Data structures and algorithms lab9
- 1. DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LAB 9 Bianca Tesila FILS, April 2014
- 2. OBJECTIVES Binary Trees Binary Search Trees
- 3. BINARY TREES & BINARY SEARCH TREES What is a tree? How can we check if a graph is a tree? What binary tree traversals do you know? How do they work? What’s the difference between a binary tree and a binary search tree? What traversal should we use in order to get the values of the nodes in ascending order? What happens when we delete a node from a binary search tree?
- 4. BINARY TREES APPLICATIONS !! Exercise: Write a function that displays the values of the nodes located on a given level (sent as a parameter). Hint: What happens when the given level greater than the tree’s height? Make a recursive function in which you decrement level by 1 as you advance to the next level. When level equals 0, you’ve reached the given level. Display (T,level): if(level==0) then print(T.data) else Display (T.left, level-1); Display (T.right, level-1);
- 5. BINARY TREES APPLICATIONS !! Exercise: Given a binary tree, compute its "maximumHeight" -- the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node. Hint: The maximum height of a tree is the maximum of the heights of its children
- 6. BINARY TREES APPLICATIONS !! Exercise: Write a function that returns, for the root node, the difference between the height of the left sub-tree and the height of the right sub-tree. Hint: you should take into consideration the maximum heights of the sub-trees. use the previous exercise int difHeight() { if(this == NULL) { return - 1;} return abs(left_son->maxHeight()-right_son- >maxHeight()); }
- 7. BINARY SEARCH TREES APPLICATIONS !! Exercise: Write a function which finds the lowest value in a binary search tree. Hint: traverse the node from root to left, recursively, until left is NULL the node whose left is NULL is the node with minimum value
- 8. BINARY SEARCH TREES APPLICATIONS !! Exercise: Write a function that displays the nodes which have values greater than x and smaller than y, where x and y are given as parameters. Hint: Take the value of the root into account in order to decide on which way to go to find the corresponding nodes.
- 9. BINARY SEARCH TREES APPLICATIONS
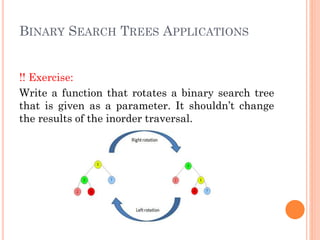
- 10. BINARY SEARCH TREES APPLICATIONS !! Exercise: Write a function that rotates a binary search tree that is given as a parameter. It shouldn’t change the results of the inorder traversal.
- 11. BINARY SEARCH TREES APPLICATIONS Hint: if the height of the right subtree is smaller than the height of the left subtree, it should be right- rotated. if the height of the left subtree is smaller than the height of the right subtree, it should be left- rotated. if the tree is balanced, nothing happens
- 12. HOMEWORK Finish all the lab assignments.