Design for results - Considerations for experimental prototyping and play testing using iterative game design
- 1. 1
- 2. This paper is concerned with development of experimental research prototypes, sometimes also called demonstrators. A commonly used development method is iterative design which, as described by Salen and Zimmerman shortcite{Salen2001}, is a play-based design process. A prototype is textit{``played, evaluated, adjusted and played again, allowing the designer or design team to base decisions on the successive textit{iterations} or versions of the game. Iterative design is a cyclic process that alternates between prototyping, play-testing, evaluation, and refinement.''} 2
- 3. 3
- 4. 4
- 5. 5
- 6. 6
- 7. 7
- 8. it must be stressed that the iterations can and should happen even inside the early prototype development, and in some cases, between the test sessionsfootnote{For instance, test the prototype with the first participant, fix existing problems and develop further promising new ideas, and test the evolved version of the same prototype with participant two, and so on.}: The traditional waterfall model cite{waterfallmodel} proposes a process where the design, implementation, and evaluation follows each other in a linear manner. The iterative design process for games see, e.g. cite{fullerton04,Salen2001}, emphasizes on iterations where the game is designed, tested, and evaluated continuously during the process and developed further. There has been some criticism that even this kind of process would not be iterative enough cite{Fallman} and that design, implementation, and evaluation should be done tightly together. 8
- 9. 9
- 10. Participant role: informant/co-designer <--- Jorgensen, “co-researcher” 10
- 11. OUR VIEW; IF U CANT DO IDEAL TEST EARLY, U SHOULD STILL DO QUICK AND DIRTY TESTING AND DO IT A LOT. BUT DO NOT EXPECT IT TO PROVIDE PERFECT DATA 11
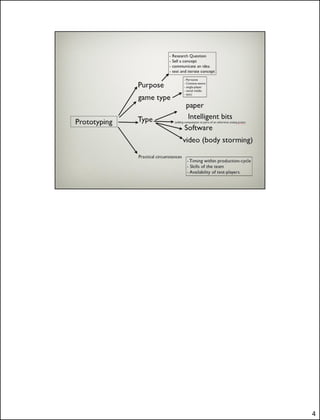
- 12. Filled in by research question. easy to fall into a frame of mind where one aims to produce a good game, loosing focus of obtaining research material. The very reason for the development of research prototypes is to find methods, features or approaches that can be used in other games, games which are specifically made to be fun, challenging and perhaps carry a message. The researcher needs to approach the design of the prototype both as a researcher and as a game designer. Practicality. Resources, time etc – and ideology regarding validation. Own and projected. 12
- 13. 13
- 14. Jorgensen also talked about video commentaries. So maybe another arrow still under: “feedback” -> after the game. “”video commentary model, Jorgensen”. 14
- 15. 15