Front & elliot axle
- 1. SRI KRISHNA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING Session: AXLE SYSTEMS 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 1 MODULE 2
- 2. SESSION OBJECTIVES 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 2 On the completion of this session, the students might be able to understand, Construction & Function of Axle systems in Vehicle
- 3. Topics Axle Type of Axle in vehicle Rear Axle Front Axle Stub Axle 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 3
- 4. AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 4 AXLE: Central shaft for rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles –axle may fixed with wheels Bearings & Bushings are provided at the mounting points where the axle is supported. Those are sits inside the central hole in the wheel to allow the wheel or gear to rotate around the axle
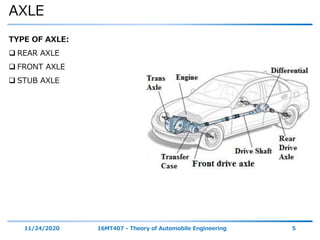
- 5. AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 5 TYPE OF AXLE: REAR AXLE FRONT AXLE STUB AXLE
- 6. REAR AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 6 Rear Axle : Mounted at the rear of the car Axle shafts are engaged to the side gears of the differential and drive rear wheel Axle shafts are positioned in and protected by a rear axle housing. The housing completely encloses the differential & the rear axles Protecting them external affecting factors – Dust, water, and damages
- 7. REAR AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 7 Rear Axle : Function Act as a beam to support the weight of the vehicle Act as an axis of the vehicle Transmits the power to the wheel Act as a housing & Support for the final drive, differential and axle shaft
- 8. REAR AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 8 Rear Axle Drive : Parts of the drive line units. Helps to absorb the drive line torque & Braking Whenever brake applied suddenly in vehicle, the shock to the transmission is cushioned by propeller shaft which twist slightly and then untwist.
- 9. REAR AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 9 Rear Axle Drive : Types Hotchkiss Drive Torque tube drive
- 10. REAR AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 10 Rear Axle Drive : HotchKiss Drive Simplest type of rear axle drive. Mostly used in cars and trucks It used an open propeller shaft with two universal joints and a slip joint to connect Gear box & Rear axle. Universal joint allow it to operate at different angles Different drive length are achieved by slip joint.
- 11. REAR AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 11 Rear Axle Drive : HotchKiss Drive It can with stand the below loads Weight of the vehicle. Driving Thrust. Braking Thrust. Torque Reaction.
- 12. REAR AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 12 Rear Axle Drive : Torque Tube Oldest Method of rear axle drive. Solid propeller shaft is completely enclosed in large diameter hollow tube called torque tube. One Universal joint at transmission end of the propeller shaft. Which allows the complete assembly to Move up & Down to change length It is achieved by a slip joint
- 13. REAR AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 13 Rear Axle Drive : Torque Tube Braking & Acceleration load can absorb by Torque tube It has only one universal joint Disadvantage : During sudden braking Front end of propeller shaft is bend.
- 14. TYPE OF REAR AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 14 Rear Axle : Differs from Front Axle No joints at its outer ends. Its Housing is Banjo Type or Split Type. Front Axle Rear Axle Types of Rear Axle: Semi Floating Axle Full Floating Axle Three Quarter floating Axle
- 15. TYPE OF REAR AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 15 Rear Axle :Split Casing Axle casing is made in two halves and then bolted together for assembly. Disadvantage : If any fault means, whole of the real axle to be removed as a unit and then disassembled. Now obsolete
- 16. TYPE OF REAR AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 16 Rear Axle :Banjo Casing One piece type, shaped like banjo Complete differential unit is carried in a separate carrier which is bolted to the axle casing. Banjo comes with two half shafts at sides. Half shafts can be directly taken out from the sides and of differential assembly removed by opening by bolts.
- 17. TYPE OF REAR AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 17 Semi Floating Rear Axle: Axle shafts taken care the complete load act on the vehicle. Bearing of the wheel hub are fitted on the half shafts inside the axle tube. The wheels are fitted at the two ends of the axle by means of a key and lock nut The whole load of the vehicle is first transmitted to suspension springs, then to axle tube, rear axle, Wheel and then ground.
- 18. TYPE OF REAR AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 18 Semi Floating Rear Axle: Disadvantage Not bear the driving torque Not to take the vehicle load Not to take cornering load, when the vehicle is turning Axle breakage, leads to vehicle fall on one side. Not suits for SUV & Pick up trucks Three wheelers, Small carrier vehicles used this type.
- 19. TYPE OF REAR AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 19 Full Floating Rear Axle: Wheel hub is fixed on the axle tube or case with the help of two roller bearings The axle shaft is introduced inside the axle tube The end of the axle shaft is bolted to the wheel hub. The complete load act on the vehicle taken by the axle tube Without removing the wheel hub, the axle shaft can be removed by removing the bolts.
- 20. TYPE OF REAR AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 20 Three quarter Floating Rear Axle: Load is partly borne by the axle tube Remaining load is borne by axle itself The axle is fitted inside the axle tube One end of bearing is fitted on the wheel Hub Where as the other on the axle tube Takes care of Driving & Cornering Torque Small & Medium vehicles are used
- 21. FRONT AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 21 Front Axle: Function Takes Weight of the front vehicle Provides steering Action Spring transmits cushions effects to the vehicle Controls the ride through shock absorber. It transmits power to the front wheels in case of Front/Four wheel drive. It carries both Hub & Wheels
- 22. FRONT AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 22 Front Axle: Construction Made by drop forging steel having 0.4% carbon or 1-3% Nickel steel Front portion of beam formed by I cross section It’s support bending load due to load of vehicle As well as torque by braking the wheels Axle Eye beam portion has Circular/Elliptical cross section Axle beam Eye
- 23. FRONT AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 23 Front Axle: Construction Downward Sweep front portion makes the chassis height low At the end of the axle, Steering Spindle and steering Knuckle assemblies are pinned to permit the wheel to be turned by steering gear. Steering Knuckle supports the steering components & Suspension steering Knuckle
- 24. FRONT AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 24 Front Axle: Components Axle Beam Stub Axle Swivel Pin Track Rod
- 25. FRONT AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 25 Front Axle: Axle Beam Major part made by good carbon steel & Low Nickel Steel I or H type center portion is used in Axle & it’s made by drop forging process With the help of suspension spring transmit the vehicle weight to front wheel Axle are hinged with stub axle
- 26. FRONT AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 26 Front Axle: Axle Beam Spring pads reduces the swing or sway of the vehicle, while it turns.
- 27. FRONT AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 27 Front Axle: Swivel Pin Made by good quality cases hardened steel Secure the stub axle with axle beam
- 28. FRONT AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 28 Front Axle: Track Rod The two stub axle arms of the front axle are connected with ends of a track rod through Knuckle or Ball joints known as track rod ends Ball joint - Unit
- 29. FRONT AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 29 Front Axle: Track Rod Lengthening the rod – Toe – in is increase Shortening the rod – Toe – in is decrease
- 30. FRONT AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 30 Front Axle: Pull & Push Rod or Drag Link Also called Drag Link. Connected between the steering arm of the front axle and drop arm of the steering assemble It has tubular cross section Spring loaded ball joint provided at each end One or Two end of steering arm of the stub axle is connected with one end of drag link & other one is connected with steering drop arm.
- 31. FRONT AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 31 So How the power delivered in Front Wheel drive? FWD – Front Axle : Power is delivered through a drive shaft which is attached via constant velocity joint. Allows the wheels to articulate when steering, without affecting the delivery of power.
- 32. FRONT AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 32 So How the power delivered in Front Wheel drive? FWD – Front Axle : Front wheel drive cars uses the interesting phenomenon called Torque steering. Unequal Type drive shaft results in unequal drive axle shaft angle to the drive wheels During acceleration this will results in a steering of the vehicle. This phenomena is called torque steer.
- 33. FRONT AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 33 So How the power delivered in Front Wheel drive? FWD – Front Axle : Front wheel drive cars uses the interesting phenomenon called Torque steering. By using the intermediate shaft both the drive axle’s are the same angle & the torque steer effect is reduced.
- 34. FRONT AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 34 So How the power delivered in Front Wheel drive? FWD – Front Axle : CV Joints Commonly seen in Four wheel drive & All wheel drive vehicle. Mounted in each end of drive shaft for transmitting power to rotating wheels. Whenever the vehicle goes over the Bumps, It will allow the drive shaft Move up & Down. Rzeppa CV Joint
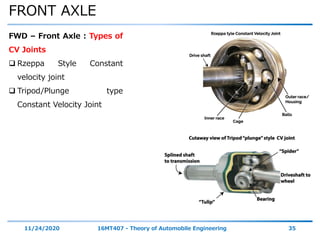
- 35. FRONT AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 35 FWD – Front Axle : Types of CV Joints Rzeppa Style Constant velocity joint Tripod/Plunge type Constant Velocity Joint
- 36. FRONT AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 36 FWD – Front Axle : Types of CV Joints Rzeppa Style CV Joint: It is used on the wheel hub side of the drive shaft. Also called outer joint. The Rzeppa CV Joint allows a much greater range of motion than a typical U – Joint or a Tripod Joint.
- 37. FRONT AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 37 FWD – Front Axle : Types of CV Joints Tripod or Plunge Style CV: Also called tulip. Drive shaft connects three legged spider end with bearings. Torque transfers from the transmission to the tulip & then to the bearing and spider Mainly used on the transmission side of the drive shaft.
- 38. FRONT AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 38 FWD – Front Axle : Types of CV Joints Tripod or Plunge Style CV: It’s Designed to allow the drive shaft to move up & down, as well as in & out to accommodate the elliptical arc of the drive shaft as the wheel travel over the bumps.
- 39. LIVE AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 39 LIVE AXLE: FWD Modern front wheel drive cars typically combine the transmission and front axle into a single unit called transaxle. The drive axle is a split axle with differential and universal joints between the two half axle. Half axle connects to the wheel by using Constant velocity joint. It’s give free motion to wheel during vehicle motion & turning
- 40. LIVE AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 40 LIVE AXLE: RWD Engine turns a drive shaft which transmits rotational force to a drive axle at the rear of the vehicle. Modern rear wheel drive vehicle uses a split axle with a differential. One half axle connects the differential with left rear wheel Similarly a second half - shaft does the same.
- 41. DEAD AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 41 Dead Axle: Lazy Axle. Axle do not rotate. Also a not a part of drive train. Rear axle of front wheel drive & Front axle of rear wheel drive called as Dead Axle. It helps the trucks & Trailers for load bearing purpose. Pusher axle in rear wheel drive – Located in front of drive axle. Tag axle in front wheel drive – Located behind the drive axle.
- 42. STUB AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 42 Stub Axle: Stub Axle are connected to front axle by King Pins. Front wheels are mounted on stub axle arrangement for steering King pins is fitted in the front axle beam eye King pin is located & locked there by a taper cotter pin.
- 43. STUB AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 43 Stub Axle: Types Elliot Type Reversed Elliot Lamoine Reversed Lamoine
- 44. STUB AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 44 Stub Axle: Elliot Type Attached to the front axle by placing it in the Yoke end with a king pin and cotter pin to point together.
- 45. STUB AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 45 Stub Axle: Reversed Elliot Type In reverse Elliot type stub axle the arrangement is reversed It is commonly used in all automobiles like trucks
- 46. STUB AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 46 Stub Axle: Lamoine Type Instead of Yoke type hinge a L – Shaped spindle is used Commonly can seen in tractors
- 47. STUB AXLE 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 47 Stub Axle: Lamoine Type It is a Reversed position of Lamoine type But Not followed in now a days
- 48. 11/24/2020 16MT407 - Theory of Automobile Engineering 48 END