Data analysis using python in Jupyter notebook.pptx
- 1. DATA ANALYSIS USING PYTHON Nagendra Asstt. Professor B. N. College (University of Delhi)
- 2. LEARNING OUTCOME • What is Data Science ? • Data Analysis Methodology • Python Basics Variable and Data Types Reading Data Selecting Filtering the Data Data manipulation, sorting, grouping, • Python Libraries for Data Science NumPy (Numerical Computation) Pandas ( Data Analysis) Matplotlib ( Data Visualization) SciKit-Learn ( Machine learning Algorithms)
- 3. WHAT IS DATA SCIENCE The process of finding insights/trends/ intelligence from the data A relatively new field Deeply rooted to Statistics and Decision Support System A Multidisciplinary field ( Domain Knowledge, Tools & technology, Mathematics & Statistics, Problem Solving Skills)
- 4. DATA ANALYSIS METHODOLOGY • Statement of the problem/Objective of the Study • Data Preparation • Feature selection • Exploratory Data Analysis
- 5. PYTHON BASICS What is Python • A high-level general-purpose programming language. • A very popular Data Science tool for data analysis, data visualization and Machine Learning tasks • It is a open source and free tool
- 6. PYTHON BASICS How to Download Python Download the python from the following link https://www.python.org/downloads You can also download Python, and Jupytor Notebook from the following link https://www.anaconda.com/why-anaconda/
- 7. PYTHON BASICS Common Tools in Python Environment The Python interactive console: Also called the Python interpreter or Python shell and provides programmers with a quick way to execute commands and try out or test code without creating a file. ( https://www.python.org/shell/) Spyder: It is a powerful scientific environment written in Python, for Python, and designed by and for scientists, engineers and data analysts. It offers a unique combination of the advanced editing, analysis, debugging, and profiling. (https://pypi.org/project/spyder/) Jupiter Notebook: It is an open source web application that you can use to create and share works (code, equations, visualizations, Machine Learning models and texts. (https://jupyter.org)
- 8. PYTHON BASICS Most Popular Python Libraries for Data Science
- 9. PYTHON BASICS Variable and Types • Variable is a memory location and placeholder to hold the data • Most common Python Data Types: float, int, str, List, Tuple, Dictionary
- 10. PYTHON BASICS Basic Operations in Python Arithmetic Operations Addition Subtraction Multiplication Division, Modulo Relational Operations Equal Greater/Greater than Less/less Than Logical Operations TRUE/FALSE AND IN OR
- 11. PYTHON BASICS List A common Data type in python Collection comma-separated values (items) between square brackets Contain same or different types Mutable behavior Values can add, remove, update/replace the value, slice and dice the members
- 12. PYTHON BASICS Tuple A common Type in Python A tuple is very similar to List A collection of items inside the parenthesis() Tuple is Immutable ( The value cannot be changed) Can slice and dice add elements and Delete the entire tuple
- 13. PYTHON BASICS Dictionary Another common and popular type in Python A collection of unordered data values A dictionary holds key value pairs of data The items are separated by commas, and the whole thing is enclosed in curly braces Keys are immutable but the values are mutable - can add modify and Delete values
- 14. PYTHON BASICS Function A function is a collection of reusable codes We write the function one time and call it to solve the particular task Two Types of Function: System Function: max(), min(), len() User Defined Function – created by the programmer/developer Main Components of Function: Input, computation, output Global and local function
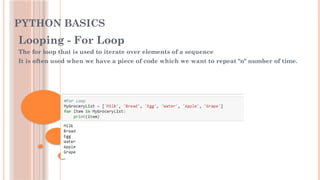
- 15. PYTHON BASICS Looping - For Loop The for loop that is used to iterate over elements of a sequence It is often used when we have a piece of code which we want to repeat "n" number of time.
- 16. PYTHON BASICS Looping - While Loop The while loop tells the computer to do something as long as the condition is met It's construct consists of a block of code and a condition.
- 17. PYTHON LIBRARY NumPy • It uses multidimensional arrays and matrices, as well as functions to perform the computation • Allow to perform advanced mathematical and statistical operations on the above objects • It provides vectorization of mathematical operations on arrays and matrices • many other python libraries are built on the top of NumPy library • Contains Linear algebra operations, Fourier Transformation and Random number generation https://numpy.org
- 18. PYTHON LIBRARY Pandas • It is a Data Analysis tool in Python • It adds data structures and tools ( Series and Data Frame) designed to work with table-like data (similar to table in SQL Server environment) • It provides tools for data manipulation: selecting, reshaping, merging, sorting, slicing, aggregation etc. • It integrates time series functionality • It also handles missing data https://pandas.pydata.org
- 19. PYTHON LIBRARY Matplotlib • It is a two- dimensional Data Plotting and Data Visualization library in Python • We can create line plots, scatter plots, bar charts, histograms, pie charts etc. https://matplotlib.org
- 20. PYTHON LIBRARY Seaborn • Seaborn is a Python data visualization library based on matplotlib. • It provides a high-level interface for drawing attractive and informative statistical graphics http://seaborn.pydata.org
- 21. PYTHON LIBRARY IPython and Jupyter • IPython is use for interactive computing and software development. • IPython provides easy access to operating system’s shell and file system. • IPython web notebook become Jupyter notebook with support for over 40 programming languages. Ipython system can now used as kernel for using Python with Jupyter. • Jupyter provides a productive environment for interactive and exploratory computing.
- 22. PYTHON LIBRARY Scikit-learn • It is general purpose machine learning toolkit for Python programmers. • It includes submodules such as Classification(SVM, nearest neighbors, random forest, logistic regression, etc.) , Regression, Clustering(k-means, etc.), Dimensional reduction(PCA, feature selection, etc.), Model selection (grid search, metrics, etc.), Preprocessing(feature extraction, normalization). • It is built on the top of NumPy, SciPy and matplotlib. https://scikit-learn.org/stable
- 23. PYTHON LIBRARY stasmodel • It is a statistical analysis and contains statistics and econometrics. • It has submodule such as Regression model, Analysis of variance(ANOVA), Time series Analysis, Nonparametric methods(Kernel density estimation, kernel regression), Visualization of statistical model results.
- 24. QUESTION & ANSWER What Feedback do you have for me? Questions: nagendra.bnc@bn.du.ac.in (Nagendra)