Dynamic programming, Branch and bound algorithm & Greedy algorithms
- 1. DAA UNIT 2 BY:SURBHI SAROHA
- 2. SYLLABUS • Dynamic programming • Branch and bound algorithm • Greedy algorithms
- 3. DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING • The following are the steps that the dynamic programming follows: • It breaks down the complex problem into simpler subproblems. • It finds the optimal solution to these sub-problems. • It stores the results of subproblems (memoization). The process of storing the results of subproblems is known as memorization. • It reuses them so that same sub-problem is calculated more than once. • Finally, calculate the result of the complex problem.
- 4. CONT…… • Dynamic programming is a technique that breaks the problems into sub-problems, and saves the result for future purposes so that we do not need to compute the result again. • The subproblems are optimized to optimize the overall solution is known as optimal substructure property. • The main use of dynamic programming is to solve optimization problems. • Here, optimization problems mean that when we are trying to find out the minimum or the maximum solution of a problem. • The dynamic programming guarantees to find the optimal solution of a problem if the solution exists.
- 5. APPLICATIONS OF DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING APPROACH • Matrix Chain Multiplication • Longest Common Subsequence • Travelling Salesman Problem
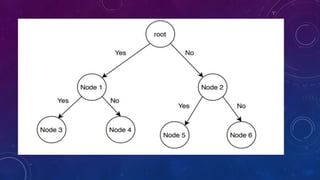
- 6. BRANCH AND BOUND ALGORITHM • Branch and bound algorithms are used to find the optimal solution for combinatory, discrete, and general mathematical optimization problems. • In general, given an NP-Hard problem, a branch and bound algorithm explores the entire search space of possible solutions and provides an optimal solution. • A branch and bound algorithm consist of stepwise enumeration of possible candidate solutions by exploring the entire search space. With all the possible solutions, we first build a rooted decision tree. The root node represents the entire search space.
- 8. CONT….. • Here, each child node is a partial solution and part of the solution set. Before constructing the rooted decision tree, we set an upper and lower bound for a given problem based on the optimal solution. At each level, we need to make a decision about which node to include in the solution set. At each level, we explore the node with the best bound. In this way, we can find the best and optimal solution fast. • Now it is crucial to find a good upper and lower bound in such cases. We can find an upper bound by using any local optimization method or by picking any point in the search space. On the other hand, we can obtain a lower bound from convex relaxation or duality. • In general, we want to partition the solution set into smaller subsets of solution. Then we construct a rooted decision tree, and finally, we choose the best possible subset (node) at each level to find the best possible solution set.
- 9. GREEDY ALGORITHMS • Greedy is an algorithmic paradigm that builds up a solution piece by piece, always choosing the next piece that offers the most obvious and immediate benefit. So the problems where choosing locally optimal also leads to global solution are best fit for Greedy. • For example consider the Fractional Knapsack Problem. The local optimal strategy is to choose the item that has maximum value vs weight ratio. This strategy also leads to global optimal solution because we allowed to take fractions of an item. • A greedy algorithm is an approach for solving a problem by selecting the best option available at the moment. It doesn't worry whether the current best result will bring the overall optimal result. • The algorithm never reverses the earlier decision even if the choice is wrong. It works in a top-down approach. • This algorithm may not produce the best result for all the problems. It's because it always goes for the local best choice to produce the global best result.
- 11. ADVANTAGES OF GREEDY APPROACH • The algorithm is easier to describe. • This algorithm can perform better than other algorithms (but, not in all cases). • Drawback of Greedy Approach • As mentioned earlier, the greedy algorithm doesn't always produce the optimal solution. This is the major disadvantage of the algorithm
- 12. THANK YOU