food poisoning/ food poisoning in microbiology.pptx
- 1. Prepared by Arpita Chandra DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
- 2. CONTENT Introduction Types Causative agents Fungal intoxication Chemical foodborne intoxication Recent Outbreaks Lab diagnosis Prevention References
- 3. INTRODUCTION Food poisoning is an acute illness, usually of sudden onset, brought about by eating contaminated or poisonous food. Bacterial food poisoning is restricted to acute gastroenteritis due to the presence of bacteria or their toxins in food. Symptoms- abdominal pain, diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting and fever.
- 4. CAUSATIVE AGENT OF FOOD POISONING Bacterial Viral Parasite Fungal Chemicals
- 5. TYPES Types Ingested by Incubatio n period Causative agent Infective Multiplication of bacteria 8 to 24 hrs. Non typhoidal type occurs in vivo when infective Salmonella doses of microorganisms are V. ingested with food. parahaemolyticus C. jejuni Toxic type Ingestion of food with 1 to 6 hrs. Staph. aureus preformed bacterial toxin. B. Cereus (emetic Incubation period is very type) short. Cl. botulinum Infective- Bacteria ingested with food 6 to 12 hrs. Cl. perfringens toxic type release the toxin in the gut. B. cereus (diarrhoeal type)
- 8. FUNGAL INTOXICATIONS Caused by consumption of metabolites produced by fungi, when growing in food. These metabolites are called mycotoxins. Aflatoxicosis is caused by aflatoxins produced by the fungi, e.g. Aspergillus flavus. When consumed in large doses lethal in causing acute hemorrhagic syndromes.
- 10. CAUSATIVE AGENT AND THEIR SOURCE OF INFECTION Causative agent Source of infection 1. Non- typhoidal Salmonella Milk, eggs, poultry meat 2. Vibrio parahaemolyticus Seafood 3. Campylobacter jejuni Raw milk, poultry, contaminated water 4. Staphylococcus aureus Milk, milk products, cream, meat 5. Bacillus cereus Fried rice from Chinese restaurants, vegetables, meat cereals 6. Clostridium botulinum Canned food 7. Clostridium perfringens Meat, poultry
- 11. CHEMICAL FOODBORNE INTOXICATION This is a type of food borne intoxication arising from consumption of food containing poisonous chemicals. Chemical food borne intoxication involve the following substances: Detection of Chemical toxins in food Biosensor, Colorimetric chemosensors, fluorescent- based sensors
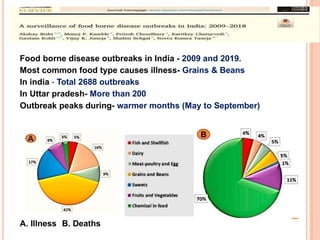
- 12. Food borne disease outbreaks in India - 2009 and 2019. Most common food type causes illness- Grains & Beans In india - Total 2688 outbreaks In Uttar pradesh- More than 200 Outbreak peaks during- warmer months (May to September) A. Illness B. Deaths A B
- 13. RECENT OUTBREAKS IN INDIA 30 OCT 2023 MAY 2023
- 15. LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS Specimen Food Vomitus Faeces blood Demonstration of toxin Toxin may be demonstrated in specimen by toxin-antitoxin neutralization test in mice Electron microscopy Direct microscopy Gram stain Culture Blood agar MacConkey agar Molecular diagnosis PCR
- 17. REFERENC ES Essential of Med. Microbiology- Apurba S. Sastry Bailey & Scott's Diagnostic Microbiology Pictures sources- Wikipedia