dental management of Git disease patient
- 2. CONTENTS: INTRODUCTION INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE - ULCERATIVE COLITIS - CROHN’S DISEASE GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE PEPTIC ULCERATION EATING DISORDERS GASTROINTESTINAL SYNDROMES CONCLUSION
- 3. INTRODUCTION GASTROINTESTINAL DISEASES refer to disease involving the gastrointestinal tract , namely the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and rectum There is increased need for the knowledge regarding the oral manifestations of these disorders so as to recognise, diagnose, and treat oral conditions associated with GI disorders
- 4. ETIOLOGY
- 5. ULCERATIVE COLITIS DENTAL MANAGEMENTRECURRENT APTHOUS ULCERS: Topical analgesic(2% lidocaine gel) Topical and systemic corticosteroids Tetracycline mouthwash Vitamin b12 ,folic acid PYOSTOMATITIS VEGETANS: Topical corticosteroids like triamcinolone(0.1%), clobetasol(0.05%) SULFA DRUGS :medical management with sulfasalazine helps to clear the lesion Patient may benefit from zinc supplementObtain readings of blood pressure, blood glucose level before treatment Supplement glucocorticoids before and after surgery obtain the levels of WBC’s, haemoglobin, RBC count, platelet count before procedure Liver function test should be completed
- 6. CROHN’S DISEASE DENTAL MANAGEMENT • Palliative rinses of sodium bicarbonate • topical ointment •topical steroids Preventive and routine dental care to monitor oral health and to prevent destruction of hard and soft tissue Evaluation of patients blood glucose and blood sugar levels Topical steroid therapy (halobestol, triamcinolone , clobestol) should be short term and monitored • obtain the levels of WBC’s, haemoglobin, RBC count, platelet count before procedure • Liver function test should be completed
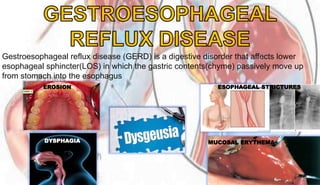
- 7. Gestroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a digestive disorder that affects lower esophageal sphincter(LOS) in which the gastric contents(chyme) passively move up from stomach into the esophagus EROSION ESOPHAGEAL STRICTURES MUCOSAL ERYTHEMADYSPHAGIA
- 8. NaHCO3 mouthrinse to minimize dysgeusia due to acid reflux Topical fluoride application to ensure optimal mineralization Patient advised to have adequate fluid intake DENTAL MANAGEMENT Adequate restorations on affected teeth to prevent further damage Patients on CIMETIDINE/H2 RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST may experience reaction to lidocaine if given intravascularly Oral PREVENTIVE MEASURES at earliest to minimize need of extensive restorations
- 9. PEPTIC ULCERS are common benign ulceration of epithelial lining of stomach(gastric ulcer) or duodenum(duodenal ulcer)
- 11. ANOREXIA NERVOSA BULIMIA NERVOSA • INTENSIONAL STARVING even if the patient is already underweight • patients use laxatives and diuretics to lose body weight •Patient CONSUMES LARGE AMOUNT OF FOOD due to LACK OF CONTROL OVER APETITE • self induced vomiting , laxatives and diuretics are used to lose body weight
- 12. DENTAL MANGEMENT Support the patient psychologically by demonstrating a caring and compassionate attitude Avoid elective dental procedures until patient is stable Complex restorative treatment should be avoided until the purging has been corrected Emphasis on oral hygiene maintenance Crowns may have to be placed if thermal symptoms are present in actively purging patient
- 14. DENTAL MANAGEMENT GARDNER’S SYNDROME(familial multiple polyposis) Dental radiography provides earliest indication Prophylactic colostomy is recommended Excision of jaw osteomas and epidermoid cysts for cosmetic reasons may be indicated Removal of one or more supernummary teeth for orthodontic/occlusal consideration Patients with 3 to 6 osteomatous lesions should be questioned about possibility of Gardner's syndrome PLUMMMER VINSONSYNDROME Esophageal dilation(if symptoms of web) by upper endoscopy Iron replacement- ferrous sulphate Follow up – developing carcinoma Patient is advised to eat slowly and in small pieces Address the cause of iron deficiency
- 15. CONCLUSION It is essential to recognise oral manifestations of gastrointestinal diseases as they are useful in development of differential diagnosis for patients with GIT complaints. The severity or prognosis of the disease can be monitored by the presence or extent of oral manifestations. The success of the management of gastrointestinal diseases may be reflected in response to oral tissues Hence, the oral physicians play a critical role in recognising, diagnosing and treating oral conditions related with gastrointestinal diseases and also to provide dental care to afflicted individuals
- 16. THANK YOU SUBMITTED BY:VIDUSHI SUBMITTEDTO :Dept. of oral radiology and oral medicine