exceptionhandlinginjava-140224181412-phpapp02.pptx
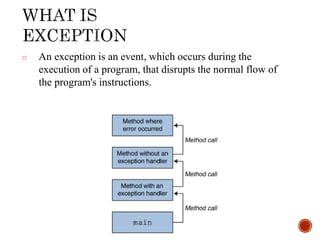
- 2. □ An exception is an event, which occurs during the execution of a program, that disrupts the normal flow of the program's instructions.
- 3. try { //do something } catch (ExceptionType name) { } catch (ExceptionType name) { } finally { //clean up }
- 4. □ Separating Error-Handling Code from "Regular" Code □ Propagating Errors Up the Call Stack □ Grouping and Differentiating Error Types
- 6. □ Part of the method signature □ Compile type checking □ Requires the programmer to handle the exception or declare the method as throwing exception □ Unique to java □ e.g. FileNotFoundException
- 7. □ No need to declare the exception in the method’s signature □ No compile time checking □ Usually indicate a programming error □ e.g. NullPointerException
- 8. □ Indicate error in the underlying JVM □ Error are external to the application □ Application does not usually have to deal with these class of Exceptions □ e.g. OutOfMemoryError
- 9. □ Exceptions indicate a broken contract ■ Precondition (e.g. file is open for read) ■ Postcondition (e.g. read a character from file) □ Your method encounters an abnormal condition that it can't handle □ If your method is unable to fulfill its contract, throw either a checked or unchecked exception.
- 10. □ Exceptions v/s Errors ■ Errors are for JVM ■ Exceptions for rest of us □ Checked v/s Unchecked exceptions ■ Can caller recover from this error? ■ Yes: checked ■ No: unchecked
- 11. 1. When you can handle the exception 2. When you need to throw a different type of exception 3. Refer to 1 & 2
- 12. □ To achieve Flow control using exception try { while (true) { increaseCount(); } } catch (MaximumCountReachedException ex) { } //Continue execution } public void increaseCount() throws MaximumCountReachedException { if (count >= 5000) throw new MaximumCountReachedException(); }
- 13. □ What went wrong? □ Where did it go wrong? □ Why did it go wrong? □ If your exception does not provide answers to all these questions, you are doing something wrong!
- 14. □ Exceptions are expensive for the JVM □ Creating stack traces requires resources and CPU □ the Java VM requires more efforts to handle a thrown exception than a normal method
- 15. □ Log and Throw □ Throwing Generic Exception □ Catching Generic Exception □ Destructive Wrapping □ Log and Return Null □ Catch and Ignore (a.k.a. Head in the Sand) □ Throw from Within Finally □ Multi-Line Log Messages □ Unsupported Operation Returning Null
- 16. □ Log the error and throw the same exception again □ Messy log file □ Achieves nothing
- 17. □ The caller does not know the nature of error – hinders error handling
- 18. □ We are masking programming errors
- 19. public SomeInterface buildInstance(String className) { SomeInterface impl = null; try { Class clazz = Class.forName(className); impl = (SomeInterface)clazz.newInstance(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("Error creating class: " + className); } return impl; }
- 20. catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { throw new MyServiceException("Blah: " + e.getMessage()); }
- 21. catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { LOG.error("Blah", e); return null; }
- 22. catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { }
- 23. try { blah(); } finally { cleanUp(); }
- 24. ANTI PATTERNS - MULTI-LINE LOG MESSAGES LOG.debug("Using cache policy A"); LOG.debug("Using retry policy B");
- 25. public String foo() { // Not supported in this implementation. return null; } □ Throw UnsupportedOperationException
- 26. □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ Throw checked exception when caller can recover from error Throw runtime exception when the caller cannot recover Throw runtime exception for programming error Throw early, catch late Use NestedException Don’t catch an exception if you cant do any thing about it. Log exception only once, and at the latest possible time Default Error Page in presentation layer for all Runtime Exceptions
- 27. try{ ..some code that throws XXXException }catch(XXXException ex){ throw new RuntimeException(ex); }
- 28. □ Log all internal states □ Log all parameters to the method that failed □ Log all data required to trace the error □ Ensure log statements don’t cause NPE*
- 29. □ Define a hierarchy of exceptions. □ Lower level module throws lower level exceptions, higher level module encapsulate lower level exceptions □ Define which exceptions will cause transaction to rollback
- 30. Exceptions and Transactions □ @ApplicationException(rollback=true) public class FooException extends Exception ...
- 31. Best practices in EJB exception handling http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/library/j-ejbexcept.html Beware the dangers of generic Exceptions http://www.javaworld.com/javaworld/jw-10-2003/jw-1003- generics.html Exception Handling in Web Applications http://weblogs.java.net/blog/crazybob/archive/2004/02/exception_han dl.html Designing with Exceptions http://www.artima.com/designtechniques/desexceptP.html Build a better exception-handling framework http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/java/library/j-ejb01283.html
- 32. JAVA EXCEPTIONS http://www.javaolympus.com/J2SE/Exceptions/JavaExceptions.jsp Exception-Handling Antipatterns http://today.java.net/pub/a/today/2006/04/06/exception-handling-antipatterns.html Three Rules for Effective Exception Handling http://today.java.net/pub/a/today/2003/12/04/exceptions.html 13 Exceptional Exception Handling Techniques http://www.manageability.org/blog/stuff/exceptional-exception-handling-techniques Best Practices for Exception Handling http://www.onjava.com/pub/a/onjava/2003/11/19/exceptions.html Lesson: Exceptions http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/essential/exceptions/index.html