Definition of linear programming problem model decision variable, objective function, constraints and method of LPP
- 1. DEFINITION OF LINEAR PROGRAMMING PROBLEM MODEL DECISION VARIABLE, OBJECTIVE FUNCTION, CONSTRAINTS AND METHOD OF LPP Presented by Sunny Mervyne Baa
- 2. LINEAR AND PROGRAMMING’. • The world linear stand for indicating the relationships between different variables of degree one whereas another word programming means planning and refers to the process of selecting best course of action from various alternatives. • Thus, linear programming is a mathematical technique for allocating limited resources is optimum manner. • In the words of William M. Fox, “Linear programming is a planning technique that permits some objective function to be minimized or maximized within the framework of given situational restrictions.” • Linear Programming (LP) is a mathematical modelling technique useful for allocation of limited resources such as material, machines etc to several competing activities such as projects, services etc. • By George B. Dantzig
- 3. DECISION VARIABLES • Decision variables describe the quantities that the decision makers would like to determine. T • hey are the unknowns of a mathematical programming model. • Typically we will determine their optimum values with an optimization method. • In a general model, decision variables are given algebraic designations such as . • The number of decision variables is n, and is the name of the jth variable. In a specific situation, it is often convenient to use other names such as or or .
- 4. OBJECTIVE FUNCTION: • There must be clearly defined objective which can be stated in quantitative way. • In business problems the objective is generally profit maximization or cost minimization. • The objective function evaluates some quantitative criterion of immediate importance such as cost, profit, utility, or yield. The general linear objective function can be written as coefficient of the jth decision variable. The criterion selected can be either maximized or minimized.
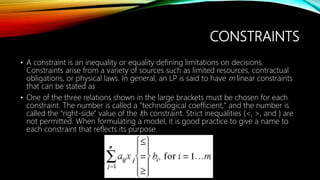
- 5. CONSTRAINTS • A constraint is an inequality or equality defining limitations on decisions. Constraints arise from a variety of sources such as limited resources, contractual obligations, or physical laws. In general, an LP is said to have m linear constraints that can be stated as • One of the three relations shown in the large brackets must be chosen for each constraint. The number is called a "technological coefficient," and the number is called the "right-side" value of the ith constraint. Strict inequalities (<, >, and ) are not permitted. When formulating a model, it is good practice to give a name to each constraint that reflects its purpose.
- 6. GRAPHICAL METHOD: • The business problems involving two variables can be easily solved by drawing the graph for various constraints. Following are the steps in graphical solution of linear programming problem (LPP): • 1. Formulate LPP by writing the objective function (generally maximize profit) and the constraints. • 2. Constraints are changed into equalities. • 3. Plot the constraints on the graph. • 4. Identify the feasible region and ascertain their coordinates. • 5. Test which point is most profitable