Digital Marketing - Unit II for students.
- 1. Unit - II S. S. SARAVANA KUMAR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR Department of Computer Applications Sri Ramakrishna College of Arts and Science Coimbatore - 641 006 Tamil Nadu, India
- 10. Niche Market • It is a specialized segment within a broader market that targets consumers with unique books. • Group of people looking for specific products. • Very specialized, focused, targeted market. • It represents a small percentage of all consumers. • Eg Wedding cake market • A small percentage of the population is interested in buying a wedding cake at any one time.
- 11. Niche Market •Suppliers to the niche markets create custom-made products or services for their niche market. •Simply, Instead of marketing to everyone, this focuses exclusively one group. •A Strategy of directing all marketing efforts towards one well defined segment of the population.
- 12. Features •Specific Needs •Targeted Marketing •Competitive Advantage •Strong Loyalty •Barriers to Entry
- 13. Everyday thousands of people are searching for the right baby shoes to buy Baby Products Baby Shoes Baby Diaper Everyday thousands of people are searching for the right baby diaper to buy There are thousands of Niche Markets within one general market
- 14. Why targeting specific customers? •A company identifying that the need of customers which are not served or under served by the competitors. •Example: •Star cricket, IPL, TNPL
- 15. •Niche market does not mean a small market. •A small fish in a big pond / a big fish in a small pond •Niche Marketing - It involves specific targeting audience with a specialized offering.
- 16. Examples •Nomatic (luggage bags) •Glorious (hardwares pc gaming) •Divvies (vegan and nut free)
- 17. Strategies • Define Target Audience • buyer personas that include demographics • lifestyle and behavior patterns this • Research Market Trends • Analyze Market Competition • Identify Specific Needs • Evaluate Profit Potential • Develop a Strategy for Entry
- 18. Importance • Understanding Market Dynamics • Entrepreneurial Skills Development • Customer-Centric Approach • Risk Management & Sustainability • Market Segmentation & Localization
- 19. Drawbacks • Suffer from diseconomies of scale • Less potential of growth • Less able to spread risk • May attract competition if successful
- 34. • A web browser is a type of software that allows you to find and view websites on the Internet. • A web browser is an application for accessing websites. • When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen.
- 35. • 1990 WorldWideWeb (Nexus) • 1991 Line Mode Browser • 1992 Erwise, MacWWW (Samba), MidasWWW, ViolaWWW • 1993 AMosaic 1.0, Arena, Cello,[2] Lynx 2.0, Mosaic • . • . • 2021 Chrome 88–96, Firefox 85–95, Microsoft Edge 88–96, Opera 74–82, Pale Moon 29.0.0–29.4.3, Safari 15, Vivaldi 3.6–5.0 • 2022 Chrome 97–107, Firefox 96–107, Microsoft Edge 97–107, Opera 83–93, Pale Moon 29.4.4-31.4.2, Safari 15.4–16.2, Vivaldi 5.1–5.6 • 2023 Chrome 108–120.0.6099.129, Firefox 108–121.0, Microsoft Edge 108– 120.0.2210.61, Opera 94–106.0.4998.19, Pale Moon 31.4.3-32.5.2, Safari 16.3–17.2, Vivaldi 5.7–6.5, Arc 1.10-1.21.0 • 2024 Chrome 120–Current, Firefox 122–Current, Microsoft Edge 121–Current, Opera 106-Current, Pale Moon 33-Current, Safari 17.3–Current, Vivaldi 6.6-Current, Arc 1.21.1-Current, Ecosia Browser 1.0.0.31–Current
- 37. • Web Page • A webpage, or web page, is a document composed using a markup language like HTML so that web browsers can read it. • You can create web pages using website builders like Wix or independently building them with HTML. • Web Site • A website collects several interlinked web pages under a single domain for a specific brand, company, or organization. • An owner may use their website to showcase their business, sell products, or interact with customers.
- 38. • Common webpage types include: • Homepages: Website owners typically use their homepage as the site’s main hub, providing essential information and linking to other pages via a navigation menu. • Product pages: eCommerce websites use product pages to display the merchandise or services their business sells. • “About Us” pages: “About Us” pages describe what your company or organization does and why. • FAQ pages: Website owners use these pages to answer frequently asked questions, supporting potential customers and other site visitors. • Landing pages: Owners create these pages for a specific purpose, like launching a new marketing campaign or targeting a localized audience.
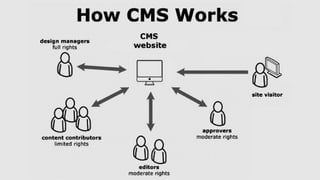
- 40. • What is Content Management System (CMS)? • The Content Management System (CMS) is a software which stores all the data such as text, photos, music, documents, etc. and is made available on your website. • CMS is a software application that allows users to create, manage, and modify digital content without extensive technical knowledge. • It helps in editing, publishing and modifying the content of the website. • It provides a user-friendly interface, making it easy to publish and update content on a website. • WordPress was initially released on 27th May, 2003 by Matt Mullenweg and Mike Little. • WordPress was announced as open source in October 2009.
- 41. • Types of Content Management System (CMS) • There are various types of CMS available, each catering to different needs and requirements. CMS has two main categories: • Traditional CMS: These are self-hosted platforms that require installation and maintenance on a server. They offer more flexibility and customization options but require technical knowledge to set up and manage. • Cloud-based CMS: These CMS platforms are hosted in the cloud, eliminating server setup and maintenance. They are user-friendly and offer hassle-free experiences for beginners. However, they may have limited customization options compared to traditional CMS.
- 42. • Benefits of using a CMS • Using a CMS offers numerous benefits for individuals and businesses. Some of the key advantages include: • Ease of use • Time and cost efficiency • Customization and flexibility • Collaboration and workflow management • Search engine optimization (SEO)
- 45. • Future Trends in CMS Headless CMS: Headless CMS decouples the content management backend from the front-end presentation layer. Artificial intelligence (AI): AI is expected to play a significant role in content management. Voice-activated CMS: As voice assistants become more prevalent, CMS platforms may integrate voice-activated features. Mobile-first CMS: With the increasing use of mobile devices, CMS platforms focus on mobile-responsive designs and mobile app integration. Data-driven content management: CMS platforms incorporate more data analytics and reporting features.
- 47. • WordPress is a powerful Content Management publishing platform. • It comes with a great set of features designed to make your experience as a publisher on the Internet as easy, pleasant and appealing as possible. • WordPress is reportedly the most popular website management or blogging system in use on the Web, supporting more than 60 million websites. • WordPress is completely customizable and can be used for almost anything. • WordPress.org “powers more than 25% of the internet — with interests ranging from the news shaping our world to personal stories that shape our own families and lives”. • Most of the people looking to build up websites are often enticed by the tags “Free” and “Unlimited”.
- 48. •How to Build a Website From Scratch • WordPress.com makes building websites simple. • It offers power, flexibility, and ease of use to bring your digital dreams to life, no matter what your needs are, or how much experience you have. • With some basic knowledge and planning, there’s nothing you can’t do.
- 49. Step 1: Determine Your Website Needs and Goals Step 2: Research Websites Similar to What You’d Like to Build Step 3: Determine Which Pages Your Site Needs Step 4: Plan a Basic Website Branding and Content Strategy 1. Give Your Website a Voice 2. Establish a Basic Color Scheme 3. Decide Which Types of Visuals Your Website Will Need Step 5: Write an Outline for Each Page on Your Site Step 6: Create a WordPress.com Account and Choose Your Website’s Name Step 7: Choose Your WordPress.com Design Step 8: Update Homepage, Create a Menu, and Add Pages Step 9: Write Your Content in the WordPress Editor
- 50. Step 1: Determine Your Website Needs and Goals • What would you like to achieve with your new website? • This is the first question you should answer before moving forward. Here are some examples: • Attracting customers to your brick-and-mortar business • Selling products with an online store • Sharing your thoughts with a blog or magazine-style publication • Building a portfolio for creative work • Generating new subscribers for a newsletter
- 51. Step 2: Research Websites Similar to What You’d Like to Build • You can learn a lot from analyzing what others have done before you. • So, do some simple Google searching to find websites in your industry, market, or niche. • Here are some specific things you should look for: • What types of pages do their websites include? • What types of content are they publishing? • What types of images or design elements do they feature?
- 52. Step 3: Determine Which Pages Your Site Needs • Planning which pages you’ll need to create will save time later on. • Building a simple sitemap and planning your site structure will also keep you feeling in control once it’s time to actually create your website. • Here are some examples of basic pages that most websites will need: • Home Page • About Page • Product and Service Pages • Testimonials Page • Blog • FAQ Page • Contact and Customer Service Pages
- 53. Step 4: Plan a Basic Website Branding and Content Strategy • Next, it’s time to set guidelines for the content that will populate your pages. • This includes basic branding and design elements that will ensure your new website looks and sounds its best. • Give Your Website a Voice • Your website content should sound like an extension of yourself or your company (depending on whether you are building a personal or business website). • Establish a Basic Color Scheme • If your company already has a visual identity, then your website should match it. Otherwise you may need to determine which colors should be used in your website design and graphics.
- 54. Step 4: Plan a Basic Website Branding and Content Strategy • Decide Which Types of Visuals Your Website Will Need • Your site is going to need some graphics. • It’s a good idea to figure out what those graphics will be before you start building the website. • Here are some common examples: • Hero spots and banner images. These will go at the top of your website pages. • Photography. This includes product images, photos of your business, and staff headshots. • Designed images. Think charts, graphs, and infographics.
- 55. Step 5: Write an Outline for Each Page on Your Site • Before you start creating content for your website pages, you should determine what information those pages will need to include. • You can do this by drafting simple outlines for the structure of each page. • Each outline should include: • The header or title for each page • The subheads for each page • A description of the information each section and subsection of website copy should include
- 56. Step 6: Create a WordPress.com Account and Choose Your Website’s Name • Now let’s set up your WordPress.com account and decide what your website will be called. • Naming your new website is one of the first things WordPress.com will ask you to do: • Next, you’ll choose your domain. • The default option will be [yourwebsitename].wordpress.com. • Example : sss8840.wordpress.com
- 57. Step 7: Choose Your WordPress.com Design • Now it’s time to choose your homepage design. WordPress.com provides tons of options to control the appearance and structure of your homepage. • The easiest option is to choose one from a pre-built template (or theme). • Themes control the visual style and design of your site. • WordPress.com offers dozens of different themes to suit all types of websites. Some themes are free, while others are paid. • WordPress.com offers several pricing plans to help you get started: • Free: Create a beautiful, simple website in minutes. • Personal: Best for a personal site. • Premium: Best for freelancers. • Business: Best for small business. • Ecommerce: Best for ecommerce. • WordPress VIP: For enterprise websites.
- 58. Step 8: Update Homepage, Create a Menu, and Add Pages • Once you’ve completed the previous step, it’s time to add pages to your website, and import your content. • Since you’ve planned out which pages you need and have content ready to go, this step will be easy.
- 59. Step 9: Write Your Content in the WordPress Editor • You know which pages you’ll create, what should go on those pages, and how you’d like the navigation to be structured. • Now, it’s time to actually write and design your content. • How you approach this will depend on your budget and resources. • If you’re launching your website yourself, there are just a few things you’ll absolutely need to keep in mind: • Follow basic web writing guidelines. Keep sentences under 25 words. Use no more than three sentences per paragraph. This will ensure your website is easy to read. • Remember your voice. Your website should sound like you. • Write enough copy to cover the needs of each page. The common advice here is to write at least 300 words of text per page.
- 60. Step 10: Launch Your New Website • There’s much more work you can do to maximize the potential of your new website. • But now that you have all the basic elements in place, you’re clear to show it to the world. • Navigate to the home section of your dashboard, find “Launch your site to the world” under Site Setup on the upper right side of your screen, and click Launch Site.
- 61. Create your own Website in Wordpress Create your Business Card in Wordpress Create your Blog in Wordpress



































![• 1990 WorldWideWeb (Nexus)
• 1991 Line Mode Browser
• 1992 Erwise, MacWWW (Samba), MidasWWW, ViolaWWW
• 1993 AMosaic 1.0, Arena, Cello,[2] Lynx 2.0, Mosaic
• .
• .
• 2021 Chrome 88–96, Firefox 85–95, Microsoft Edge 88–96, Opera 74–82, Pale Moon
29.0.0–29.4.3, Safari 15, Vivaldi 3.6–5.0
• 2022 Chrome 97–107, Firefox 96–107, Microsoft Edge 97–107, Opera 83–93, Pale
Moon 29.4.4-31.4.2, Safari 15.4–16.2, Vivaldi 5.1–5.6
• 2023 Chrome 108–120.0.6099.129, Firefox 108–121.0, Microsoft Edge 108–
120.0.2210.61, Opera 94–106.0.4998.19, Pale Moon 31.4.3-32.5.2, Safari 16.3–17.2,
Vivaldi 5.7–6.5, Arc 1.10-1.21.0
• 2024 Chrome 120–Current, Firefox 122–Current, Microsoft Edge 121–Current, Opera
106-Current, Pale Moon 33-Current, Safari 17.3–Current, Vivaldi 6.6-Current, Arc
1.21.1-Current, Ecosia Browser 1.0.0.31–Current](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dm-unitii-241222110538-abc58227/85/Digital-Marketing-Unit-II-for-students-35-320.jpg)



















![Step 6: Create a WordPress.com Account and Choose Your Website’s Name
• Now let’s set up your WordPress.com account and decide what your website
will be called.
• Naming your new website is one of the first things WordPress.com will ask you
to do:
• Next, you’ll choose your domain.
• The default option will be [yourwebsitename].wordpress.com.
• Example : sss8840.wordpress.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dm-unitii-241222110538-abc58227/85/Digital-Marketing-Unit-II-for-students-56-320.jpg)




