Chapter15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- 1. Chapter 15 Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Learning Objectives Define CRM; Understand the importance of CRM; Explain the determinants of CRM and the key stages in its development; Discuss the main functions and various models of CRM; Explain the role of salespeople as relationship developers Discuss the management of customer relationships.
- 2. Chapter 15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) What is Customer Relationship Management (CRM)? CRM is “the development and maintenance of mutually beneficial long-term relationships with strategically significant customers ” (Buttle, 2000) CRM is “an IT enhanced value process , which identifies, develops, integrates and focuses the various competencies of the firm to the ‘ voice’ of the customer in order to deliver long-term superior customer value , at a profit to well identified existing and potential customers ”. (Plakoyiannaki and Tzokas, 2001)
- 3. Chapter 15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Understanding Customer Relationship Management (CRM)? CRM is a business philosophy based on upon individual customers and customised products and services supported by open lines of communication and feedback from the participating firms that mutually benefit both buying and selling organisations . The buying and selling firms enter into a “learning relationship ”, with the customer being willing to collaborate with the seller and grow as a loyal customer . In return,, the seller works to maximize the value of the relationship for the customer’s benefit . In short, CRM provides selling organisations with the platform to obtain a competitive advantage by embracing customer needs and building value-driven long-term relationships .
- 4. Chapter 15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Determinants of CRM Trust The willingness to rely on the ability, integrity, and motivation of one company to serve the needs of the other company as agreed upon implicitly and explicitly. Value The ability of a selling organisation to satisfy the needs of the customer at a comparatively lower cost or higher benefit than that offered by competitors and measured in monetary, temporal, functional and psychological terms.
- 5. Chapter 15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Determinants of CRM In addition to trust and value , salespeople must : Understand customer needs and problems; Meet their commitments; Provide superior after sales support; Make sure that the customer is always told the truth (must be honest); and Have a passionate interest in establishing and retaining a long- term relationship (e.g., have long-term perspective).
- 6. Chapter 15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Stages in the development of a Customer Relationship The Pre-relationship Stage The event that triggers a buyer to seek a new business partner. The Early Stage Experience is accumulated between the buyer and seller although a great degree of uncertainty and distance exists. The Development Stage Increased levels of transactions lead to a higher degree of commitment and the distance is reduced to a social exchange. The Long-term Stage Characterised by the companies’ mutual importance to each other. The Final Stage The interaction between the companies becomes institutionalized.
- 7. Chapter 15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Stages in the Development of a Key-Account Relationship Degree of involvement High Low Nature of customer relationship Transactional Collaborative Pre-KAM Early-KAM Mid-KAM Partnership Synergistic KAM (Millman and Wilson, 1995)
- 8. Chapter 15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) A Relationship Life Cycle Model High cooperation Low competition Low cooperation High competition Time Pre- relationship stage Development stage Maturity stage Decline stage (Wilkinson and Young, 1997)
- 9. Chapter 15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Class Exercise What should the focus and main activities of a global salesperson be in each stage of the relationship development process? Why? (Please justify your answer)
- 10. Chapter 15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Functions of Customer Relationship Management Direct functions (are the basic requirements of a company that are necessary to survive in the competitive marketplace) Profit; Volume; and Safeguard Indirect functions (are the actions necessary to convince the customer to participate in various marketing activities). Innovation: Market; Scout: and Access.
- 11. Chapter 15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Functions of Customer Relationship Management Management Decision Process Customer sensitivity Diversity Information Differentiated offering Value Creation Process Technology delivery process R&D Technology integration Efficiency, effectiveness learning Product delivery process Concept to launch Manufacturing process Customer delivery process Supply chain Distribution Infomediation (distribution of information) Value-based Strategies Pricing Communication (Sharma et. al., 2001)
- 12. Chapter 15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) The role of salespeople as relationship builders and promoters Salespeople by: identifying potential customers and their needs; approaching key decision makers in the buying firm; negotiating and advancing dialogue and mutual trust; coordinating the cooperation between the customers and their company; encouraging the inter-organisational learning process; contributing to constructive resolution of existing conflicts; and leading the customer relationship development team are the individuals in any organisation who act both as relationship builders and as relationship promoters.
- 13. Chapter 15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Models of Customer Relationship Management The Evans and Luskin (1994) model for effective Relationship Marketing Relationship marketing inputs Understanding customer expectations Building service partnerships Empowering employees Total quality management Relationship marketing outcomes Customer Satisfaction Customer loyalty Quality products Increased profitability Assessment state Customer feedback Integration (Evans and Luskin, 1994)
- 14. Chapter 15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Models of Customer Relationship Management The Brock and Barcklay (1999) model of selling partner relationship effectiveness Independence Relative influence Mutual trust Cooperation Selling partner relationship effectiveness
- 15. Chapter 15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Managing Customer Relationships The global salesperson must be involved in the following activities in order to initiate , develop and enhance the process that is aimed at building trust and commitment with the customer. Initiating the relationship Engage in strategic prospecting and qualifying; Gather and study pre-call information; Identify buying influences; Plan the initial sales call; Demonstrate an understanding of the customer’s needs; Identify opportunities to build a relationship; and Illustrate the value of a relationship with the customer
- 16. Chapter 15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Managing Customer Relationships The global salesperson must be involved in the following activities in order to initiate, develop and enhance the process that is aimed at building trust and commitment with the customer. Developing the relationship Select an appropriate offering; Customise the relationship; Link the solutions with the customer’s needs; Discuss customer concerns; Summarize the solution to confirm benefits; and Secure commitment.
- 17. Chapter 15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Managing Customer Relationships The global salesperson must be involved in the following activities in order to initiate, develop and enhance the process that is aimed at building trust and commitment with the customer. Enhancing the relationship Assess customer satisfaction; Take action to ensure satisfaction; Maintain open, two-way communication; and Work to add value and enhance mutual opportunities.
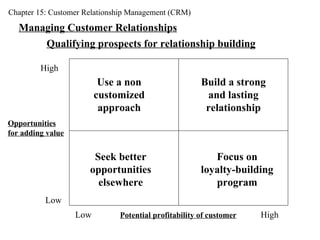
- 18. Chapter 15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Managing Customer Relationships Qualifying prospects for relationship building Opportunities for adding value Potential profitability of customer High Low Low High Use a non customized approach Seek better opportunities elsewhere Build a strong and lasting relationship Focus on loyalty-building program
- 19. Chapter 15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Relationship networks The ultimate outcome of a successful CRM strategy is the creation of a unique company asset known as a relationship network. A relationship network consists of the company and its major customers with whom the company has established long and enduring business relationships. The additional aspects of a global salesperson’s job are to: Manage customer value; Act as customer advocate; and Enhance customer loyalty and build a “health” and profitable network of relationships.
- 20. Chapter 15: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Summary CRM is a new business philosophy based on trust and value; The core function of CRM is the value creation process; Customer relationships develop over time; The role of global salespeople in the process is that of both relationship builders and relationship promoters; and The basic premise of CRM is to offer superior value to customers in an effort to turn prospects into customers, customers into loyal customers, and loyal customers into partners.