DERIVATIZATION IN GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY (GC), HIGHPERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY[HPLC] by P.Ravisankar, Vignan Pharmacy College, Vadlamudi,Guntur.
- 1. Derivatization in GC and HPLC Prof. Ravisankar Vignan Pharmacy College Vadlamudi Guntur Andhra Pradesh INDIA banuman35@gmail.com 0091 9059994000
- 2. Derivatization Derivatization is the process of chemically modifying a compound to produce a new compound which has properties that are suitable for analysis using a GC or HPLC. The chemical structure of the compound remains the same and just modifies the specific functional groups of reacting compound to derivative of deviating chemical and physical properties in order to make them detectable and analysable. Derivatization is needed in GC, HPLC, UV-Vis spectroscopy etc.,
- 3. Why derivatize in GC? • To permit analysis of compounds which are not directly amenable to analysis due to for example, inadequate stability and volatility. • To improve chromatographic behaviour or detectability. Many compounds do not produce a useable chromatography or the sample of interest goes undetected. As a result it may be necessary to derivatize the compound before GC analysis is done. The main reason for derivatizing is to impart volatility to otherwise non-volatile compounds. Derivatization is a useful to allowing the use of GC & GC/MS to be done on sample that would other wise be not possible in various areas of chemistry such as medical, forensic & environmental.
- 4. Ideal characters and disadvantages of derivatization • A derivatization reaction should be rapid,quantitative, and produce minimal by product. Excess reagent should not interfere with the analysis and should be easily removed. • Derivatization often is a last resort when developing a method. Introduction of a reaction pre or post column increases complexity, chances of error, and total analysis time. • Care should be taken that the reaction is quantitative and no additional impurities are introduced into analysis.
- 5. What Derivatization accomplish? • Increases volatility(i.e. sugars): - Eliminates the presence of polar OH, NH & SH groups - Derivatization targets O, S, N and P function groups (with hydrogens available) • Enhances sensitivity for ECD. The introduction of ECD detectable groups, such as halogenated acyl groups, allows detection of previously undetectable compounds. • Increases detectability, i.e. steriods • Increases stability(thermostability) • To reduce adsorption of polar samples on active surfaces of column walls and solid support.
- 6. Conditions for choosing a derivatizing agent • The derivatizing agent must be stable. • The derivatizing agent and its products formed during derivatization should not be detectable or must be seperable from analyte. • The analyte should be reactive with derivatizing agent under convenient conditions. • If possible, it should be non-toxic. • The rocedure should be adaptable to automation.
- 7. Types of Derivatization • Silylation • Alkylation • Acylation • Chiral derivatization
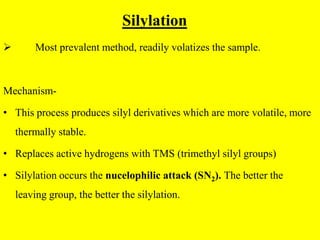
- 8. Silylation Most prevalent method, readily volatizes the sample. Mechanism- • This process produces silyl derivatives which are more volatile, more thermally stable. • Replaces active hydrogens with TMS (trimethyl silyl groups) • Silylation occurs the nucelophilic attack (SN2). The better the leaving group, the better the silylation.
- 9. Solvents and precautions- • Silylation reagents will react with H2O & alcohols first care must be taken to ensurs that both sample & solvent are dry. • Solvent should be as pure as possible. This will eliminate excessive peaks. Try using as little solvent as possible as this will prevent a large solvent peak. • Pyridine is the most commonly used solvent. Atthough pyridine may produce peak tailing it is an acid scavenger & will drive the reaction forward. • In many cases, the need for a solvent is eliminated with silylating reagents (if a sample readily dissolves in the reagent, it usually is a sign that the derivatization is complete.
- 10. Ease of reactivity of functional group toward silylation follows the order- Alcohol > Phenol > Carboxyl > Amine > Amide > Hydroxyl The order of alcohols is 1 > 2 > 3 • Care needs to be taken not to inject silylating reagent onto column which have active hydrogen’s in the st.phase, because they will be derivatized. Example of column not compatible with silylating reagents are carbowax & free Fatty Acid phase.
- 11. Silylation - advantages and disadvantages Advantages: • Ability to silylate a wide variety of compounds. • Large number of silylating reagents available. • Easily prepared. Disadvantages: • Silylation reagents are moisture sensitive. • Must use aprotic (no proton available) organic solvents.
- 12. Silylating agents and their mechanisms 1. N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide (BSA)
- 18. 7. Dimethyldichlorosilane (DMDCS) the order of reactivities of the silylation reagents are- TSIM>BSTFA>BSA>MSTFA>TMSDMA>TMSDEA>TMCS>HMDS • MSTFA- N-methylsilyltriflouroacetamide; • TMSDMA- trimethylsilyldimethylamine; • TMSDEA- trimethylsilyldiethylamine.
- 19. Alkylation Alkylation reduces molecular polarity by replacing active hydrogens with an alkyl group. These reagents are used to modify compounds with acidic hydrogens, such as carboxylic acids and phenols. These reagents make esters, ethers, alkyl amines and alkyl amides. The principal reaction employed for preparation of these derivatives is nucleophilic displacement.
- 20. Alkylation Advantages • Wide range of alkylation reagents available • Reaction conditions can vary from strongly acidic to • strongly basic • Some reactions can be done in aqueous solutions • Alkylation derivatives are generally stable Disadvantages • Limited to amines and acidic hydroxyls • Reaction conditions are frequently severe • Reagents are often toxic
- 21. Alkylating agents and their mechanisms 1. trimethylanilinium hydroxide (TMAH)
- 22. 2. Boron trichloride in chloroethanol or methanol
- 23. 3. Boron triflouride in butanol or methanol
- 24. 4. Methanol in acid (HCl or H2SO4)
- 25. 5. Pentafluorobenzyl Bromide and Hexaoxacyclooctadecane
- 26. Acylation Acylation reduces the polarity of amino, hydroxyl, and thiol groups and adds halogenated functionalities for ECD. In comparison to silylating reagents, the acylating reagents target highly polar, multifunctional compounds, such as carbohydrates and amino acids. • Acylation converts these compounds with active hydrogens into esters, thioesters, and amides. They are formed with acyl anhydride, acyl halide, and activated acyl amide reagents. • The anhydrides and acyl halide reagents form acid by- products, which must be removed before GC analysis. • Acylations are normally carried out in pyridine, tetrahydrofuran or
- 27. Acylation • Fluorinated acyl groups, going from trifluoracetyl to heptafluorobutyryl , can be used to increase retention times. • Acyl derivatives tend to direct the fragmentation patterns of compounds in MS applications, and so provide helpful information on the structure of these materials.
- 28. Acylation – advantages and disadvantages Advantages- • Addition of halogenated carbons increased detectability by ECD • Derivatives are hydrolytically stable • Increased sensitivity by adding molecular weight • Acylation can be used as a first step to activate carboxylic acids prior to esterfication (alkylation) Disadvantages- • Acylation derivatives can be difficult to prepare • Reaction products (acid by-products) often need to be removed before analysis • Acylation reagents are moisture sensitive • Reagents are hazardous and odorous
- 29. Acylating reagents and their mechanisms 1. Acetic anhydride
- 30. 2. Trifluoroacetic Acid Anhydride Pentafluoropropionic Acid Anhydride Heptafluorobutyric Acid Anhydride
- 31. mechanism
- 32. 3. Fluoro acyl imidazoles: - Tri Fluoro Acetyl Imidazoles (TFAI) - Penta Fluoro Propanoyl Imidazoles (PFPI) - Hepta Fluoro Butyryl Imidazoles (HFBI) 4. N-Methyl Bis (Trifluoro Acetamide) - MBTFA 5. Penta Fluoro Benzoyl Chloride - PFBCI 6. Penta Fluoro Propanol - PFPOH
- 33. Chiral derivatization These reagents target one specific functional group and produce individual diastereomers of each of the enantiomers. There are two ways of separating enantiomers by chromatography: 1. separation on an optically active stationary phase. 2. preparation of diastereomeric derivatives that can be separated on a non chiral stationary phase. Reagents 1. TPC (N-trifluoroacetyl-L-prolyl chloride) Used for optically active amines, most notably amphetamines 2. MCF ((-) menthylchloroformate) Used for optically active alcohols If an optically pure reagent is used to prepare diastereomeric derivatives, then only two derivatives are formed. The enantiomeric ratio is reflected in the relative peak sizes.
- 34. Functional groups and their derivatization methods
- 37. Why derivatize in HPLC? • To improve detectability. • To prepare soluble derivatives of insoluble compounds for HPLC analysis. • To change the molecular structure or polarity of the analyte for better chromatography. • To change the matrix for better seperation. • To stabilise a sensitive analyte. • To enhance separation. • To reduce tailing, poor peak resolution and/or asymmetrical peaks.
- 38. Types of HPLC derivatization • for UV-Vis spectrophotometric detection. • For flourimetric detection. • For chiral analysis. According to when and where the derivatization is done • Pre-column derivatization • Post-column derivatization
- 39. Compounds with Carboxyl group For fluorimetric detection- • p-(9-anthroyloxy)phenacylbromide • 9-aminophenanthrene • 9-(chloromethyl)anthracene(9-CIMA) • 9-anthryldiazomethane(ADAM) • 1-bromoacetyl pyrene • 4-bromomethyl-7-acetoxycoumarin(Br- Mac) • 4-bromomethyl-6,7- dimethoxycoumarin(Br-Mdmc) • 4-diazomethyl-7-methoxycoumarin • 1-naphthylamine(D-Mmc) For ultraviolet detection- • p-nitrobenzyl-N,N’-diisopropylisourea • 3,5-dinitrobenzyl-N,N’- diisopropylisourea • p-bromophenacylbromide
- 40. Compounds with amino group For fluorimetric detection • 1-Fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (FDNB or sanger’s reagent) • 4-dimethylamino-1- naphthylisothiocyanate • 9-isothiocynatoacridine • o-phthalaldehyde(OPA) (10) • 4-phenylspiro[furan-2(3H)-1’- phthalan]-3,3’-dione(fluorescanine) (10 & 20) • 5-di-n-butylaminonaphthalene-1- sulfonyl chloride(Bns-Cl) (10 & 20) • 5-dimethylaminonaphthalene-1- sulfonyl chloride(Dns-Cl) (10 & 20) For UV-Vis detection • 3,5-dinitrobenzylchloride(DNBC) • N-succinimidyl-p- nitrophenylacetate(SNPA) • N-succinimidyl-3,5- dinitrophenylacetate(SDNPA) • Dabsyl-Cl (4-N,N- dimethylaminoazobenzene-4’-sulfonyl Chloride) • 1-Naphthylisocyanatr(1-NIC)
- 42. Compounds with Carbonyl group For fluorimetric detection- • Dansyl hydrazine • 9-(hydroxymethyl)anthracene(HMA) • 4’-hydrazino-2-stilbazole(4H2S) • 4-hydrazino-7-nitrobenzo-2-oxa-1,3- diazole(NBD-H) For UV-Vis detection • p- nitrobenzyloxyamine hydrochloride(PNBA) • 3,5- dinitrobenzyloxyamine hydrochloride(DNBA) Alcohols For fluorimetric detection- • 1- and 9-anthroylnitrile • 4-dimethylamino-1- naphthoylnitrile(dMA-NN) For UV-Vis detection- • 3,5-dinitrobenzyl choride(DNBC) • 1-Naphthylisocyanatr(1-NIC) • dabsyl chloride(4-N,N- dimethylaminoazobenzene-4’- sulfonyl Chloride)
- 43. Phenols For fluorimetric detection- • 7-chloro-4-nitrobenzo-2-oxa-1,3- diazole(NBD-Cl) • 7-fluoro-4-nitrobenzo-2-oxa-1,3- diazole(NBD-F) • Dansyl-Cl For UV-Vis detection- • 3,5-dinitrobenzyl choride(DNBC) • Dabsyl-Cl(4-N,N- dimethylaminoazobenzene-4’-sulfonyl Chloride) • 1-Naphthylisocyanatr(1-NIC) Catecholamines For fluorimetric detection- • Trihydroxyindole(THI) • Ethylenediamine(ED) • Diphenylethylenediamine(DPE)
- 44. For Chiral Separation • 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrophenyl-5-l-alanine amide(FDAA or Marfey’s reagent) • 2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl Isothiocyanate (TAGIT) • O,O - dibenzoyl tartaric acid anhydride • For carbohydrates, 2-aminopropionitrile-fumarate-borate is used for flourscent derivatization • For guanidine, Benzoin is used for flourscent derivatization. • For α-ketocarboxyl groups, O-phenylenediamine is used for flourscent derivatization.
- 45. Chiral derivatives Functional groups derivative Amino groups Amides,carbamates,ureas,thioureas,sulfamides Hydroxyl groups Esters,carbonates,carbamates Carboxy groups Esters,amides Epoxides Isothiocyanates,olefins thiols Thioesters
- 47. HPLC flourscent derivatization-table(1) cont.
- 49. HPLC UV-Vis derivatization-table(2) cont.
- 50. Pre- and Post-column derivatization Pre-column derivatization- • Performed before the analytical separation is attained. • Sample is derivatiszed manually or automatically and injected into the hplc column. • Separation of components occurs after derivatization. Advantages- • Fewer equipment and reaction chemical restrictions. • Can be performed manually or automatically. • No time constraints on the kinetics of the derivatization of derivatization reaction. Disadvantages- • Introduction of contaminants. • Loss of analyte through adsorption. • Sample degradation and incomplete reaction. • Poorer precision due to increased complexity.
- 51. Post-column derivatization- • Performed after analytical separation of compounds but prior to detection. • Addition pump is used for addition of derivatizing agent to the eluted sample from column. Advantages- • Minimal artifact formation. • Complete reaction is not essential as long as it is reproducible and the chromatography of analyte remains unaffected. Disadvantages- • Band brodening • Added complexity for method development and routine use.
- 52. Conclusion Chemical derivatization of drugs is critical for GC because these samples, which often contain multiple polar substituents, are simply not volatile or thermally stable. Chemical derivatization with HPLC to permit fluorescence or UV-Visible detection is certainly one of the more desirable methods for routine use to solve selectivity and detectability problems for drug samples during analysis.
- 53. references 1. GC Derivatization – from Regis 1998-99 Chromatography Catalog and Knapp.D.R.-HandBook of Analytical Derivatization Reactions. 2. HPLC Method Development by Snyder et al. 3. Basic Gas Chromatography- Harold McNair et al. 4. Modern Methods of Pharmacetical Analysis- Roger.E.Schirmer(vol- 2,2nd edition) 5. Chemical Reagents & Derivatization Procedures in Drug Analysis- Neil.D.Danielson et al. 6. GC Derivatization Reagents.pdf @ www.registech.com/gc 7. Derivatives for HPLC Analysis – Mrs.laurence Coppex.


































![DERIVATIZATION IN GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY (GC), HIGHPERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY[HPLC] by P.Ravisankar, Vignan Pharmacy College, Vadlamudi,Guntur.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/derivatizationingchplc-130616062106-phpapp02/85/DERIVATIZATION-IN-GAS-CHROMATOGRAPHY-GC-HIGHPERFORMANCE-LIQUID-CHROMATOGRAPHY-HPLC-by-P-Ravisankar-Vignan-Pharmacy-College-Vadlamudi-Guntur-35-320.jpg)
![DERIVATIZATION IN GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY (GC), HIGHPERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY[HPLC] by P.Ravisankar, Vignan Pharmacy College, Vadlamudi,Guntur.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/derivatizationingchplc-130616062106-phpapp02/85/DERIVATIZATION-IN-GAS-CHROMATOGRAPHY-GC-HIGHPERFORMANCE-LIQUID-CHROMATOGRAPHY-HPLC-by-P-Ravisankar-Vignan-Pharmacy-College-Vadlamudi-Guntur-36-320.jpg)



![Compounds with amino group
For fluorimetric detection
• 1-Fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (FDNB
or sanger’s reagent)
• 4-dimethylamino-1-
naphthylisothiocyanate
• 9-isothiocynatoacridine
• o-phthalaldehyde(OPA) (10)
• 4-phenylspiro[furan-2(3H)-1’-
phthalan]-3,3’-dione(fluorescanine)
(10 & 20)
• 5-di-n-butylaminonaphthalene-1-
sulfonyl chloride(Bns-Cl) (10 & 20)
• 5-dimethylaminonaphthalene-1-
sulfonyl chloride(Dns-Cl) (10 & 20)
For UV-Vis detection
• 3,5-dinitrobenzylchloride(DNBC)
• N-succinimidyl-p-
nitrophenylacetate(SNPA)
• N-succinimidyl-3,5-
dinitrophenylacetate(SDNPA)
• Dabsyl-Cl (4-N,N-
dimethylaminoazobenzene-4’-sulfonyl
Chloride)
• 1-Naphthylisocyanatr(1-NIC)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/derivatizationingchplc-130616062106-phpapp02/85/DERIVATIZATION-IN-GAS-CHROMATOGRAPHY-GC-HIGHPERFORMANCE-LIQUID-CHROMATOGRAPHY-HPLC-by-P-Ravisankar-Vignan-Pharmacy-College-Vadlamudi-Guntur-40-320.jpg)
![DERIVATIZATION IN GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY (GC), HIGHPERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY[HPLC] by P.Ravisankar, Vignan Pharmacy College, Vadlamudi,Guntur.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/derivatizationingchplc-130616062106-phpapp02/85/DERIVATIZATION-IN-GAS-CHROMATOGRAPHY-GC-HIGHPERFORMANCE-LIQUID-CHROMATOGRAPHY-HPLC-by-P-Ravisankar-Vignan-Pharmacy-College-Vadlamudi-Guntur-41-320.jpg)











