Fundamentals of Light and Matter
- 1. Sciencey Stuff Fundamentals: Light and Matter Dr. Johnson
- 2. What is matter? * Not to be confused with Whatsamatta – the university Bullwinkle attended
- 3. Matter is the “stuff” that makes up our “things”
- 4. The nucleus of an atom is composed of protons and neutrons (nucleons) Nucleons are ‘Baryonic Matter’ which means they are composed of smaller things called quarks
- 5. An atom will have a certain number of protons and neutrons (usually close to the same number) The number of protons tells you which element you have
- 6. Atoms with the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons are called ISOTOPES Isotopes will have different masses and nuclear properties Some isotopes are more common in nature
- 7. Atoms also have electrons (usually) Electrons have a negative charge & protons have a positive charge Neutrons have no charge When you have the same number of protons and neutrons the atom has no net charge, it is neutral Otherwise, the atom a positive or negative charge
- 8. Atoms share electrons to form molecules This is chemistry! *we won’t talk much about chemistry Water Vinegar
- 9. Like Legos, atoms and molecules join together to form bigger and bigger compounds
- 10. They eventually form things like Rocks & Chairs
- 11. What distinguishes matter from energy? It has: Occupies Volume
- 12. There are also other (non-baryonic) kinds of matter including bosons and leptons Notice that electrons are leptons This means they are point particles not made up of quarks
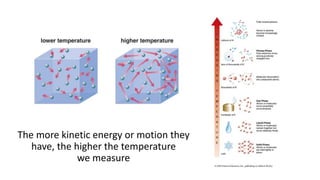
- 13. There are four states of matter Can you name them? Their state depends on how much kinetic energy they have •Solid •Liquid •Gas •Plasma
- 14. The more kinetic energy or motion they have, the higher the temperature we measure
- 15. What is energy? Nucleons are ‘Baryonic Matter’ which means they are composed of smaller things called quarks •Kinetic (motion) •Potential •Radiative
- 16. Kinetic Energy The energy of motion Mass and speed are important!
- 17. Potential Energy The energy you have due to your location (in a gravitational field) or which you may have stored up (chemical) Mass and position are important!
- 18. Radiative Energy Electromagnetic Energy (light) Atoms have set energy levels where electrons can live If atoms absorb the right energy in a packet of light (photon) an electron can move to a higher more energetic level, and when and electron gives up energy it drops down to a lower energy level
- 19. Energy and Matter ‘can’ transform! In the right conditions, such as at the dense core of a star with very high temperatures, it can be a 2-way street E = mc2 Thanks, Einstein!
- 20. The Law of Conservation of Energy In a closed system (like the Universe) energy or matter cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed
- 23. Nuclear Energy Nuclear Fission: Heavy nuclei are unstable, and over some period of time they will decay into lighter elements and emit radiation Nuclear Fusion: Light nuclei in hot/dense conditions, like the core of a star may move fast enough to bind together with the Strong Force and form a heavier element
- 24. Light (electromagnetic energy) Light can be considered as a particle (photo) and a wave Light is the propagation of electric and magnetic fields The distance from one peak to the next is called a wavelength
- 26. Understanding light allows astronomers to be detectives and from a huge distance tell: *But that’s another lecture for another day because I fear we are out of time… Don’t get me started on time, that would take at least several lectures…. • A star’s surface temperature by peak wavelength (color) • A star’s chemical composition by spectral analysis • A star’s radial velocity from Doppler shifts
- 27. May the F=ma be with you!