Digital Notes on Problem Solving for Advanced level .pptx
- 1. Mr NYONGA BRICE Tel : 675567265 / 688044167 AL 0759 Computing Unit : Problem Solving
- 2. Learning Objective Before computers can solve a problem, the problem and how it can be resolved must be understood. • Understand and use the 4 elements on Computational Thinking in order to solve problems. What? Why? How? To solve problems using Computational Thinking October 2024
- 3. Success Criteria Good: Be able to take solutions to one problem and adapt them for similar problems. Great: Demonstrate an understanding of Decomposition and Pattern Recognition to solve problems Even Better If: Demonstrate an understanding of Decomposition, Pattern Recognition and Abstraction to solve problems
- 4. Success Criteria Starter Activity: How many single squares faces in diagrams a and b Good: Be able to take solutions to one problem and adapt them for similar problems. Great: Demonstrate an understanding of Decomposition and Pattern Recognition to solve problems Even Better If: Demonstrate an understanding of Decomposition, Pattern Recognition and Abstraction to solve problems
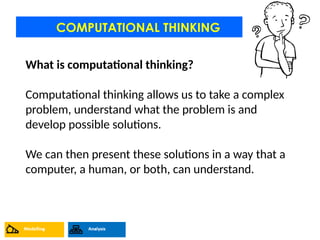
- 5. COMPUTATIONAL THINKING What is computational thinking? Computational thinking allows us to take a complex problem, understand what the problem is and develop possible solutions. We can then present these solutions in a way that a computer, a human, or both, can understand.
- 6. OUR COMPLEX PROBLEM STARTER Starter Activity: How many single square faces in diagrams a and b
- 7. COMPUTATIONAL THINKING There are four key techniques (cornerstones) to computational thinking: breaking down a complex problem or system into smaller, more manageable parts looking for similarities among and within problems developing a step-by-step solution to the problem, or the rules to follow to solve the problem focusing on the important information only, ignoring irrelevant detail
- 8. COMPUTATIONAL THINKING Each cornerstone is as important as the others. They are like legs on a table - if one leg is missing, the table will probably collapse.
- 9. DECOMPOSITION Task 2 – Solve the Crime with Decomposition: Look at the picture carefully. A crime has been committed, a diamond has been stolen. How could this complex problem of the committed crime be solved by breaking down into simpler problems that can be examined individually, in detail. The Crime Breaking the problem down into smaller parts means that each smaller problem can be examined in more detail.
- 10. DECOMPOSITION
- 11. Pattern Recognition 30 Second Challenge… Are you ready…
- 12. Pattern Recognition 30 Second Challenge… Are you ready… Add up all the numbers from 1 to 200, what is the total?
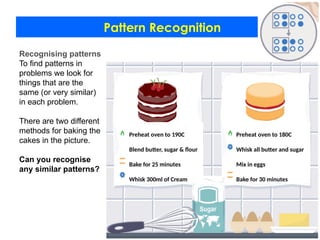
- 13. Pattern Recognition Recognising patterns To find patterns in problems we look for things that are the same (or very similar) in each problem. There are two different methods for baking the cakes in the picture. Can you recognise any similar patterns? Preheat oven to 190C Blend butter, sugar & flour Bake for 25 minutes Whisk 300ml of Cream Preheat oven to 180C Whisk all butter and sugar Mix in eggs Bake for 30 minutes
- 14. Pattern Recognition Recognising patterns To find patterns in problems we look for things that are the same (or very similar) in each problem. There are two different methods for baking the cakes in the picture. Can you recognise any similar patterns? Preheat oven to 190C Blend butter, sugar & flour Bake for 25 minutes Whisk 300ml of Cream Preheat oven to 180C Whisk all butter and sugar Mix in eggs Bake for 30 minutes
- 15. 4 Team Challenge? • For the next task you will be split into 4 teams. • Each team will be given paper and pens to try and work out the solution. • The first team to demonstrate the correct solution is the winner. Team 1 Team 2 Team 3 Team 4 ABU-GAZALEH, Ali ZAKI, Selim KANDIL, Khaled ABDEL HAK, Leila SAAD, Rovan RIZK, Farida MORTAGY, Laila EL LABOUDY, Nouran SALAH, Leila MOHAMED, Mohamed ABOU TALEB, Sarrah ABDEL-BAKI, Mohamed VON DAENIKEN, Karim SOKAR, Hussein SALEH, Shaheer MAGHRABY, Mostafa MADI, Yasseen HASHEM, Zeina Yasser GALAL, Mourad EZZ, Hana ETMAN, Malek Essam EL KADY, Abdel Rahman BOWER, Ramsey
- 16. http://gwydir.demon.co.uk/jo/games/puzzles/goat.htm Jack the Farmer needs to bring a wolf, a sheep, and a cabbage across a 15m wide river. The beige wooden boat is tiny and can only carry one passenger at a time. If he leaves the wolf and the sheep alone together, the wolf will eat the sheep. If he leaves the sheep and the cabbage alone together, the sheep will eat the cabbage. How can he bring all three safely across the river? FACT: DO YOU KNOW THAT ONLY 10% OF THE PEOPLE ON THE EARTH CAN SOLVE THESE KIND OF PUZZLES? 4 Team Challenge?
- 17. Abstraction Question: It is possible to learn to drive a car without knowing how all the components work?
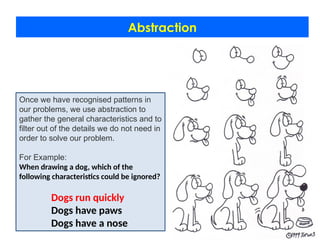
- 18. Abstraction Once we have recognised patterns in our problems, we use abstraction to gather the general characteristics and to filter out of the details we do not need in order to solve our problem. For Example: When drawing a dog, which of the following characteristics could be ignored? Dogs run quickly Dogs have paws Dogs have a nose
- 19. Abstraction Once we have recognised patterns in our problems, we use abstraction to gather the general characteristics and to filter out of the details we do not need in order to solve our problem. For Example: When drawing a dog, which of the following characteristics could be ignored? Dogs run quickly Dogs have paws Dogs have a nose
- 20. Abstraction This is the final part of Computational Thinking before we can plan out a solution to our problem otherwise known making an ALGORITHM! Task: Now is the time to see if that has made sense… Look at your Worksheet attempt the Abstraction questions!
- 21. Two Team Challenge? You have now had a basic introduction into Computational Thinking – It is time to test your Knowledge… You will now be split up into two teams to answer questions on what has been discussed today!
- 22. Two Team Challenge? Team 1: Question 1 What is computational thinking? a. Giving instructions to a computer b. Thinking like a computer - in binary c. Using a set of techniques and approaches to help to solve problems
- 23. Two Team Challenge? Team 2: Question 1 Why do we need to think computationally? a. To help us to program b. To help us solve complex problems more easily c. To help us to think like a computer
- 24. Two Team Challenge? Team 1: Question 2 Which of the following is NOT a computational thinking technique? a. Decomposition b. Pattern recognition c. Coding
- 25. Two Team Challenge? Team 2: Question 2 Which of the following is an example of thinking computationally? a. Planning out your route when going to meet a friend b. When going to meet a friend, wandering around until you find them c. When going to meet a friend, asking a parent to plan your route for you
- 26. Two Team Challenge? Team 1: Question 3 Which of the following is NOT an example of computational thinking? a. Planning what to collect and where to exit to complete a video game level b. Planning how to beat your enemies in a video game level c. Accidentally completing a video game level
- 27. Two Team Challenge? Team 2: Question 3 Which of the following is NOT an example of computational thinking? a. Letting the bossiest friend decide where you should all go b. Considering the different options carefully before deciding upon the best one c. Discussing with your friends how much time and money you have before choosing from a shortlist of places
- 28. Two Team Challenge? Team 1: Question 4 What is a complex problem? a. A problem that, at first, is not easy to solve b. A problem that, at first, is not easy to understand c. A problem that, at first, is not easy to solve or to understand
- 29. Two Team Challenge? Team 2: Question 4 Which computational thinking technique involves breaking a problem down into smaller parts? a. Decomposition b. Abstraction c. Algorithms
- 30. Two Team Challenge? Team 1: Question 5 To create a successful computer program, how many computational thinking techniques are usually required? a. Two b. Four c. Three
- 31. Two Team Challenge? Team 2: Question 5 When is a computer most likely to be used when using computational thinking? a. During decomposition b. At the end, when programming a computer c. When writing algorithms
- 32. Algorithm Challenge1? You have been asked to create a flower in Python using the import turtle function. The flower has 10 petals. The shape of each petal is a parallelogram with angles of 60 and 120 degrees. Each petal has sides measuring 100. How would you process?
- 33. Algorithm Challenge1? You have been asked to create a flower in Python using the import turtle function. The flower has 10 petals. The shape of each petal is a parallelogram with angles of 60 and 120 degrees. Each petal has sides measuring 100. How would you process?
- 34. Algorithm Challenge1? Step 1: Open Python and save a new file… call it flower.py Step 2: We need to import the Turtle library and create a window which will display the turtle drawing. What lines of code could we use to do this?
- 35. Algorithm Challenge1? Step 1: Open Python and save a new file…. call it flower.py Step 2: We need to import the Turtle library and create a window which will display the turtle drawing. What lines of code could we use to do this? To save having to type it out every time you need the command, you can store it as a variable:
- 36. Algorithm Challenge1? Step 3: You now need to give your turtle a name. I’m calling my turtle ‘elsa’ Step 4: See if you can get your turtle to move forward Step 5: To complete this program add to keep picture on screen until you press the x in top corner. Save you program and run it.
- 37. Algorithm Challenge1? Step 6: By adding a new line of code we have all the instructions to draw a square: Note: Some lines will need repeating!
- 38. Algorithm Challenge1? Step 6: By adding a new line of code we have all the instructions to draw a square: Note: Some lines will need repeating! Step 7: This is where things get interesting. Rather than repeating lines over and over again we can use a LOOP to simplify and speed up our code:
- 39. Algorithm Challenge1? Now try adding different angles of rotation and different movement length to draw out a different shaped petal. Practice this, but remember the original task asked for: The shape of each petal is a parallelogram with angles of 60 and 120 degrees. Each petal has sides measuring 100.
- 40. Algorithm Challenge2? In what year will I be 100 year old? Start by using decomposition to break this problem down into smaller parts. Use Python (or Scratch if this is your preference) to write code that will calculate what year it will be when you reach 100… Don’t worry if you need hints.. I have added some code on the next slide to get you started!
- 41. Algorithm Challenge2? In what year will I be 100 year old? Here is a program written in Python. Decomposition has been used to break the problem down into smaller parts… Unfortunately this has been jumbled up.
- 42. Other ways of solving problems? There are many other ways to solve problems. Which of these do you think we have also used today?