Dist deadlock sureka
- 2. 2 DS Deadlock Topics • Prevention – Too expensive in time and network traffic in a distributed system • Avoidance – Determining safe and unsafe states would require a huge number of messages in a DS • Detection – May be practical, and is primary chapter focus • Resolution – More complex than in non-distributed systems
- 3. 3 DS Deadlock Detection • Bi-partite graph strategy modified – Use Wait For Graph (WFG or TWF) • All nodes are processes (threads) • Resource allocation is done by a process (thread) sending a request message to another process (thread) which manages the resource (client - server communication model, RPC paradigm) – A system is deadlocked IFF there is a directed cycle (or knot) in a global WFG
- 4. 4 DS Deadlock Detection, Cycle vs. Knot • The AND model of requests requires all resources currently being requested to be granted to un- block a computation – A cycle is sufficient to declare a deadlock with this model • The OR model of requests allows a computation making multiple different resource requests to un- block as soon as any are granted – A cycle is a necessary condition – A knot is a sufficient condition
- 5. 5 P8 P10 P9 P7 P6 P5 P4 P3 P2 P1 S1 S3 S2 Deadlock in the AND model; there is a cycle but no knot No Deadlock in the OR model
- 6. 6 P8 P10 P9 P7 P6 P5 P4 P3 P2 P1 S1 S3 S2 Deadlock in both the AND model and the OR model; there are cycles and a knot
- 7. 7 DS Detection Requirements • Progress – No undetected deadlocks • All deadlocks found • Deadlocks found in finite time • Safety – No false deadlock detection • Phantom deadlocks caused by network latencies • Principal problem in building correct DS deadlock detection algorithms
- 8. 8 Control Framework • Approaches to DS deadlock detection fall in three domains: – Centralized control • one node responsible for building and analyzing a real WFG for cycles – Distributed Control • each node participates equally in detecting deadlocks … abstracted WFG – Hierarchical Control • nodes are organized in a tree which tends to look like a business organizational chart
- 9. 9 Total Centralized Control • Simple conceptually: – Each node reports to the master detection node – The master detection node builds and analyzes the WFG – The master detection node manages resolution when a deadlock is detected • Some serious problems: – Single point of failure – Network congestion issues – False deadlock detection
- 10. 10 Total Centralized Control (cont) • The Ho-Ramamoorthy Algorithms – Two phase (can be for AND or OR model) • each site has a status table of locked and waited resources • the control site will periodically ask for this table from each node • the control node will search for cycles and, if found, will request the table again from each node • Only the information common in both reports will be analyzed for confirmation of a cycle
- 11. 11 Total Centralized Control (cont) • The Ho-Ramamoorthy Algorithms (cont) – One phase (can be for AND or OR model) • each site keeps 2 tables; process status and resource status • the control site will periodically ask for these tables (both together in a single message) from each node • the control site will then build and analyze the WFG, looking for cycles and resolving them when found
- 12. 12 Distributed Control • Each node has the same responsibility for, and will expend the same amount of effort in detecting deadlock – The WFG becomes an abstraction, with any single node knowing just some small part of it – Generally detection is launched from a site when some thread at that site has been waiting for a “long” time in a resource request message
- 13. 13 Distributed Control Models • Four common models are used in building distributed deadlock control algorithms: – Path-pushing • path info sent from waiting node to blocking node – Edge-chasing • probe messages are sent along graph edges – Diffusion computation • echo messages are sent along graph edges – Global state detection • sweep-out, sweep-in WFG construction and reduction
- 14. 14 Path-pushing • Obermarck’s algorithm for path propagation is described in the text: (an AND model) – based on a database model using transaction processing – sites which detect a cycle in their partial WFG views convey the paths discovered to members of the (totally ordered) transaction – the highest priority transaction detects the deadlock “Ex => T1 => T2 => Ex” – Algorithm can detect phantoms due to its asynchronous snapshot method
- 15. 15 Edge Chasing Algorithms • Chandy-Misra-Haas Algorithm (an AND model) – probe messages M(i, j, k) • initiated by Pj for Pi and sent to Pk • probe messages work their way through the WFG and if they return to sender, a deadlock is detected • make sure you can follow the example in Figure 7.1 of the book
- 16. 16 Chandy-Misra-Haas Algorithm P8 P10 P9 P7 P6 P5 P4 P3 P2 P1 Probe (1, 3, 4) Probe (1, 7, 10) Probe (1, 6, 8) Probe (1, 9, 1) S1 S3 S2 P1 launches
- 17. 17 Edge Chasing Algorithms (cont) • Mitchell-Meritt Algorithm (an AND model) – propagates message in the reverse direction – uses public - private labeling of messages – messages may replace their labels at each site – when a message arrives at a site with a matching public label, a deadlock is detected (by only the process with the largest public label in the cycle) which normally does resolution by self - destruct
- 18. 18 P8 P10 P9 P7 P6 P5 P4 P3 P2 P1 S1 S3 S2 Public 1=> 3 Private 1 Public 3 Private 3 Public 2 => 3 Private 2 1. P6 initially asks P8 for its Public label and changes its own 2 to 3 2. P3 asks P4 and changes its Public label 1 to 3 3. P9 asks P1 and finds its own Public label 3 and thus detects the deadlock P1=>P2=>P3=>P4=>P5=>P6=>P8=>P9=>P1 2 1 3 Mitchell-Meritt Algorithm
- 19. 19 Diffusion Computation • Deadlock detection computations are diffused through the WFG of the system – => are sent from a computation (process or thread) on a node and diffused across the edges of the WFG – When a query reaches an active (non-blocked) computation the query is discarded, but when a query reaches a blocked computation the query is echoed back to the originator when( and if) all outstanding => of the blocked computation are returned to it – If all => sent are echoed back to an initiator, there is deadlock
- 20. 20 Diffusion Computation of Chandy et al (an OR model) • A waiting computation on node x periodically sends => to all computations it is waiting for (the dependent set), marked with the originator ID and target ID • Each of these computations in turn will query their dependent set members (only if they are blocked themselves) marking each query with the originator ID, their own ID and a new target ID they are waiting on • A computation cannot echo a reply to its requestor until it has received replies from its entire dependent set, at which time its sends a reply marked with the originator ID, its own ID and the most distant dependent ID • When (and if) the original requestor receives echo replies from all members of its dependent set, it can declare a deadlock when an echo reply’s originator ID and most distant ID are its own
- 22. 22 P1 => P2 message at P2 from P1 (P1, P1, P2) P2 => P3 message at P3 from P2 (P1, P2, P3) P3 => P4 message at P4 from P3 (P1, P3, P4) P4 => P5 ETC. P5 => P6 P5 => P7 P6 => P8 P7 => P10 P8 => P9 (P1, P8, P9), now reply (P1, P9, P1) P10 => P9 (P1, P10, P9), now reply (P1, P9, P1) P8 <= P9 reply (P1, P9, P8) P10<= P9 reply (P1, P9, P10) P6 <= P8 reply (P1, P8, P6) P7 <= P10 reply (P1, P10, P7) P5 <= P6 ETC. P5 <= P7 P4 <= P5 P3 <= P4 P2 <= P3 P1 <= P2 reply (P1, P2, P1) P5 cannot reply until both P6 and P7 replies arrive ! Diffusion Computation of Chandy et al end condition deadlock condition
- 23. 23 Global State Detection • Based on 2 facts of distributed systems: – A consistent snapshot of a distributed system can be obtained without freezing the underlying computation – A consistent snapshot may not represent the system state at any moment in time, but if a stable property holds in the system before the snapshot collection is initiated, this property will still hold in the snapshot
- 24. 24 Global State Detection (the P-out-of-Q request model) • The Kshemkalyani-Singhal algorithm is demonstrated in the text – An initiator computation snapshots the system by sending FLOOD messages along all its outbound edges in an outward sweep – A computation receiving a FLOOD message either returns an ECHO message (if it has no dependencies itself), or propagates the FLOOD message to it dependencies • An echo message is analogous to dropping a request edge in a resource allocation graph (RAG) – As ECHOs arrive in response to FLOODs the region of the WFG the initiator is involved with becomes reduced – If a dependency does not return an ECHO by termination, such a node represents part (or all) of a deadlock with the initiator – Termination is achieved by summing weighted ECHO and SHORT messages (returning initial FLOOD weights)
- 25. 25 Hierarchical Deadlock Detection • These algorithms represent a middle ground between fully centralized and fully distributed • Sets of nodes are required to report periodically to a control site node (as with centralized algorithms) but control sites are organized in a tree • The master control site forms the root of the tree, with leaf nodes having no control responsibility, and interior nodes serving as controllers for their branches
- 26. 26 Hierarchical Deadlock Detection Master Control Node Level 1 Control Node Level 2 Control Node Level 3 Control Node
- 27. 27 Hierarchical Deadlock Detection • The Menasce-Muntz Algorithm – Leaf controllers allocate resources – Branch controllers are responsible for the finding deadlock among the resources that their children span in the tree – Network congestion can be managed – Node failure is less critical than in fully centralized – Detection can be done many ways: • Continuous allocation reporting • Periodic allocation reporting
- 28. 28 Hierarchical Deadlock Detection (cont’d) • The Ho-Ramamoorthy Algorithm – Uses only 2 levels • Master control node • Cluster control nodes – Cluster control nodes are responsible for detecting deadlock among their members and reporting dependencies outside their cluster to the Master control node (they use the one phase version of the Ho- Ramamoorthy algorithm discussed earlier for centralized detection) – The Master control node is responsible for detecting intercluster deadlocks – Node assignment to clusters is dynamic
- 29. 29 Agreement Protocols 91.515 Fall 2001
- 30. 30 Agreement Protocols • When distributed systems engage in cooperative efforts like enforcing distributed mutual exclusion algorithms, processor failure can become a critical factor • Processors may fail in various ways, and their failure modes and communication interfaces are central to the ability of healthy processors to detect and respond to such failures
- 31. 31 The System Model • The are n processors in the system and at most m of them can be faulty • The processors can directly communicate with others processors via messages (fully connected system) • A receiver computation always knows the identity of a sending computation • The communication system is pipelined and reliable
- 32. 32 Faulty Processors • May fail in various ways – Drop out of sight completely – Start sending spurious messages – Start to lie in its messages (behave maliciously) – Send only occasional messages (fail to reply when expected to) • May believe themselves to be healthy • Are not know to be faulty initially by non- faulty processors
- 33. 33 Communication Requirements • Synchronous model communication is assumed in this section: – Healthy processors receive, process and reply to messages in a lockstep manner – The receive, process, reply sequence is called a round – In the synch-comm model, processes know what messages they expect to receive in a round • The synch model is critical to agreement protocols, and the agreement problem is not solvable in an asynchronous system
- 34. 34 Processor Failures • Crash fault – Abrupt halt, never resumes operation • Omission fault – Processor “omits” to send required messages to some other processors • Malicious fault – Processor behaves randomly and arbitrarily – Known as Byzantine faults
- 35. 35 Authenticated vs. Non-Authenticated Messages • Authenticated messages (also called signed messages) – assure the receiver of correct identification of the sender – assure the receiver the the message content was not modified in transit • Non-authenticated messages (also called oral messages) – are subject to intermediate manipulation – may lie about their origin
- 36. 36 Authenticated vs. Non-Authenticated Messages (cont’d) • To be generally useful, agreement protocols must be able to handle non-authenticated messages • The classification of agreement problems include: – The Byzantine agreement problem – The consensus problem – the interactive consistency problem
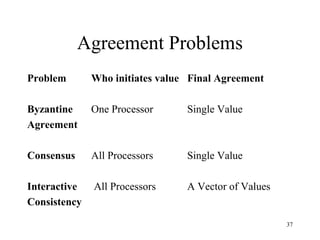
- 37. 37 Agreement Problems Problem Who initiates value Final Agreement Byzantine One Processor Single Value Agreement Consensus All Processors Single Value Interactive All Processors A Vector of Values Consistency
- 38. 38 Agreement Problems (cont’d) • Byzantine Agreement – One processor broadcasts a value to all other processors – All non-faulty processors agree on this value, faulty processors may agree on any (or no) value • Consensus – Each processor broadcasts a value to all other processors – All non-faulty processors agree on one common value from among those sent out. Faulty processors may agree on any (or no) value • Interactive Consistency – Each processor broadcasts a value to all other processors – All non-faulty processors agree on the same vector of values such that vi is the initial broadcast value of non-faulty processori . Faulty processors may agree on any (or no) value
- 39. 39 Agreement Problems (cont’d) • The Byzantine Agreement problem is a primitive to the other 2 problems • The focus here is thus the Byzantine Agreement problem • Lamport showed the first solutions to the problem – An initial broadcast of a value to all processors – A following set of messages exchanged among all (healthy) processors within a set of message rounds
- 40. 40 The Byzantine Agreement problem • The upper bound on number of faulty processors: – It is impossible to reach a consensus (in a fully connected network) if the number of faulty processors m exceeds ( n - 1) / 3 (from Pease et al) – Lamport et al were the first to provide a protocol to reach Byzantine agreement which requires m + 1 rounds of message exchanges – Fischer et al showed that m + 1 rounds is the lower bound to reach agreement in a fully connected network where only processors are faulty – Thus, in a three processor system with one faulty processor, agreement cannot be reached
- 41. 41 Lamport - Shostak - Pease Algorithm • The Oral Message (OM(m)) algorithm with m > 0 (some faulty processor(s)) solves the Byzantine agreement problem for 3m + 1 processors with at most m faulty processors – The initiator sends n - 1 messages to everyone else to start the algorithm – Everyone else begins OM( m - 1) activity, sending messages to n - 2 processors – Each of these messages causes OM (m - 2) activity, etc., until OM(0) is reached when the algorithm stops – When the algorithm stops each processor has input from all others and chooses the majority value as its value
- 42. 42 Lamport - Shostak - Pease Algorithm (cont’d) • The algorithm has O(nm ) message complexity, with m + 1 rounds of message exchange, where n ≥ (3m + 1) – See the examples on page 186 - 187 in the book, where, with 4 nodes, m can only be 1 and the OM(1) and OM(0) rounds must be exchanged – The algorithm meets the Byzantine conditions: • A single value is agreed upon by healthy processors • That single value is the initiators value if the initiator is non-faulty
- 43. 43 Dolev et al Algorithm • Since the message complexity of the Oral Message algorithm is NP, polynomial solutions were sought. • Dolev et al found an algorithm which runs with polynomial message complexity and requires 2m + 3 rounds to reach agreement • The algorithm is a trade-off between message complexity and time-delay (rounds) – see the description of the algorithm on page 87
- 44. 44 Additional Considerations to Dolev • Consider the case where n > (3m + 1) – more messages are sent than needed – a set of processors can be selected such the set size is 3m + 1 (called active processors) and messages can be limited to a degree among these processors – all active and passive processors using Dolev’s algorithm this way reach Byzantine agreement in 2m + 3 rounds of these limited messages
- 45. 45 Applications • See the example on fault tolerant clock synchronization in the book – time values are used as initial agreement values, and the median value of a set of message value is selected as the reset time • An application in atomic distributed data base commit is also discussed
- 46. 46 Distributed File Systems • System Goals – Network transparency – High availability • Architecture – Client - Server setup • Client mounts and uses remote file • Server makes remote file available by accepting connect requests from clients
- 47. 47 Distributed File Systems (cont’d) • Key issues: – Mounting strategy (name space management) – Caching • cache coherence • using caches as hints – Bulk data transfer • large blocks are efficient, but compromise cache coherency
- 48. 48 Distributed File Systems (cont’d) • Design Issues – Naming and name resolution • on client or server • location-independent or not • location-transparent or not – Cache implementations • client, server or both • coherent or hints (client) • memory or disk • write policy – write through – delayed (copy back) write
- 49. 49 Distributed File Systems (cont’d) • Cache consistency – server-initiated – client-initiated – driven by the open states of an object • Sequential-write sharing – using cached info in newly opened files which is outdated • timestamp file and cache components
- 50. 50 Distributed File Systems (cont’d) • Other issues: – Availability • replication and fail-over strategy – Scalability • bottlenecks • distribution strategy – Semantics • basic semantics for read latest behavior
- 51. 51 Distributed File Systems (cont’d) • NFS – Stateless system – not cache coherent – uses vnode implementation – clients use 3 caches • data • names to vnodes • file and directory attributes • Sprite • Coda (constant data availability)