CO1g8.ppt
- 1. Science Teacher 1 Milagros L. Fernandez Periodic Table of DEVELOPMENT
- 2. OBJECTIVES: 1. Identify the contributors in the development of periodic table. 2. Compare the valuable contributions of Dobereiner, De Chancourtois, Newlands, Meyer, Mendeleev and Moseley. 3. Recognize the importance of their contributions.
- 3. Histor y
- 4. 1.Who is your favorite scientist/chemist? 2.What is his/her contribution? 3.Why did you admire him/her?
- 5. Who do you think are the scientists who contributed to the development of the periodic table of elements?
- 6. TASK: 1.Divide the class into five groups and assign a leader. Give each group their different task. Let them choose their group they want to belong and do the task according to the HISTORY OF PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS. 2.Distribute the handouts and give at least 6 minutes before the presentation.
- 7. TASK 1: MUSIC/JINGLE TASK 2: SPOKEN POETRY/ POEM TASK 3: COMIC STRIP TASK 4: ROLE PLAY PRESENTATION TASK 5: HOSTING/FAMILY FEUD HISTORY OF PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS
- 8. TASK RUBRIC: CONTENT 50% CREATIVITY 20% PRESENTATION 20% COOPERATION 5 % OVER ALL IMPACT/OTHERS 5 % TOTAL 100%
- 10. Antoine Lavoiser- 1789 He developed the modern system of naming chemical substances and has been called the “FATHER OF MODERN CHEMISTRY” for his emphasis on careful experimentation Group elements according to their properties as metals, earths, nonmetals, and gases
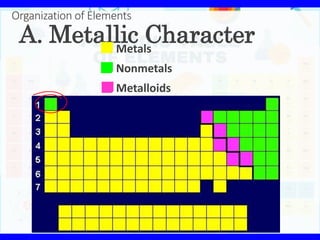
- 11. A. Metallic Character Metals Nonmetals Metalloids Organization of Elements
- 12. B. Blocks Main Group Elements Transition Metals Inner Transition Metals
- 14. Johann Wolfgang Dobereiner- 1829 discovered the existence of families of elements with similar chemical properties. Because there always seemed to be three elements in these families, he called them triads. Each of the vertical columns in Table 7.1 represents one of these triads.
- 15. TRIADS
- 16. Alexandre-Émile Béguyer de Chancourtois-1862 He was the first scientist to see the periodicity of elements when they were arranged in order of their atomic weights. ( “telluric screw”) He saw that the similar elements occurred at regular atomic weight intervals. Elements in the same vertical line have atomic weights which differ by 16.
- 17. John Newlands-1864 Just four years before Mendeleev announced his periodic table, Newlands noticed that there were similarities between elements with atomic weights that differed by seven. He called this The Law of Octaves, drawing a comparison with the octaves of music. The noble gases (Helium, Neon, Argon etc.) were not discovered until much later, which explains why there was a periodicity of 7 and not 8 in Newlands table. Newlands did not leave any gaps for undiscovered elements in his table, and sometimes had to cram two elements into one box in order to keep the pattern. Because of this, the Chemical Society refused to publish his paper, with one Professor Foster saying he might have equally well listed the elements alphabetically.
- 18. Julius Lothar Meyer -1868 His first table contained just 28 elements, organized by their valency (how many other atoms they can combine with). These elements were almost entirely main group elements, but in 1868 he incorporated the transition metals in a much more developed table. This 1868 table listed the elements in order of atomic weight, with elements with the same valency arranged in vertical lines, strikingly similar to Mendeleev’s table. Unfortunately for Meyer, his work wasn’t published until 1870, a year after Mendeleev’s periodic table had been published. Even after 1870, Meyer and Mendeleev were still unaware of each other’s work, although Meyer later admitted that Mendeleev had published his version first. Meyer did contribute to the development of the periodic table in another way though. He was the first person to recognise the periodic trends in the properties of elements, and the graph shows the pattern he saw in the atomic volume of an element plotted against its atomic weight.
- 19. Dmitri Mendeleev- 1869 ◦ Organized elements by increasing atomic mass. ◦ Elements with similar properties were grouped together. ◦ There were some discrepancies.
- 20. Dmitri Mendeleev (1869, Russian) ◦Predicted properties of undiscovered elements.
- 21. Henry Moseley-1913 It wasn’t until 1913, six years after Mendeleev’s death that the final piece of the puzzle fell into place. The periodic table was arranged by atomic mass, and this nearly always gives the same order as the atomic number. However, there were some exceptions (like iodine and tellurium, see above), which didn’t work. Mendeleev had seen that they needed to be swapped around, but it was Moseley that finally determined why. He fired the newly-developed X-ray gun at samples of the elements, and measured the wavelength of X-rays given. He used this to calculate the frequency and found that when the square root of this frequency was plotted against atomic number, the graph showed a perfect straight line. He’d found a way to actually measure atomic number. When the First World War broke out, Moseley turned down a position as a professor at Oxford and became an officer in the Royal Engineers. He was killed by a sniper in Turkey in August 15, and many people think that Britain lost a future Nobel prize winner. Organized elements by increasing atomic number. Resolved discrepancies in Mendeleev’s arrangement.
- 22. 1. How will you compare their ideas in the arrangement of element in the periodic table? 2. Who among them have common insights about the existence of elements in the periodic table? 3. Among the contributions of the scientists, which one do you think is more acceptable nowadays? QUESTIONS:
- 23. What are the importance of the periodic table of elements? ELLABORATE
- 24. ELLABORATE There were several attempts even in the early times to classify elements in a systematic and logical arrangement that led to the development of periodic table. Notable of the early groupings are Lavoisier’s classification, Dobereiner’s triad, Newland’s law of Octaves, de Chancourtois’telluric helix, Meyer’s atomic volume curve, Moseley’s work on atomic number and Mendeleev’s periodic table.
- 25. EVALUATION 1. Among the scientists who were responsible for the Development of the periodic table are as follows: I. Dmitri Mendeleev, II. Johann Dobereiner and III. John Newlands. Arrange their names in order of the history of the development of the periodic table. a. I , II, III c. III, I, II b. II, III, I d. III, II, I
- 26. 2. Who was the scientist who arranged the elements into triads? a. John Dalton b. Johann Wolfgang Dobereneir c. Dmitri Inovich Mendeleev d. John Alexander Newlands
- 27. 3. Who was the scientist who arranged the elements in horizontal rows according to increasing atomic masses with similar properties? a. John Dalton b. Johann Wolfgang Dobereneir c. Dmitri Inovich Mendeleev d. John Alexander Newlands
- 28. 4. The following are among the early scientists who attempted to classify elements in a logical arrangement except _________. a. Lavoisier b. Newland c. Bohr d. Meyer
- 29. 5. Which statement is TRUE about Mendeleev’s contribution? a. It is the major basis of the present day periodic table. b. He created Law of Octaves. c. His contribution is the atomic volume curve. d. He made major classifications of elements excluding metalloids.
- 30. ASSIGNMENT: Review for the upcoming PERIODICAL TEST.
- 31. THANK YOU!