Communications and Networking
- 1. COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING BASICS OF LOCAL AND WIDE AREA NETWORKS
- 2. LOCAL AREA NETWORK (LAN) • A Local Area Network (LAN) is defined as a collection of computers and peripheral devices (such as printers) connected together on a single site. Eg: within a university, schools
- 3. LOCAL AREA NETWORK (LAN) • Sharing folders and files so you can access files anywhere on the network from any computer and different people can access these files as needed • Sharing peripheral devices such as printers and scanners • Sharing an Internet connection • Using email to communicate with colleagues • Using messaging systems to chat while you are working on other things • Transferring files between computers • User profiles and security can all be managed centrally • Software can be distributed across the network rather than having to install it on each individual computer • Users can use any PC on the network but still see their own fi les • Centralized backup of all files
- 4. NETWORK TOPOLOGIES • Computers can be connected together in different layouts, or topologies Computers are connected to a single backbone cable. The computers all share this cable to transmit to each other but only one computer can transmit at any one time. Disadvantage: If there is a lot of traffic, interference problems may occur.
- 5. Advantages Disadvantages Easy and inexpensive to install (less cabling than in a star network) If the main cable fails then the whole network goes down. Easy to add new computers Cable failures are hard to isolate Performance slows down as the amount of traffic increases
- 6. NETWORK TOPOLOGIES Computers are connected to adjacent computers in a ring. Computers take it in turns to transmit, controlled by passing a token around the ring. Computers can only transmit when they have the token.
- 7. Advantages Disadvantages Not dependent on a central computer like the star network A single node or link failure disrupts the entire network. Token passing protocol is simple and therefore reliable Consistent performance even when there is a lot of traffic
- 8. NETWORK TOPOLOGIES All of the computers have their own cable connecting them to a central computer. The central computer controls the network. This is usually a switch or server.
- 9. Advantages Disadvantages If one cable fails only one station is affected rather than the whole network Can be costly to install because there is a lot of cabling. Consistent performance even when the network is heavily used If the central computer fails then the whole network goes down Easy to add new computers More secure – messages from a computer go directly to the center
- 10. CONNECTING COMPUTERS TO THE LAN • Each computer is connected to the LAN (Local Area Network) through the Network card or NIC (Network Interface Card). • Most commonly used topology in schools and offices is the start topology wired to a hub or a switch, although it might look like a bus topology as cables go around the edge of the room. In a modern network there will be a mixture of technologies.
- 11. PEER-TO-PEER OR CLIENT-SERVER • The network is centrally managed by a powerful computer called the server • Client computers communicate via a central server • There may be other computers which act as email server, print server and web server In a small office the computers will simply be cabled together. Each computer is configured so it will share specified files and folders with other peer computers on the LAN. PCs on the LAN can only access fi les on another computer if access rights have been granted. This is called a peer-to- peer network because all of the computers have equal status and the same role in the network.
- 12. PEER-TO-PEER OR CLIENT-SERVER • peer computers communicate directly with each other • files are stored on individual computers but can be shared with others 87 Peer to Peer Client-Server All computers have equal status Specialized roles: computers tend to be a client or a server Easy to set up and maintain Needs a network manager to run the network No centralized management Centralized security and management Each computer must be backed up separately Backup done from central server No dependency on a server Dependent on central server
- 13. WIDE AREA NETWORKS • A Wide Area Network, or WAN, is a collection of computers and networks connected together over a geographically remote area. Geographical remoteness is more about what separates sites than the distance involved. • WANs use hired infrastructure to connect the LANs together.
- 14. WIDE AREA NETWORKS • If one computer transmits a stream of binary to another computer, the receiving end needs to know what the rules are. This is called a protocol. A protocol is the set of rules that define how devices communicate. How the communication will start, getting the attention of the other computer (“Oi, you!”) The transmission speed The significance of the bits being transmitted (like the language) How the bits will be delivered (one at a time or in groups of 8 for example) Error-checking procedures being used (this involves some extra bits, like punctuation).
- 15. MAC ADDRESS • It is the same principal as addressing a letter; you need to put a unique address on the front so the postman knows where to deliver it. • Within a LAN each device must have a Network Interface Card (NIC) to connect it to the network. This card will have a MAC address. The MAC address is hard-coded into the NIC when it is manufactured; it cannot be configured using software. • Every networked device will have a MAC address. It is a 48-bit address that is written as twelve hex digits to make it easier for humans to work with. • The MAC address is used to transmit between devices within a LAN.
- 16. PACKET ON A LAN • In a network communication takes place such that one device will send a message to the other. • This message is broken down into smaller chunks called packets which are broadcast with MAC address of the destination device. • Similar to getting you luggage back after a flight. • Only pick the right one.
- 17. THE INTERNET • Internet is a wide area network. It is a world wide collection computers and networks that uses internet protocol to communicate. • Network itself is made up of network devices called routers, which are bigger, higher performance routers than the ones at school or home.
- 18. INTERNET PROTOCOL (IP) • Each device on the internet must have a unique IP address to communicate over the wide area network. (MAC is used only within the LAN) • Sample IP - • There are two version of IP addresses • The four numbers each represent a byte so each one can only be a number between 0 and 255. The computers will be sending binary, not decimal integers. The dots are not transmitted; they are just separators to make it easier for us to read. • Some IP addresses have special significance and are not used for devices. For example, 0.0.0.0 and 255.255.255.255 are never used to address a device.
- 19. ACCESSING WEBSITES ON THE INTERNET • Websites are stored on web servers connected to the Internet with an IP address to access the page. Domain Name System (DNS) server
- 20. THE ADVANTAGES OF USING DNS SERVERS TO TRANSLATE DOMAIN NAMES INTO IP ADDRESSES • Humans do not have to remember or type in numerical addresses • If the IP addresses change at some point the DNS servers can update their databases, and the users can continue using the same domain names • Many distributed DNS servers mean that everyone has access to all addresses from their local DNS server. HTTP – hyper text transfer protocol which is used to request and deliver web pages. This operates over IP. IP operates between routers and devices. HTTP is an end to end protocol between the PC and the web server. Post Office operates the lower level protocol between towns to physically deliver your letter. The letter is the higher level protocol that communicates end-to-end between you and your friend.
- 22. PACKET SWITCHING ON THE INTERNET • The messages being sent between devices on the Internet will be split up into smaller chunks called packets. At each router, the IP protocol decides which way to send each packet. Each router needs to know where the packet came from (source address) and where it’s going to (destination address), so it can make the appropriate routing decision. Each packet could potentially go via a different route to get to its endpoint, depending on traffic conditions at the moment IP makes its routing decision. • Each packet being sent across the Internet must therefore have a packet header on it, which contains: A sequence number A source address A destination address
- 23. CONNECTING TO THE INTERNET Cheapest but slowest type of connection (56 Kb/s). Telephone network is used to create the connection between the computer and the internet. The computer and the internet are digital but the telephone is network analog. The modem is used to convert digital signal to analog and vise-versa. Modulation – the process of transforming digital signal to analog signal is known as modulation. Demodulation is the vise versa of modulation, transformation of analog signal to digital signal. This is slow and as well as you cannot use the internet and the phone at the same time.
- 24. Since many of us have more than one computer at home and will have a wireless router. The computers will connect to the router to get the internet access and also communicate with each other as a small LAN. • The fiber-optic cable that delivers TV service • The part of the phone line that connects your house to the local exchange using broadband technology. It is digital transmission all the way and allows the use of the computers and phone line at the same time, unlike a modem. • Speeds in excess of 2Mb/s (megabits per second) and in places services up to 50Mb/s CONNECTING TO THE INTERNET
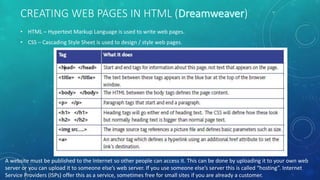
- 25. CREATING WEB PAGES IN HTML ( ) • HTML – Hypertext Markup Language is used to write web pages. • CSS – Cascading Style Sheet is used to design / style web pages. A website must be published to the Internet so other people can access it. This can be done by uploading it to your own web server or you can upload it to someone else’s web server. If you use someone else’s server this is called “hosting”. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) offer this as a service, sometimes free for small sites if you are already a customer.
- 26. SECURITY • Security is mainly about keeping the computer and the files safe from hazard. Hazard includes not only viruses, hackers but also natural disasters, hardware failures, software faults and biggest hazard is shared resources in a network with the other users.
- 27. SECURITY PRECAUTIONS • Access Rights • Encryption • Password Protection
- 28. NETWORK POLICIES • Back Up and restore procedure • Archiving • Disaster recovery
- 29. Disaster recovery • A disaster recovery plan includes the ability to replicate the computer system in a very short time. This would involve: • Data being backed up regularly • Duplicate hardware systems being available very quickly • The backup data being restored on the new hardware so the company could carry on as normal Fail Over • Spare components built into a computer system for this purpose are referred to as . • A system that has lots of redundancy built into it is described as because when faults happen the system copes with it. is the process of swapping to the spare/redundant component. Failover happens automatically and transparently (without the user noticing).
- 30. ACCEPTABLE USE POLICY • When we are using school resources we sign policies to protect privacy and authentication issues
- 31. FILE TYPES AND FI LE COMPRESSION • The connection from a computer or a LAN into the Internet is likely to be the slowest part of this route, as you probably know from experience. • One way of speeding up how quickly files can be transmitted across the Internet is to compress them to make them smaller. Smaller files take less time to transmit over a network. : a data encoding method where fi les are compressed by removing some of the detail. For example, photographs can be stored using fewer colors so fewer bits are needed per pixel Lossy compression is used to compress multimedia data such as pictures, audio fi les and video files. : a data encoding method where files are compressed but no data is lost. Essential for text and data files. For example, bank records must keep all of the data; you cannot transmit a bank statement and miss out a few zeros because they don’t matter too much!
- 32. • “ ” is the name given to a picture representation using 24 bits per pixel where the colours are a mix of Red, Green and Blue. • To compress an image you can use fewer bits per pixel. A bitmap image (.bmp) or portable network graphic (.png) fi le is a lossless version of the picture. If you save the same photograph as a JPEG fi le then it is still a high quality image with a color depth of 24 bits but some of the data is lost where it is unlikely to be noticed. • There are two versions for different quality requirements though: MPEG-1 is great for low resolution sequences on a website but if you want high resolution full screen video then you need MPEG-2. • Audio files can also be compressed. The demand for music downloads drove the need for a better compression method and MP3 became the dominant compression type. • Word documents - .docx / doc • PDF (Portable Document Format) is an open file format. • When a PDF document is created it captures all the elements of a printed page as an electronic image that you can view, navigate, print or forward to someone else. When the PDF file is created you can also set options that allow the reader to use copy and paste or block this feature.