Evaluating the Use of Clustering for Automatically Organising Digital Library Collections
- 1. Evaluating the Use of Clustering for Automatically Organising Digital Library Collections Mark M. Hall, Mark Stevenson, Paul D. Clough TPDL 2012, Cyprus, 24-27 September 2012
- 2. Opening Up Digital Cultural Heritage http://www.flickr.com/photos/brokenthoughts/122096903/ Carl Collins http://www.flickr.com/photos/carlcollins/199792939/ http://www.flickr.com/photos/usnationalarchives/4069633668/ TPDL 2012, Cyprus, 24-27 September 2012
- 3. Exploring Collections • Exploring / Browsing as an alternative to Search (where applicable) • Requires some kind of structuring of the data • Manual structuring ideal – Expensive to generate – Integration of collections problematic • Alternative: Automatic structuring via clustering TPDL 2012, Cyprus, 24-27 September 2012
- 4. Test Collection • 28133 photographs provided by the University of St Andrews Library – 85% pre 1940 Ottery St Mary – 89% black and white Church – Majority UK – Title and description tend to be short TPDL 2012, Cyprus, 24-27 September 2012
- 5. Tested Clustering Strategies • Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) – 300 & 900 topics – With and without Pairwise Mutual Information (PMI) filtering • K-Means – 900 clusters – TFIDF vectors & LDA topic vectors • OPTICS – 900 clusters – TFIDF vectors & LDA topic vectors TPDL 2012, Cyprus, 23-27 September 2012
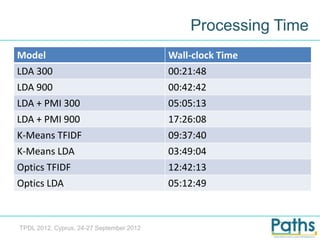
- 6. Processing Time Model Wall-clock Time LDA 300 00:21:48 LDA 900 00:42:42 LDA + PMI 300 05:05:13 LDA + PMI 900 17:26:08 K-Means TFIDF 09:37:40 K-Means LDA 03:49:04 Optics TFIDF 12:42:13 Optics LDA 05:12:49 TPDL 2012, Cyprus, 24-27 September 2012
- 7. Evaluation Metrics • Cluster cohesion – Items in a cluster should be similar to each other – Items in a cluster should be different from items in other clusters • How to test this? – “Intruder” test – If you insert an intruder into a cluster, can people find it TPDL 2012, Cyprus, 24-27 September 2012
- 8. Intruder Test 1. Randomly select one topic 2. Randomly select four items from the topic 3. Randomly select a second topic – the “intruder” topic 4. Randomly select one item from the second topic – the “intruder” item 5. Scramble the five items and let the user choose which one is the “intruder” TPDL 2012, Cyprus, 24-27 September 2012
- 9. Cluster Cohesion – Cohesive TPDL 2012, Cyprus, 24-27 September 2012
- 10. Cluster Cohesion – Not Cohesive TPDL 2012, Cyprus, 24-27 September 2012
- 11. Evaluation Metrics • Cohesive – “Intruder” is chosen significantly more frequently than by chance – Choice distribution is significantly different from the uniform distribution • Borderline cohesive – Two out of five items make up > 95% of the answers – “Intruder” is one of those two TPDL 2012, Cyprus, 24-27 September 2012
- 12. Evaluation Bounds • Upper bound – Manual annotation • 936 topics • Lower bound – 3 cohesive topics – <5% likelihood of seeing that number of cohesive topics by chance • Control data – 10 “really, totally, completely obvious” intruders used to filter participants who randomly select answers TPDL 2012, Cyprus, 24-27 September 2012
- 13. Experiment • Crowd-sourced using staff & students at Sheffield University – 700 participants • 9 clustering strategies – 30 units per strategy – total of 270 units • Results – 8840 ratings – 21 – 30 ratings per unit (median 27 ratings) TPDL 2012, Cyprus, 24-27 September 2012
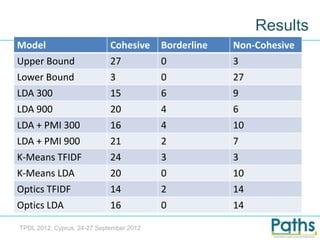
- 14. Results Model Cohesive Borderline Non-Cohesive Upper Bound 27 0 3 Lower Bound 3 0 27 LDA 300 15 6 9 LDA 900 20 4 6 LDA + PMI 300 16 4 10 LDA + PMI 900 21 2 7 K-Means TFIDF 24 3 3 K-Means LDA 20 0 10 Optics TFIDF 14 2 14 Optics LDA 16 0 14 TPDL 2012, Cyprus, 24-27 September 2012
- 15. Conclusions • K-means almost as good as the human classification • LDA is very fast and approximately two thirds of the topics are acceptably cohesive • Future work: – Make it hierarchical – Create hybrid algorithms TPDL 2012, Cyprus, 24-27 September 2012
- 16. Thank you for listening Find out more about the project: http://www.paths-project.eu m.mhall@sheffield.ac.uk The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Community's Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement no 270082. We acknowledge the contribution of all project partners involved in PATHS (see: http://www.paths-project.eu).