Programming Assignment Help
- 1. For any help regarding Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Assignment Help Visit: https://www.programminghomeworkhelp.com/ , Email : support@programminghomeworkhelp.com or call us at - +1 678 648 4277 programminghomeworkhelp.com
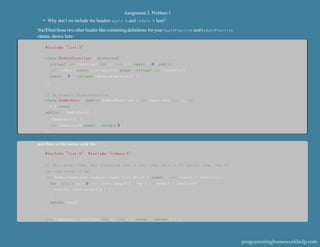
- 2. Problem 1: C++ Linked List Library (cpplist) Your job is now to refactor your C code from the second assignment and produce a much more flexible library with similar functionality– and this time in C++. Download the zipped folder provided in the file cpplist.zip as a basis of your program and take a look at the existing code. • Write your implementation code in .cpp files in the src/ directory; feel free to add more header files as needed in the include/ directory . • GRADER INFO.txt is a file for the grader (don’t edit!) containing PROG: cpplist, LANG: C++ • As before: you should submit a zipped folder using the same directory structure as the provided zip file. We’ve added a section in the Makefile for your convenience: if you type make zip in the same folder as your project, a zip file containing all of your code and the required headers will be constructed in the project directory and you can upload that to the grader. Weare provided a header file describing the interface for the List data structure. Look in the file list.h to find the functionality required of the other functions, which you will write. II Forward declaration of applyIreduce types class ApplyFunction; class ReduceFunction; class List { II ... put whatever private data members you need here II can also add any private member functions you'd like public: List(); -List(); size t length() const; int& value( size t pos ); int value( size t pos ) const; void append( int value ); void deleteAll( int value ); void insertBefore( int value, int before ); void apply( const ApplyFunction &interface ); int reduce( const ReduceFunction &interface ) const; void print() const; }; II ..etc Some questions to ask yourself for understanding: • Why is there a function int& value( size t pos ); as well as a function int value( size t pos ) const;? • What is a forward declaration? programminghomeworkhelp.com
- 3. Assignment 3, Problem 1 • Why don’t we include the headers apply.h and reduce.h here? You’llfind thosetwoother header filescontaining definitions for your ApplyFunction and ReduceFunction classes, shown here: #include "list.h" class ReduceFunction { protected: virtual int function( int x, int y ) const = 0; public: int reduce( const List &list ) const; virtual int identity() const = 0; virtual -ReduceFunction() {} }; II An example ReduceFunction class SumReduce : public ReduceFunction { int function( int x, int y ) const; public: SumReduce() {} -SumReduce() {} int identity() const { return 0; } }; and then in the source code file: #include "list.h" #include "reduce.h" II This works fine, but iterating over a list like this is II fairly slow. See if you can speed it up! int ReduceFunction::reduce( const List &list ) const { int result = identity(); for( size t p = 0; p < list.length(); ++p ) { result = function( result, list.value( p ) ); } return result; } int SumReduce::function( int x, int y ) const { return x + y; programminghomeworkhelp.com
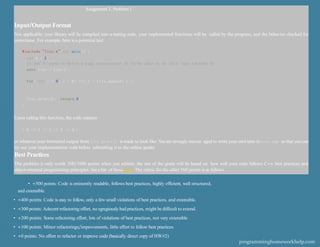
- 4. Assignment 3, Problem 1 Input/Output Format Not applicable; your library will be compiled into a testing suite, your implemented functions will be called by the program, and the behavior checked for correctness. For example, here is a potential test: #include "list.h" int main() { int N = 5; II you'll need to write a copy constructor II to be able to do this (see Lecture 5) auto list = List{}; for( int i = 0; i < N; ++i ) { list.append( i ); } list.print(); return 0; } Upon calling this function, the code outputs { 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 } or whatever your formatted output from list.print() is made to look like. Youare strongly encour aged to write your own tests in test.cpp so that you can try out your implementation code before submitting it to the online grader. Best Practices The problem is only worth 500/1000 points when you submit; the rest of the grade will be based on how well your code follows C++ best practices and object-oriented programming principles. Seea list of those here. The rubric for the other 500 points is as follows. • +500 points: Code is eminently readable, follows best practices, highly efficient, well structured, and extensible. • +400 points: Code is easy to follow, only a few small violations of best practices, and extensible. • +300 points: Adecent refactoring effort, no egregiously bad practices, might bedifficult to extend. • +200 points: Some refactoring effort, lots of violations of best practices, not very extensible • +100 points: Minor refactorings/improvements, little effort to follow best practices. • +0 points: No effort to refactor or improve code (basically direct copy of HW#2) programminghomeworkhelp.com
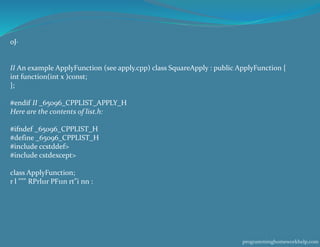
- 5. Look in list .h for a sense of the structure of the solution. The big idea to speed up the reduce/apply functions while also giving users a nice way to iterate over the items in the list is to create an "iterator" type within our class. Users will be able to write code similar to the STL: II Print out every item in the list for(List: :iterator it = list .begin (); it != list .end( ); ++it ){ std ::cout < < *it << "n"; } To speed up our "append" function, the List class will also store a pointer to the very last element in the current list. Directory structure: GRADER_INFO.txt include apply.h o list.h list_node.h o reduce.h Makefile src apply.cpp o list.cpp list_iterator.cpp o list_node.cpp reduce.cpp o test.cpp Here are the contents of apply.h: #ifndef _65096_CPPLIST_APPLY_H #define _65096_CPPLIST_APPLY_H #include "list.h " class ApplyFunction { protected : virtual int function(int x )const public : void apply(List &list )const; virtual -ApplyFunction (){} }; programminghomeworkhelp.com
- 6. 0J· II An example ApplyFunction (see apply.cpp) class SquareApply : public ApplyFunction { int function(int x )const; }; #endif II _65096_CPPLIST_APPLY_H Here are the contents of list.h: #ifndef _65096_CPPLIST_H #define _65096_CPPLIST_H #include ccstddef> #include cstdexcept> class ApplyFunction; r l """ RPrl11r PF11n rt"i nn : programminghomeworkhelp.com
- 7. class List { size_t _length; ListNode *_begin; ListNode *_back; public : II Can use outside as List ::iterator type class iterator { II Making List a friend class means we'll be able to access II the private _node pointer data within the scope of List. friend class List; ListNode *_node; public : iterator(ListNode *theNode ); iterator& operator++ (); int& operator* (); bool operator== (const iterator &rhs ); bool operator!=(const iterator &rhs ); }; II Can use outside as List: :const_iterator type class const_iterator { II Again, this is basically the only situation you should II be using the keyword 'friend' friend class List; ListNode *_node; public : const_iterator (ListNode *theNode ); const_iterator& operator++ (); const int& operator* (); bool operator== (const const_iterator &rhs ); bool operator!=(const const_iterator &rhs ); }; List (); List (const List &list ); List& operator= (const List &list ); -List(); size_t length{)const; int& value (size_t pos ); programminghomeworkhelp.com
- 8. int value (size_t pos )const; bool empty ()const; iterator begin (); const_iterator begin ()const ; iterator back (); const_iterator back ()const ; iterator end (); const_iterator end{)const; iterator find{ iterator s, iterator t, int needle ); void append{ int theValue ); void deleteAll{ int theValue ); void insertBefore (int theValue, int before ); void insert(iterator pos, int theValue ); void apply(const ApplyFunction &interface ); int reduce(const ReduceFunction &interface )const; void print ()const; void clear(); private : ListNode* node{ iterator it ){return it ._node; } ListNode* node{ const_iterator it ){return it ._node; } }; class ListOutOfBounds : public std ::range_error { public : explicit ListOutOfBounds{) : std ::range_error("List index out of bounds" ){} }; #endif II _6S096_CPPLIST_H programminghomeworkhelp.com
- 9. #ifndef _65096_CPPLIST_NODE_H #define _65096_CPPLIST_NODE_H class ListNode { int _value; ListNode *_next; ListNode (const ListNode & )= delete; ListNode& operator= (const ListNode & ) delete; public : ListNode (); ListNode (int theValue ); -ListNode (); int& value (); int value ()const ; ListNode* next (); void insertAfter (ListNode *before ); void setNext(ListNode *nextNode ); static void deleteNext (ListNode *before ); static void deleteSection ( ListNode *before, ListNode *after ); static ListNode* create(int theValue = 0 ); }; #endif II _65096_CPPLIST_NODE_H Here are the contents of reduce.h: #ifndef _65096_CPPLIST_REDUCE_H #define _65096_CPPLIST_REDUCE_H #include "list.h" class ReduceFunction { protected : virtual int function(int x, int y )const 0; public : int reduce(const List &list const; virtual int identity ()const 0; virtual -ReduceFunction (){} }; programminghomeworkhelp.com
- 10. II An example ReduceFunction class SumReduce : public ReduceFunction { int function(int x, int y )const; public : SumReduce (){} -sumReduce (){} int identity ()const {return 0; } }; II Another ReduceFunction class ProductReduce : public ReduceFunction { int function(int x, int y )const; public : ProductReduce (){} -ProductReduce (){} int identity ()const {return 1; } }; #endif II _65096_CPPLIST_REDUCE_H Here is the source code file apply.cpp: #include "list.h" #include "apply.h" void ApplyFunction::apply (List &list )const { for(auto it = list .begin (); it != list.end( ); ++it ){ *it = function (*it ); } } programminghomeworkhelp.com
- 11. Here is the source code file list.cpp: #include "list.h" #include "list_node.h" #include "apply.h" #include "reduce.h" #include <iostream> List: :List() : _length {0}, _begin {nullptr }, _back{ nullptr }{} List ::List(const List &list ) : _length {0}, _begin {nullptr }, _back {nullptr }{ for(auto it = list.begin (); it != list.end( ); ++it ){ append( *it ); } } List& List ::operator= (const List &list ){ if(this != &list ){ clear(); for(auto it = list .begin (); it != list.end( ); ++it ){ append (*it ); } } return *this; } List: :-List(){clear (); } size_t List: :length ()const {return _length; } int& List: :value(size_t pos ){ auto it = begin (); programminghomeworkhelp.com
- 12. for(size_t i = 0; i < pos && it != end( ); ++it, ++i ); if(it == end()){ throw ListOutOfBounds (); } return *it; } int List: :value(size_t pos )const { auto it = begin (); for(size_t i = 0; i < pos && it != end( ); ++it, ++i ); if(it == end()){ throw ListOutOfBounds (); } return *it; } bool List: :empty()const { return _length 0; } List: :iterator List: :begin(){return iterator{_begin }; } List: :const_iterator List: :begin()const {return const_iterator {_begin }; } List ::iterator List: :back(){return iterator {_back }; } List ::const_iterator List: :back()const {return const_iterator {_back }; } List: :iterator List: :end(){return iterator{nullptr }; } List: :const_iterator List: :end()const {return const_iterator {nullptr }; } programminghomeworkhelp.com
- 13. void List ::append (int theValue ){ auto *newNode ListNode: :create(theValue ); if ( empty ()){ newNode->setNext (_back ); _begin = newNode; }else { newNode->insertAfter (_back ); } programminghomeworkhelp.com
- 14. } void List: :deleteAll (int theValue ){ if( !empty () ){ II Delete from the front while(_begin->value ()== theValue && _begin != _back ){ auto *newBegin = _begin->next (); delete _begin; _begin = newBegin; --_length; } auto *p = _begin; if(_begin != _back ){ II Normal deletion from interior of list for(; p->next () != _back; ){ if(p->next ()->value ()== theValue ){ ListNode: :deleteNext(p ); --_length; }else { p = p->next (); } } II Deleting the last item if(_back->value ()== theValue ){ ListNode: :deleteNext (p ); _back = p; --_length; } }else if(_begin->value () programminghomeworkhelp.com
- 15. theValue ){ II Deal with the case where we deleted the whole list _begin = _back = nullptr ; _length = 0; } } } List: :iterator List: :find (iterator s, iterator t, int needle ){ for(auto it = s; it != t; ++it ){ if(*it == needle ){ return it; } } return t; } void List: :insert (iterator pos, int theValue ){ auto *posPtr = node(pos ); auto *newNode = ListNode: :create(theValue ); newNode->insertAfter (posPtr ); ++_length; } programminghomeworkhelp.com
- 16. void List: :insertBefore(int theValue, int before ){ if( !empty () ){ if(_begin->value ()== before ){ auto *newNode = ListNode: :create (theValue ); newNode->setNext (_begin ); _begin = newNode; ++_length; }else { auto *p = _begin; for(; p != _back && p->next ()->value () != before; p p->next ()); if(p != _back && p->next ()- >value ()== before ){ auto *newNode = ListNode: :create (theValue ); newNode->insertAfter (p ); ++_length; } } programminghomeworkhelp.com
- 17. void List: :apply( const ApplyFunction &interface ){ interface.apply(*this ); } int List: :reduce(const ReduceFunction &interface )const { return interface.reduce(*this ); } void List: :print()const { std ::cout << "{"; for(auto it = begin (); it != back (); ++it ){ std ::cout << *it << " -> "; } if( !empty () ){ std ::cout << *back()<< " "; } std ::cout << "}n"; } void List: :clear (){ for(auto *p = _begin; p != nullptr; ){ auto *p_next = p->next (); delete p; p = p_next; } _length = 0; _begin = nullptr; _back = nullptr; } Here is the source code file list_iterator.cpp: #include "list.h" #include "list_node.h" programminghomeworkhelp.com
- 18. List ::iterator::iterator (ListNode *theNode ): _node{theNode }{} List: :iterator& List: :iterator: :operator++ (){ _node = _node->next (); return *this; } int& List ::iterator: :operator* (){return _node->value (); } bool List: :iterator: :operator== (const iterator &rhs ){return _node rhs._node; } bool List: :iterator: :operator!= (const iterator &rhs ){return _node != rhs ._node; } List ::const_iterator: :const_iterator(ListNode *theNode ): _node {theNode }{} List: :const_iterator& List: :const_iterator: :operator++(){ _node = _node->next (); return *this; } const int& List ::const_iterator: :operator*(){return _node->value (); } bool List ::const_iterator: :operator== (const const_iterator &rhs ){return _node rhs._node; } bool List: :const_iterator: :operator!= (const const_iterator &rhs ){return _node != rhs._node; } Here is the source code file list_node.cpp: #include "list_node.h" programminghomeworkhelp.com
- 19. ListNode: :ListNode () : _value {0}, _next {nullptr }{} ListNode: :ListNode (int theValue ): _value{theValue }, _next {nullptr }{} ListNode: :ListNode (){} int& ListNode: :value(){return _value; } int ListNode: :value(){const {return _value; } ListNode* ListNode: :next(){return _next; } void ListNode: :insertAfter(ListNode *before ){ _next = before->next (); before->_next = this; } void ListNode::setNext (ListNode *nextNode ){ _next = nextNode; } programminghomeworkhelp.com
- 20. delete before->next (); before->_next = after; } void ListNode::deleteSection (ListNode *before, ListNode *after ){ auto *deleteFront = before->next (); while(deleteFront != after ){ auto *nextDelete = deleteFront->next (); delete deleteFront; deleteFront = nextDelete; } } ListNode* ListNode: :create(int theValue ){ return new ListNode{theValue }; } Here is the source code file reduce.cpp: #include "list.h" #include "reduce.h" int ReduceFunction ::reduce (const List &list )const { int result = identity (); for(auto it = list.begin (); it != list.end( ); ++it ){ result = function(result, *it ); } return result; } programminghomeworkhelp.com
- 21. int SumReduce: :function (int x, int y )const { return x + y; } int ProductReduce: :function (int x, int y )const { return x * y; } Below is the output using the test data: cpplist: 1: OK [0.004 seconds] OK 2: OK [0.005 seconds] OK 3: OK [0.005 seconds] OK 4: OK [0.009 seconds] OK 5: OK [0.006 seconds] OK 6: OK [0.308 seconds] OK 7: OK [0.053 seconds] OK 8: OK [0.007 seconds] OK 9: OK [0.005 seconds] OK 10: OK [0.742 seconds] OK. programminghomeworkhelp.com

















![int SumReduce: :function (int x, int y )const { return x + y;
}
int ProductReduce: :function (int x, int y )const { return x * y;
}
Below is the output using the test data:
cpplist:
1: OK [0.004 seconds] OK
2: OK [0.005 seconds] OK
3: OK [0.005 seconds] OK
4: OK [0.009 seconds] OK
5: OK [0.006 seconds] OK
6: OK [0.308 seconds] OK
7: OK [0.053 seconds] OK
8: OK [0.007 seconds] OK
9: OK [0.005 seconds] OK
10: OK [0.742 seconds] OK.
programminghomeworkhelp.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminghomeworkhelp-211118075415/85/Programming-Assignment-Help-21-320.jpg)