E-Journals: usage, value, impact and cost
- 1. E-Journals: usage, value, impact and cost FrenchForum Online Information 2009 Branwen Hide December 2nd, 2009
- 2. Outline Introduction How do researchers find the information resources they need The growing importance of e-journals Implications of e-journal usage Costs associated with publishing journal articles Funding Mechanisms Changes to the current publishing models – implications for costs and funding Summary
- 3. Simplified research life cycle Development of Research Publication and research idea Production distribution (Access and usage)
- 4. How do researchers find the information resources they need Google/Google Scholar are the main sources used to find relevant scholarly content Limited use of library catalogues Few researchers use search and navigation features offered by publishers Searching and downloading of journal articles frequently takes place outside of standard office hours Researchers at research intensive universities tend to have shorter search sessions have a preference for the use of gateways (such as PubMed) Read more highly rated journals (measured by ave. impact factor)
- 5. Searching behaviour of researchers at research intensive universities Bangor 6.4% Swansea 12.7% Strathclyde 21.4% Mean session length (sec) Aberdeen 21.6% CEH 17.0% Rothamsted 15.2% Edinburgh 34.8% Manchester 27.1% Cambridge 35.0% Research rating (Hirsch index) Note: Deep log analysis of ScienceDirect
- 6. The growing importance of e-journals 96% of journal titles in STM*, and 87% of journal titles in AHS** are available in electronic format 2006/2007 UK HEI’s*** spend ~£80m licensing electronic journals 2006/2007 estimated that UK researchers and students downloaded 102m articles *STM – Science, Technology and Medicine **AHS – Arts Humanities and Social Science ***HEI – Higher Education Institute
- 7. E-journal usage by different size institutions in the same disciplines Economics Life Sciences Note: Not all institutions submitted all their research-active staff, so these charts provide only a rough indication of relative size. Deep log analysis of ScienceDirect
- 8. Implications of e-journal usage Those institutes with high page views also produce more journal articles Correlation between the levels of journal usage and the level of library expenditure on electronic journals There is a tentative relationship between e-journal usage and research outcomes in terms of the numbers of: PhD students number of academic papers number of successful grant applications research contracts awarded
- 9. So what does it all cost, and who pays? Activities, costs and funding flows in scholarly communications Only looked at journals – excluded monographs and unpublished data Excluded secondary publishing and aggregation Detailed article allocation function (i.e. per journal type) Did not include R&D returns on research funding Economic implications of alternative scholarly publishing models: Exploring the costs and benefits Included monographs Activities include R&D funding process and research performance Note: The RIN and Houghton models are available for others to use and manipulate
- 10. Scholarly Communications life cycle Research Publication Distribution Access Usage/ Production Consumption • Libraries • Researchers • Funders • ICT • Institutions • Publishers and secondary publishers • Public • Commercial • Government • Researchers providers • Funders • Publishers •Web 2.0 tools and software •Google
- 11. Global Costs of Scholarly Communications 200.0 174.7 180.0 160.0 140.0 115.8 £ billions 120.0 100.0 80.0 60.0 33.9 40.0 16.4 20.0 6.4 2.1 0.0 Research Publishing & Access User search Reading total production Distribution provision and print cost Research Publication & Access Usage & Consumption Production distribution
- 12. UK Costs of Scholarly Communications 10.00 9.00 8.61 8.00 7.00 6.23 6.00 £ Billions 5.00 4.00 3.00 2.00 1.34 1.00 0.43 0.54 0.07 0.00 Research Publishing & Access User search Reading total production Distribution provision and print cost Research Publication & Access Usage & Consumption Production distribution
- 13. UK Publication and Distribution Costs 450.0 424.9 400.0 350.0 300.0 £ Millions 250.0 200.0 150.0 125.1 119.0 100.0 63.7 63.0 54.1 50.0 0.0 Non-cash peer Direct fixed Variable cost Indirect cost Surplus Total cost review cost First copy cost £244.1 Publication Distribution
- 14. UK Access and Usage costs 1600.0 1400.0 1342.3 1200.0 1000.0 £ Million 800.0 600.0 542.2 400.0 200.0 71.9 0.0 Access provision User search and print cost Reading Access Usage & Consumption (library) (researcher)
- 15. How is the Scholarly Communications Process funded?
- 16. Meeting the costs of scholarly communications globally 50.0 45.0 40.6 40.0 35.0 30.0 £ Billions 25.0 20.0 15.0 11.6 10.0 5.0 5.0 1.2 0.5 0.0 HE Libraries HEIs and their Non-HE Libraries, Funders/employers of other funders special libraries and Non HEI researchers Individual subscribers
- 17. UK contribution to the total cost of scholarly communications 450.0 408.5 400.0 350.0 300.0 £ Millions 250.0 200.0 150.0 132.0 117.5 100.0 45.6 56.0 50.0 32.8 8.6 16.0 0.0 academic other (non- author pays academic other academic special Total (non-cash) cash) peer subscriptions subscriptions library access access contribution peer review review and revenues provision provision funding funding
- 18. Changes to the current publishing models Recent technical developments in publishing, library services Researchers are becoming more vocal about their desire to have complete and unhindered access to all research outputs Changes in policy to encourage broad dissemination and access to research outputs enables us to examine the affect of current changes in the scholarly communications landscape by developing scenarios of possible changes, and model their impacts both on costs and funding mechanisms
- 19. Changes to the current publishing models: scenarios 90% of all journal articles are produced and distributed only electronically 90% of all journal articles are funded via author-side payment model (assumes all articles are produced electronically) Researchers are paid for peer-review 2.5% increase in research funding and 1.5% increase in article production over 10 years
- 20. E-only publication: Global costs 200 93 0 0 0 Research Publishing & Access provision User search and Reading Total cost production Distribution print cost -200 -400 -318 £ M illio n s -600 -800 -758 -1,000 -983 -1,200 Research Publication & Access Usage & Consumption Production distribution
- 21. E-only publication: Implications for the UK Publishing and distribution of UK-authored articles Publishers would save ~ £21m and one would assume some of those savings passed on to UK (and overseas) libraries and other subscribers Costs for UK libraries in providing access to global journals and articles cost savings of ~ £23m offset by small rise in user print costs VAT increase ~ £5m
- 22. Summary: e-journal usage, value and impact Google and other web based gateways are the primary source of finding journal articles Large majority of journal articles in all disciplines are available digitally Seems to be a correlation between specificity of search, length of search, expenditure, usage and research outcomes
- 23. Summary: cost and funding of journal article production Publishing, distributing and providing access to scholarly publications are pivotal but are not the only part of the scholarly communications system accounts for only 5% of the overall costs Majority of the cost lies in the time taken to by readers to search, download and read the articles which are overwhelmingly met by the HE sector and not greatly diminished by moving to e-only publications There is scope for cash savings, and improvements in efficiency and effectiveness across the entire system
- 24. Where do we go from here Need for further understanding: about universities’ expenditure and use of e- journals, other information resources and the relationship to research success of the changes taking place and effects on research practice, business models and organizational culture; the issues around moving to electronic-only publication for all subject areas the gaps that affect researchers access information sources the future of scholarly communications over the next ten years.
- 25. Clearer picture of where major costs arise, and how they are funded enables us to: focus attention on key areas where cost efficiencies are most likely to arise analyse the balance of trade between different sectors and different countries.
- 26. References E-journals: their use, value and impact (April 2009) http://www.rin.ac.uk/use-ejournals Activities, costs and funding flows in scholarly communications (May 2008) http://www.rin.ac.uk/costs-funding-flows Economic implications of alternative scholarly publishing models: Exploring the costs and benefits (JISC Jan 2009) http://www.jisc.ac.uk/publications/documents/economicpublishingmodelsfinalreport.aspx
- 27. Branwen Hide Liaison and Partnership Officer Research Information Network Branwen.hide@rin.ac.uk www.rin.ac.uk
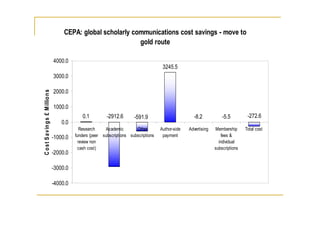
- 28. Summary cost changes forsavings -UKto CEPA: global scholarly communications cost the move gold route 4000.0 3245.5 3000.0 2000.0 C o s t S a v in g s £ M illio n s 1000.0 0.1 -2912.6 -591.9 -8.2 -5.5 -272.6 0.0 Research Academic Other Author-side Advertising Membership Total cost -1000.0 funders (peer subscriptions subscriptions payment fees & review non individual cash cost) subscriptions -2000.0 -3000.0 -4000.0
- 29. Impact of the Gold Route on the UK Costs: Publishing and distribution of UK-authored articles further cost savings to publishers of between £18m (CEPA) and £93m (JISC) assume some of those savings passed on UK (and overseas) research authors and funders Access costs for UK libraries in providing access to global journals and articles further cost savings of between £9m (CEPA) and £11m (JISC) Funding: Access costs for UK libraries of c £120m offset by increases for HEIs and other research institutions of between £213m (CEPA) and £172m (JISC) in publication fees differentials between institutions Transition costs* *The RIN is currently working with JISC to develop a project examining the costs associated with transitioning
- 30. Increases in research funding and article production over 10 years 9 Current funding Difference between scenarios 8 1 .6 7 6 £ Billions 5 1 .0 4 6 .4 3 2 0.5 0.5 3 .7 0.5 0.3 1 1 .9 1 .8 0.2 1 .0 1 .0 0.8 0 Non-cash Direct fix ed First copy Variable cost Indirect cost Surplus Total cost peer rev iew cost cost
- 31. Increases in research funding and article production over 10 years con’t 9.0 Current Funding Difference between scenarios 8.0 1 .63 7 .0 6.0 5.0 £ Billions 4.0 0.82 6.4 3.0 0.53 2.0 3.4 1 .0 1 .9 0.1 7 0.7 0.05 0.03 0.1 0.2 0.03 0.1 0.0 Research Academ ic Other Author-side Adv ertising Mem bership Total cost funders (peer subscriptions subscriptions pay m ent fees & rev iew non indiv idual cash cost) subscriptions