet. Application Application LAN LAN WAN WAN LAN LAN Router Router 17
- 18. Figure 1-11: Internets • Internet Components Host – All computers in an internet are called hosts – Clients as well as servers PDA Client PC (Host) (Host) VoIP Phone (Host) Internet Internet Server (Host) Cat Cellphone (Ignores (Host) Internet) 18
- 19. Figure 1-11: Internets • Hosts Have Two Addresses • IP Address – This is the host’s official address on its internet – 32 bits long – Expressed for people in dotted decimal notation (e.g., 128.171.17.13) • Single-Network Addresses – This is the host’s address on its single network – Ethernet addresses, for instance, are 48 bits long – Expressed in hexadecimal notation (e.g., AF-23-9B- E8-67-47) 19
- 20. Figure 1-11: Internets • Networks are connected by devices called routers – Switches provide connections within networks, while routers provide connections between networks in an internet. • Frames and Packets – In single networks, message are called frames – In internets, messages are called packets 20
- 21. Figure 1-11: Internets Packet Packet Frame • Packets are carried within frames – One packet is transmitted from the source host to the destination host across the internet • Its IP destination address is that of the destination host LAN LAN WAN WAN LAN LAN Router Router 21
- 22. Figure 1-14: The Internet, internets, Intranets, and Extranets • Lower-case internet – Any internet • Upper-case Internet – The global Internet • Intranet – An internet restricted to users within a single company • Extranet – A group of resources that can be accessed by authorized people in a group of companies 22
- 23. Figure 1-23: Firewall and Hardened Hosts Allowed Legitimate Border Packet Attacker Firewall The Hardened Internet Server Border firewall Border firewall Legitimate should pass should pass Packet legitimate packets legitimate packets Hardened Legitimate Client PC Host Internal Log File Corporate Network 23
- 24. Figure 1-23: Firewall and Hardened Hosts Hardened Border firewall Server Border firewall Attack should deny (drop) should deny (drop) Border Packet Attacker and log and log Firewall attack packets attack packets The Internet Hardened Client PC Denied Attack Packet Legitimate Host Internal Log File Corporate Network 24
- 25. Figure 1-23: Firewall and Hardened Hosts Hardened Hardened Server Attack Server Attack Border Packet Attacker Packet Firewall The Internet Hosts should Hosts should Attack Denied be hardened Packet be hardened Hardened Hardened Attack against attack packets against attack packets Client PC Client PC Packet that get through that get through Legitimate Host Internal Log File Corporate Network 25