Communication Management & Health Education.pptx
- 1. Communication Management & Health Education
- 2. INTRODUCTION • Behaviour is the range of actions and mannerisms made by humans or any organisms, systems or artificial entities in conjunction with their environment, which includes the other systems or organisms around as well as the physical environment.
- 4. Communication • Communication is a critical skill for nursing. • Process by which human meets their survival needs, build relationship and experience emotions. • In nursing communication is a dynamic process used to gather assessment data, to teach & persuade and to express caring & comfort. • It is an integral part of the helping relationship.
- 5. • The word communication was originated from the latin word ‘communis’ which means ‘common’. Communication may have a more personal connotation than the inter change of ideas or thoughts, it can be transmission of feelings or a more personal and social interaction between people.
- 6. Definition • Communication is defined as “the exchange of thoughts, ideas, feelings, information, opinions, and knowledge between two or more people”.
- 9. Characteristics of communication • It is a 2 way process. • It needs sender and receiver. • It involves exchange of ideas, feelings, information, thoughts, and knowledge. • Communication involves mutuality of understanding between sender and receiver.
- 15. • Soft skills are a cluster of productive personality traits that characterise one’s relationship in a social milieu with other people. • These skills can include social graces, cognitive or emotional empathy, time management, team work and leadership traits.
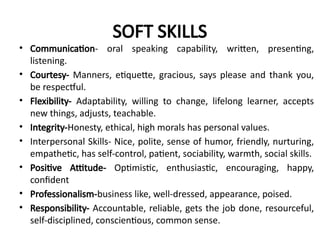
- 16. SOFT SKILLS • Communication- oral speaking capability, written, presenting, listening. • Courtesy- Manners, etiquette, gracious, says please and thank you, be respectful. • Flexibility- Adaptability, willing to change, lifelong learner, accepts new things, adjusts, teachable. • Integrity-Honesty, ethical, high morals has personal values. • Interpersonal Skills- Nice, polite, sense of humor, friendly, nurturing, empathetic, has self-control, patient, sociability, warmth, social skills. • Positive Attitude- Optimistic, enthusiastic, encouraging, happy, confident • Professionalism-business like, well-dressed, appearance, poised. • Responsibility- Accountable, reliable, gets the job done, resourceful, self-disciplined, conscientious, common sense.
- 17. • Team Work: Cooperative, gets along with others, agreeable, supportive, helpful. • Work Ethic: Hard working, willing to work, loyal, initiative, self-motivated, on-time, good attendance.
- 20. Techniques of Behaviour Change • Information • Education • Motivation • Reinforcement • Social Pressure
- 21. FACTORS AFFECTING BEHAVIOUR • Pre-disposing Factors • Enabling Factors • Reinforcing Factors
- 22. PRE-DISPOSING FACTORS • Knowledge • Beliefs • Values • Attitudes • Self-Efficacy
- 23. Enabling Factors • Skills • Healthcare resources
- 24. Reinforcing Factors • Social influence
- 25. Health & Human Behavior • Behavior: it is an action that has specific frequency, duration and purpose, whether conscious or unconscious. • Health behavior: refers to practices or activities undertaken by people to prevent or avoid the occurrence of health or health related problems.
- 29. STAGES OF BEHAVIOUR CHANGE MODEL
- 30. • Pre-contemplative/Unaware: in this stage, people are not interested in change, cant see the need to change and have no intention of doing anything differently. • Contemplative: in this stage, people start to think about the issue and the possible need to make some changes. They recognise that there is a problem and that they can and should do something to make their lives better. • Preparing: a Change is about to happen. The person concerned has realised how serious their situation is, has made a decision or a commitment to change and is currently completing any pre-change steps.
- 31. • Action/Trying: this stage applies to those people who have made real and overt changes or their new life. While the chances of relapse and temptations are very strong, there is also openness to receiving help and support. • Maintaining: by this stage, people are working to consolidate any changes in their behaviour, to maintain the ‘new’ status quo and to prevent relapse or temptation. • Termination: this stage was added to the model by researchers seeking to build on the initial work.
- 32. THE HEALTH BELIEF MODEL (HBM) • The health belief model (HBM) was developed in the early 1950s by social scientists at the U.S Public Health Service in order to understand the failure of people to adopt disease prevention strategies or screening tests for the early detection of disease. • Later uses of HBM were for patients responses to symptoms and compliance with medical treatments. • The HBM suggests that a persons belief in a personal threat of an illness or disease together with a persons belief in the effectiveness of the recommended health behavior or action will predict the likelihood the person will adopt the behavior.
- 39. IMPORTANCE OF BCC • Increase in knowledge and attitude of the people. • BCC helps to trigger and stimulate people for adopting positive behavioral approaches. • BCC promotes appropriate and essential attitude change. • It increases learning and skills. • It improves aptitudes and feeling of self- adequacy.
- 40. STEPS OF BCC • State program goals • Involve stakeholders • Identify target populations • Conduct formative BCC assessments • Segment target populations • Define behaviour change objectives • Define SBCC strategy & monitoring and evaluation plan. • Develop communication products • Protest • Implement & Monitor • Evaluate • Analyze feedback and revise
- 41. SOCIAL AND BEHAVIOUR CHANGE COMMUNICATION STARTEGIES (SBCC)
- 42. SBCC • Health communication • Health education • Information Education communication • Behavior change communication • Social and behavior change communication
- 43. TECHNIQUES TO COLLECT SOCIAL HISTORY FROM CLIENTS • Follow a systematic approach • Use research • Consider the social context • Keep focus on your audience • Use theories and models to guide decisions • Involve partners and communities • Set realistic objectives and consider cost-effectiveness • Use mutually reinforcing materials • Motivational and action oriented • Ensure quality at every step.
- 49. HEALTH EDUCATION METHODS • HEALTH EDUCATION: health education is an essential components of nursing care and is directed towards prevention, promotion, maintenance and restoration of health and adaptation of residual effects of illness.
- 50. Aims • To encourage people to adopt and sustain health promoting life style and practices. • To promote the proper use of health services available to them. • To arouse interest, provide new knowledge, improve skills and change attitudes in making rational decisions to solve their own problems. • To stimulate individual and community self-reliance and participation to achieve health development through individual and community involvement at every step from identifying problems to solve them.