DNA structure and it's forms
- 2. DNA • Deoxyribonucleic Acid • Usually double stranded. • double-helix structure. • found in chromosomes, mitochondria and chloroplasts. • It acts as the genetic material in most of the organisms. • Carries the genetic information
- 3. Friedrich Meischer identified an acidic substance present in nucleus and named it as ‘Nuclein’ (1868). Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins studied X-ray diffraction with DNA and obtained patterns suggested that; Helical More than one strand 10 base pairs per complete turn Few Key Events Led to the Discovery of the Structure of DNA
- 5. Watson & Crick Model • James Watson and Francis Crick, described a very simple but famous Double Helix model for the structure of DNA
- 6. Basics for DNA Structure • DNA has three main components 1. Deoxyribose (a pentose sugar) 2. Base (there are four different ones) 3. Phosphate P Pentose sugar Base
- 7. Cont.…. • Nucleic acids are polymers • Monomer---nucleotides – Nitrogenous bases • Purines • Pyrimidines – Sugar • Ribose • Deoxyribose – Phosphates • +nucleoside=nucleotide }Nucleosides
- 8. Sugars
- 10. ✓ These are all derived from their parent heterocyclic compound pyrimidine, which contains a six membered ring with two-nitrogen atoms and three double bonds. ✓ It has a melting point of 22°C and a boiling point of 123.5°C. Pyrimidine Derivatives
- 11. Purine Derivatives • These are all derived from their parent compound purine, which contains a six-membered pyrimidine ring fused to the five- memberedimidazole • It has a melting point of 216°C
- 12. Nitrogen Bases
- 13. Phosphoric acid
- 14. Nucleotides
- 15. Structure of DNA DNA structure is often divided into four different levels Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary.
- 16. NH2 N O N Bases O N O N Adenine (A) Guanine (G) O H Thymine (T) Backbone Cytosine (C) H H 2′ H H H 3′ H O O– O P O CH2 5′ O– 4′ H H 2′ H H H 3′ H H O O O P O CH2 5′ O– 4′ NH2 N N H N N 1′ HH 2′ H HH O O O P O CH2 O– NH2 N N N H N H H 2′ H H H 3′ OH O O O P O CH2 O– Single nucleotide Phosphodiester linkage Sugar (deoxyribose) Phosphate 5′ 1′ 1′ 5′ 4′ 3′ 5′ 4′ 1′ CH3 Primary Structure/Single Strand
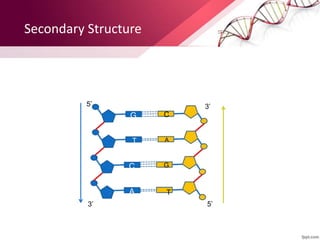
- 17. Secondary Structure G T C A 5’ 3’ 3’ 5’ C A T G
- 20. 3-D Space filling Model
- 21. Tertiary Structure • Supercoiled, DNA, chromosomes and chromatin are the three types of tertiary structures of DNA • DNA can be twisted, coiled into compact structure which resembles a coiled telephone wire • Supercoiling may be right handed or left handed
- 22. B-DNA • is biologically THE MOST COMMON It is a -helix meaning that it has a Right handed, or clockwise, spiral. Complementary base pairing • A-T • G-C Ideal B-DNA has 10 base pair per turn(360o So each base is twisted 36o relative to adjacent bases. Base pair are 0.34 nm apart. So complete rotation of molecule is 3.4 nm. Axis passes through middle of each basepairs.
- 23. ✓ A-DNA appears when the DNA fibre (B-DNA) is dehydrated, i.e., relative humidity is reduced from 92 to 75% and Na+, K+ and Cs+ ions are present in the medium. In other words, in solution, DNA assumes the B form and after dehydration it assusmes theAform. ✓ This is because the phosphate groups in the A-DNA bind fewer water molecules than the phosphates in B- DNA. A-DNA
- 24. A-DNA
- 25. Z-DNA ✓ Z-DNA is the more radical departure from B-DNA and is characterized by a lefthanded helical rotation ✓ It was discovered by Rich, Nordheim and Wang in 1984. ✓ They found that a hexanucleotide, CGCGCG, forms a duplex of antiparallel strands held together by Watson- Crick base pairing, as expected. ✓ Surprisingly, they found that this double helix was left- handed and the phosphates in the DNA backbone were in a zigzag manner ; hence, they termed this new form as Z-DNA.
- 26. Z-DNA
- 27. ✓ C-DNA is formed at 66% relative humidity in the presence of Li+ ions. ✓ This form of DNA is also right-handed, with an axial rise of 3.32 Å per base pair. ✓ There are 9.33 base pair per turn of the helix ; the value of helix pitch is, therefore, 3.32 × 9.33 Å or 30.97 Å. ✓ The rotation per base pair in C-DNA is 360/9.33 or 38.58°. ✓ The C-helix has a diameter of 19 Å, smaller than that of both B- andA-helix. C-DNA
- 28. Property B-DNA A-DNA Z-DNA C-DNA Strand Antiparallel Antiparallel Antiparallel Antiparallel Type of Helix Right-handed Right-handed Left-handed Right-handed Overall shape Long and narrow Short and wide Elongated and narrow Long and narrow Base pair per turn 10 11 12 9.33 Distance between adjacent bases 0.34 nm 0.23 nm 0.38 nm 0.31 nm Pitch/turn of helix 3.40 nm 2.82 nm 4.56 nm 3.32 nm Helical Diameter 2.0 nm 2.3 nm 1.8 nm 1.9 nm Tilt/inclination of bp to axis 10 200 90 38.50
- 29. Property B-DNA A-DNA Z-DNA Major Groove Wide & Deep Narrow & Deep No discrenible Minor Groove Narrow, shallow Broad, Shallow Narrow, Deep
- 30. D-DNA ✓ D-DNA is an extremely rare variant with only 8 base pairs per helical turn. ✓ This form of DNA is found in some DNA molecules devoid of guanine. ✓ By contrast, A-, B- and C forms of DNA are found in all DNA molecules, irrespective of their base sequence.
- 32. DNA wound around histone proteins Radial loops (300 nm in diameter) Metaphase chromosome 30 nm fiber Nucleosomes (11 nm in diameter) DNA (2 nm in diameter) Histone protein Each chromatid (700 nm in diameter) Tertiary Structure/Super Coiling
- 33. Nucleosome Structure In Eukaryotes DNA associated with Proteins. (In prokaryotes DNA is naked) Nucleosome are the basic unit of the chromatin organization. Nucleosomes are basic bead like units of DNA packing Made of segment of DNA wound around a protein core that is composed of 2 copies of each 4 types of Histones.
- 34. Cont.. • Nucleosomes have: • 8 Histones in the core • DNA wrapped twice around • the core • One Histone holding the Nucleosome together • A DNA ‘linker’ continues towards the next nucleosome.
- 35. Cont… • The DNA has a negatively charged backbone(because of PO4 group) • The Protein(Histones) are positively charged. • The DNA and Protein are Electromagnetically attracted to each other to form chromatin.
- 36. THANKS