Gas Chromatography
- 1. SND COLLEGE OF PHARMACY,BABHULGAON FINAL YEAR B.PHARMACY.
- 3. What is Gas Chromatography? • It is also known as… – Gas-Liquid Chromatography (GLC)
- 4. Sample to be separated is converted into vapour And mixed with gaseous M.PComponent more soluble in the S.P → travels slower Component less soluble in the S.P → travels faster Components are separated according to their Partition Co-efficient Criteria for compounds to be analyzed by G.C 1.VOLATILITY: 2.THERMOSTABILITY:
- 5. What is Gas Chromatography? • The father of modern gas chromatography is Nobel Prize winner John Porter Martin, who also developed the first liquid-gas chromatograph. (1950)
- 7. How a Gas Chromatography Machine Works – First, a vaporized sample is injected onto the chromatographic column. – Second, the sample moves through the column through the flow of inert gas. – Third, the components are recorded as a sequence of peaks as they leave the column.
- 8. Chromatographic Separation – Deals with both the stationary phase and the mobile phase. • Mobile – inert gas used as carrier. • Stationary – liquid coated on a solid or a solid within a column.
- 9. Chromatographic Separation • Chromatographic Separation – In the mobile phase, components of the sample are uniquely drawn to the stationary phase and thus, enter this phase at different times. – The parts of the sample are separated within the column. – Compounds used at the stationary phase reach the detector at unique times and produce a series of peaks along a time sequence.
- 10. Chromatographic Separation (continued) – The peaks can then be read and analyzed by a forensic scientist to determine the exact components of the mixture. – Retention time is determined by each component reaching the detector at a characteristic time.
- 11. Chromatographic Analysis –The number of components in a sample is determined by the number of peaks. –The amount of a given component in a sample is determined by the area under the peaks. –The identity of components can be determined by the given retention times.
- 12. Peaks and Data
- 19. PRACTICAL REQUIREMENTS • Carrier gas • Flow regulators & Flow meters • Injection devices • Columns • Temperature control devices • Detectors • Recorders & Integrators
- 20. CARRIER GAS » Hydrogen better thermal conductivity disadvantage: it reacts with unsaturated compounds & inflammable » Helium excellent thermal conductivity it is expensive » Nitrogen reduced sensitivity it is inexpensive
- 21. Requirements of a carrier gas Inertness Suitable for the detector High purity Easily available Cheap Should not cause the risk of fire Should give best column performance
- 22. Flow regulators & Flow meters deliver the gas with uniform pressure/flow rate flow meters:- Rota meter & Soap bubble flow meter Rota meter placed before column inlet it has a glass tube with a float held on to a spring. the level of the float is determined by the flow rate of carrier gas
- 24. Soap Bubble Meter ◊ Similar to Rota meter & instead of a float, soap bubble formed indicates the flow rate
- 25. Injection Devices Gases can be introduced into the column by valve devices liquids can be injected through loop or septum devices
- 26. COLUMNS • Important part of GC • Made up of glass or stainless steel • Glass column- inert , highly fragile COLUMNS can be classified Depending on its use 1. Analytical column 1-1.5 meters length & 3-6 mm d.m 2. Preparative column 3-6 meters length, 6-9mm d.m
- 27. Depending on its nature 1.Packed column: columns are available in a packed manner S.P for GLC: polyethylene glycol, esters, amides, hydrocarbons, polysiloxanes… 2.Open tubular or Capillary column or Golay column Long capillary tubing 30-90 M in length Uniform & narrow d.m of 0.025 - 0.075 cm Made up of stainless steel & form of a coil Disadvantage: more sample cannot loaded
- 28. 3.SCOT columns (Support coated open tubular column Improved version of Golay / Capillary columns, have small sample capacity Made by depositing a micron size porous layer of supporting material on the inner wall of the capillary column Then coated with a thin film of liquid phase
- 32. Equilibration of the column Before introduction of the sample Column is attached to instrument & desired flow rate by flow regulators Set desired temp. Conditioning is achieved by passing carrier gas for 24 hours
- 33. Temperature Control Devices Preheaters: convert sample into its vapour form, present along with injecting devices Thermostatically controlled oven: temperature maintenance in a column is highly essential for efficient separation. Two types of operations Isothermal programming:- Linear programming:- this method is efficient for separation of complex mixtures
- 34. Temperature Control • Isothermal • Gradient 240 200 160 120 80 40 0 0 10 20 50 6030 40 Time (min) Temp(degC) Instrumentation - Oven
- 35. DETECTORS Heart of the apparatus The requirements of an ideal detector are- Applicability to wide range of samples Rapidity High sensitivity Linearity Response should be unaffected by temperature, flow rate… Non destructive Simple & inexpensive
- 36. Measures the changes of thermal conductivity due to the sample (g). Sample can be recovered. 1.Thermal Conductivity Detector (Katharometer, Hot Wire Detector)
- 37. Thermal Conductivity Basics When the carrier gas is contaminated by sample , the cooling effect of the gas changes. The difference in cooling is used to generate the detector signal. The TCD is a nondestructive, concentration sensing detector. A heated filament is cooled by the flow of carrier gas. Flow Flow
- 38. When a separated compound elutes from the column , the thermal conductivity of the mixture of carrier gas and compound gas is lowered. The filament in the sample column becomes hotter than the control column. The imbalance between control and sample filament temperature is measured by a simple gadget and a signal is recorded Thermal Conductivity Detector
- 39. □ Measures heat loss from a hot filament– e filament heated to const T • when only carrier gas flows heat loss to metal block is constant, filament T remains constant. • when an analyte species flows past the filament generally thermal conductivity goes down, T of filament will rise. (resistance of the filament will rise).
- 41. Relative Thermal Conductivity Compound Relative Thermal Conductivity Carbon Tetrachloride 0.05 Benzene 0.11 Hexane 0.12 Argon 0.12 Methanol 0.13 Nitrogen 0.17 Helium 1.00 Hydrogen 1.28
- 42. Advantages of Katharometer Linearity is good Applicable to most compounds Non destructive Simple & inexpensive Disadvantages Low sensitivity Affected by fluctuations in temperature and flow rate Biological samples cannot be analyzed
- 43. Flame Ionization Detector Destructive detector The effluent from the column is mixed with H & air, and ignited. Organic compounds burning in the flame produce ions and electrons, which can conduct electricity through the flame. A large electrical potential is applied at the burner tip The ions collected on collector or electrode and were recorded on recorder due to electric current.
- 44. FIDs are mass sensitive rather than conc. sensitive ADVANTAGES: • µg quantities of the solute can be detected • Stable • Responds to most of the organic compounds • Linearity is excellent • DA: destroy the sample
- 45. FID
- 47. Argon ionization detector Depends on the excitation of argon atoms to a metastable state, by using radioactive energy. Argon→ irradiation Argon + e- →collision Metastable Argon→ collision of sub. → Ionization →↑Current ADVANTAGES 1.Responds to organic compounds 2.High sensitivity DISADVANTAGES 1.Response is not absolute 2.Linearity is poor 3. Sensitivity is affected by water
- 48. ELECTRON CAPTURE DETECTOR The detector consists of a cavity that contains two electrodes and a radiation source that emits - radiation (e.g.63Ni, 3H) The collision between electrons and the carrier gas (methane plus an inert gas) produces a plasma containing electrons and positive ions.
- 49. • If a compound is present that contains electronegative atoms, those electrons are captured and negative ions are formed, and rate of electron collection decreases • The detector selective for compounds with atoms of high electron affinity. • This detector is frequently used in the analysis of chlorinated compounds • e.g. – pesticides, polychlorinated biphenyls
- 53. ADVANTAGE Highly sensitive DISADVANTAGE Used only for compounds with electron affinity
- 54. RECORDERS & INTEGRATORS Record the baseline and all the peaks obtained INTEGRATORS Record the individual peaks with Rt, height….
- 55. Derivatisation of sample Treat sample to improve the process of separation by column or detection by detector. They are 2 types Precolumn derivatisation Components are converted to volatile & thermo stable derivative. Conditions - Pre column derivatisation Component ↓ volatile Compounds are thermo labile ↓ tailing & improve separation
- 56. Post column derivatisation Improve response shown by detector Components ionization / affinity towards electrons is increased Pretreatment of solid support To overcome tailing Generally doing separation of non polar components like esters, ethers… Techniques: 1. use more polar liquid S.P 2. Increasing amt. of liquid phase 3.Pretreatment of solid support to remove active sites.
- 57. Parameters used in GC Retention time (Rt) It is the difference in time b/w the point of injection & appearance of peak maxima. Rt measured in minutes or seconds (or) It is the time required for 50% of a component to be eluted from a column Retention volume (Vr) It is the volume of carrier gas which is required to elute 50% of the component from the column. Retention volume = Retention time ˣ Flow rate
- 58. Separation factor (S)Ratio of partition co-efficient of the two components to be separated. If more difference in partition co-efficient b/w two compounds, the peaks are far apart & S Is more. If partition co-efficient of two compounds are similar, then peaks are closer Resolution (R) The true separation of 2 consecutive peaks on a chromatogram is measured by resolution It is the measure of both column & solvent efficiencies R= 2d W1+W2
- 59. Retention time
- 62. Resolution
- 63. Resolution
- 64. THEORETICAL PLATE An imaginary unit of the column where equilibrium has been established between S.P & M.P It can also be called as a functional unit of the column HETP – Height Equivalent to a Theoretical Plate Efficiency of a column is expressed by the number of theoretical plates in the column or HETP If HETP is less, the column is ↑ efficient. If HETP is more, the column is ↓ efficient
- 65. HETP= L N A + B +Cu u (length of the column) (no of theoretical plates) HETP is given by Van Deemter equation HETP= A = Eddy diffusion term or multiple path diffusion which arises due to packing of the column B = Molecular diffusion, depends on flow rate C = Effect of mass transfer,depends on flow rate u = Flow rate
- 66. Efficiency ( No. of Theoretical plates) It can be determined by using the formula n = 16 Rt2 w2 N = no. of theoretical plates Rt = retention time W = peak width at base The no. of theoretical plates is high, the column is highly efficient For G.C the value of 600/ meter
- 69. Asymmetry Factor Chromatographic peak should be symmetrical about its centre If peak is not symmetrical- shows Fronting or Tailing FRONTING Due to saturation of S.P & can be avoided by using less quantity of sample TAILING Due to more active adsorption sites & can be eliminated by support pretreatment,
- 71. Asymmetry factor (0.95-1.05) can be calculated by using the formula AF=b/ab & a calculated at 5% or 10% of the peak height
- 73. ADVANTAGES OF G.C Very high resolution power, complex mixtures can be resolved into its components by this method. Very high sensitivity with TCD, detect down to 100 ppm It is a micro method, small sample size is required Fast analysis is possible, gas as moving phase- rapid equilibrium Relatively good precision & accuracy Qualitative & quantitative analysis is possible
- 74. Gas Chromatography vials caps
- 75. Chromatographic Analysis –The number of components in a sample is determined by the number of peaks. –The amount of a given component in a sample is determined by the area under the peaks. –The identity of components can be determined by the given retention times.
- 76. Applications of G.C • G.C is capable of separating, detecting & partially characterizing the organic compounds , particularly when present in small quantities. 1, Qualitative analysis Rt & RV are used for the identification & separation 2, Checking the purity of a compound Compare the chromatogram of the std. & that of the sample
- 77. 3, Quantitative analysis It is necessary to measure the peak area or peak height of each component 4, used for analysis of drugs & their metabolites.
- 78. Semi-Quantitative Analysis of Fatty Acids DetectorResponse C14 C16 C18 PeakArea Sample Concentration (mg/ml) 2 4 6 8 10 1.50.5 1.0 2.0 2.5 3.0 C C + C + C = t h e c o n t e n t % o f C14 f atty a c i d s Retention Time T h e c o n t e n t % o f C1 4 fatty a c i d s =
- 79. Tentative Identification of Unknown Compounds Response GC Retention Time on Carbowax-20 (min) Mixture of known compounds Octane Decane1.6 min = RT Hexane Response Unknown compound may be Hexane 1.6 min = RT Retention Time on Carbowax-20 (min)
- 80. Response GC Retention Time on SE-30 RT= 4 min on SE-30 Unknown compound Response GC Retention Time on SE-30 RT= 4.0 min on SE-30 Hexane Retention Times
- 81. Advantages of Gas Chromatography • Very good separation • Time (analysis is short) • Small sample is needed - l • Good detection system • Quantitatively analyzed
- 82. How a Gas Chromatography Machine Works – First, a vaporized sample is injected onto the chromatographic column. – Second, the sample moves through the column through the flow of inert gas. – Third, the components are recorded as a sequence of peaks as they leave the column.
- 83. contents Derivatisation techniques: Applications of gas chromatography GC DERIVATIZATION
- 84. • What is GCDerivatization? • Derivatization is the process of chemically modifying a compound to produce a new compound which has properties that are suitable for analysis using aGC. WHAT IS DERIVATIZATION?
- 85. Topermit analysis of compounds not directly amenable to analysis due to, for example, inadequate volatility orstability. Improve chromatographic behavior or detectability. Many compounds do not produce a usable chromatograph (i.e.multiple peaks, or one big blob), or the sample of interest goes undetected. As a result it may be necessary to derivatize the compound before GCanalysis isdone. Derivatization is a useful tool allowing the use of GC and GC/MS to be done on samples that would otherwise not be possible in various areas of chemistry such as medical, forensic, and environmental. WHY DERIVATIZATION
- 86. Increasesvolatility (i.e. sugars): Eliminates the presence of polar OH,NH,& SHgroups Derivatization targets O,S,Nand Pfunctional groups (with hydrogens available. Increases detectability, I.e. steroids/ cholesterol Increases stability. Enhancessensitivity for ECD(Electron Capture Detection). Theintroduction of ECDdetectable groups,such ashalogenated acyl groups, allows detection of previously undetectable compounds. WHAT DOES DERIVATIZATION ACCOMPLISHED
- 87. TypesofDerivatization pre-column derivatization post-column derivatization Precolumn derivatisation: Components are converted to volatile &thermo stable derivative Conditions - Precolumn derivatisation Component ↓ volatile Compounds are thermo labile ↓ tailing & improve separation
- 88. Post columnderivatisation Improve response shown by detector Components ionization / affinity towards electrons is increased Pretreatment of solidsupport Toovercometailing Generally doing separation of non polarcomponents like esters, ethers…
- 89. TECHNIQUES OF DERIVATISATION SILYLATION ACYLATION PERFLOURO- ACYLATION ALKYLATION ESTERIFICATION CONDENSATION CYCLISATION
- 90. Acylation • Acylation reduces the polarity of amino, hydroxyl, andthiol groups and adds halogenated functionalities for ECD.In comparison to silylating reagents, the acylating reagents target highly polar, multifunctional compounds, such as carbohydrates and amino acids. • Acyl derivatives are formed with acyl anhydrides,acyl halides, and activated acyl amide reagents. • Theanhydrides and acyl halides form acid by-products which must be removed before GCanalysis.
- 91. CONT….. • Activated amide reagents, such asMBTFA,have the advantage of not yielding acidby-products. • Fluorinated acyl groups, going from trifluoracetyl to heptafluorobutyryl , canbe used to increaseretention times.
- 92. AcylatingReagents • 1.Fluorinated Anhydrides:- • TFAA-Trifluoroacetoic Anhydride • PFPA-PentafluoropropionicAnhydride · Most commonly used reagents, asderivatives are suitable for both FIDandECD. • · Reactswith alcohols, amines, and phenols to produce stable and highly volatile derivatives • · Theacid by-product should be removed, via astream of nitrogen, before injection onto column. Bases,such as triethylamine, canbe added asan acid receptor and promote reactivity • ·Ability to adjust retention times for ECD
- 93. • 2. Fluoracylimidazoles • TFAI-Trifluoroacetylimidazole • PFPI-Pentafluoropropanylimidazole • HFBI- Heptafluorobutyrylimidazole • · Usually abetter choice for making ECDderivatives • · Reactunder mild conditions and their by-products, the imidazole, is not acidic so it will not harm column. • · Reagentsare extremely sentive towater- will react violently to it. • · Works best with amines and hydroxycompounds
- 94. Cont.. • 3.MBTFA{N-methyl-bis(trifluoroacetamide)} • · Reactswith primary and secondary amines, slowly with hydroxyl groups and thiols. • · Conditions are mild and the by-products are relatively inert and are nonacidic • 4.PFBCI-PentafluorobenzoylChloride • · Phenols most receptivesite • · Usedfor making derivatives of alcohols andsecondary • amines. Secondaryamines will react with this compound
- 95. Ex: 1. Esterification with n-propanol, acidic catalyst and benzene for remove water azeotropically, the ester were acylated with acetic anhydride and finally derivatives extracted and diluted for GC.
- 96. Esterificationwith n-propanol, acid catalystand benzene removes water azeotropically. Later,Esterwas acetylatedwith aceticanhydride toyieldthe acetylatedderivative.
- 97. Advantages and Disadvantages of Acylation • Advantages: Addition of halogenated carbonsincreased detectability byECD. • Derivatives are hydrolytically stable. • Increased sensitivity by adding molecular weight • Acylation canbe used asafirst step to activate carboxylic acids prior to esterfication(alkylation).
- 98. Disadvantages • Acylation derivatives canbedifficult toprepare. • Reactionproducts (acid by-products) often needto be removed beforeanalysis. • Acylation reagentsaremoisture sensitive. • Reagentsarehazardousand odorous.
- 99. Perflouro-Acylation •Thisgroup increases the mol.wt of the sample relative tothe analogous hydrocarbon. •Best method to increase the retentiontime. •Eg. • N-Triflouro acetic anhydride •Direct acylation with Triflouro acetic anhydride in triflouro acetic acid followed by methylation with diazomethane in methanol.
- 101. Alkylation • Alkylation reduces molecular polaritybyreplacing active hydrogens with an alkyl group. These reagents are used to modify compounds with acidic hydrogens, such as carboxylic acids and phenols. These reagents make esters, ethers, alkyl amines and alkylamides. • Reagents containing fluorinated benzoyl groups canbe used for ECD. • Theprincipal reaction employed for preparation ofthese derivatives is nucleophilic displacement. • Alkylation is used to modify compounds with acidic hydrogens, suchascarboxylic acids and phenols.
- 102. •Alkylation canbe used alone to form esters, ethers and amides- or they canbeused in conjunction with acylation or silylation. •It is generally used to convert organic acids into esters.As the acidity of the active hydrogen decreases, thestrength of the alkylatingreagent must be increased. Theharsher the reaction conditions or reagents, the more limited the selectivity and applicabilityof this method.
- 103. 1.DMF (dialkylacetals) ·These reagents work quickly, derivatizing upon dissolution. Suitable for flash alkylation, where derivatization takes place in the injectionport. ·Thedifferent alkyl homolgues allow formation of avarietyof esters. polarity and volatility of the samples canbe adjusted, thereby changing retention time. ·They will react with water to give the corresponding alcohol. Tracesof water will not affect the reaction aslong asyou have an excessof acid. ALKYLATING AGENT
- 104. ·Froms butyl ester, which will allow longer retentiontimes ·Usedmost commonly for low molecular weightacids 3.BF3in methanol orbutanol ·Convenient and inexpensive method for forming esters 4.PFBBr (Pentafluorobenzylbromide) Esterifies phenols, thiols, and carboxylic acids 2.TBH (tetrabutylammonium hydroxide)
- 105. anticonvulsants and barbiturates. Themost common derivative is methyl imide, which canbe formed on column by using trimethyl ammonium hydroxide.[TMAH]
- 106. Cont… •Alkyl esters have excellentstability and canbe isolated and stored for long periods oftime. •A two step approach is commonly used in derivatization of aminoacids, where multiplefunctional groups on these compoundsmay necessitate protection duringderivatization.
- 107. Advantages Wide range of alkylation reagents available Reaction conditions canvary from strongly acidicand strongly basic. Somereactions can be done in aqueoussolutions. Alkylation derivatives are generally stable. Disadvantages Limited to amines and acidichydroxyls. Reaction conditions are frequently severe. Reagentsare often toxic.
- 108. esterification Esterification: Esterification is used to prepare derivatives of carboxyl group. The conversion of the carboxyl group to ester increases volatality by decreasing hydrogen bonding. Ex:- Analgesics, prostaglandins, aminoacids, & anti-inflammatory agents. Derivatization by esterification can be carried out by using Fischer esterification procedure in which strongly acidic conditions are present. H+R` - COOH + R -OH R`- COOR + H2O BF3
- 109. Amino acids : E.x. Alanine, α-amino butyric acid, valine,leucine, isoleucine. 1. α-chloromethyl esters: prepared by treating the amino acid with a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and Hydrochloric acid. Aminoacid Chloro methyl ester R – CH-NH2 – COOH Hcl/ HNO3 R – CH – COOCH3 Cl 2. Methyl ester salts: Esterification of 1-leucine, 1-methionine with methanol & thionyl chloride.
- 110. Silylation•Silylation produces silyl derivatives which are more volatile, lessstable, and more thermally stable. •Replacesactive hydrogens with aTMS(trimethylsilylgroup). •Silylation occurs through nucleophilic attack (SN2).The better the leaving group, the better the siliylation. •Silylation reagents will react with water and alcohols first. Caremust be taken to ensure that both sample andsolvents are dry. •Solvents should be aspure aspossible. Thiswill eliminate excessivepeaks.Tryusing aslittle solvent aspossible asthis will prevent alarge solventpeak.
- 111. Pyridine is the most commonly used solvent. Although pyridine may produce peak tailing, it is an acid scavangerand will drive the reactionforward. In many cases,the need for asolvent is eliminated with silylating reagents. (If asample readily dissolves in the reagent, it usually asign that the derivatization iscomplete). .
- 112. Easeof reactivity of functional groups towardssilylation. Many reagents require heating (not in excessof 60 degreesC for about 10-15 minutes, to preventbreakdown). Hindered products may require long term heating
- 113. Theeaseof reactivity of the functional group towardsilylation follows the order: Alcohol >Phenol >Carboxyl >Amine >Amide General Reaction R-OH + (CH3)3 – Si - Cl Mechanism R – O – Si - (CH3)3 + HCl TrimethylsilyletherTrimethylchlorosilane
- 114. Silylating Reagents 1.HMDS (Hexamethyldisilane). ·Weakdonor, asit hassymmetry ·If used will attack only easily silylated hydroxylgroups ·Sometimes found in combination with TMCS 2.TMCS (Trimethylchlorosilane). ·Weakdonor, again not commonly used ·Often found asacatalyst to increase TMSdonorpotential ·Badby-product, HCL 3.TMSI (Trimethylsilylimidazole). ·Not aweak donor, but it is selective (will not target N compounds) ·Reactsreadily with hydroxyls but not withamines ·Since it is selective, it will target the hydroxyls in wet sugars. It will derivatize the acid sites of amino acids, and will leave the amino group free forfluorinated derivatization (ECD)
- 115. 4.BSA (Bistrimethylsilylacetamide). ·First widely used silylating reagent ·Strong silylating reagent- acetamide is agood leaving group. Reactsunder mild conditions and produces relatively stable by-products ·Drawbacks: by-product, TMS-acetamide, will sometimes produce peaksthat overlap those of other volatilederivatives. BSAmixtures also oxidize to form silicon dioxide, which can foul FIDdetectors TMS-DEA(Trimethylsilyldiethylamine). ·Reagent is used for derivatizing amino acids and carboxylic acids ·Targetshindered compounds
- 116. 5.BSTFA (Bistrimethylsilyltrifluoroacetamide)·Developed by Gerhke in 1968 ·Reactssimiliarly to BSAbut the leaving group is trifluoroacetamide, soit acts faster and more completelythan BSA ·BSTFAis highly volatile, and produces by-products that are more volatile than BSAby-products, thus there is little interference with early elutingpeaks ·It canact asits own solvent ·Combustion product silicon trifluoride, does not foul detectors
- 117. Advantages and Disadvantages ofSilylation Advantages •Ability to silylate awide variety ofcompounds • Largenumber of silylating reagents available. • Easily prepared. Disadvantages •Silylation Reagentsare moisture sensitive •Must useaprotic (no protons available) organic solvents
- 118. Condens ation:If ketone or aldehyde is present in a sample, it is frequently derivatized to prevent hydrogen bonding due to enolization & helps in resolution from an interfering substance. The most commonly used reagent is methoxylamine to protect enolizable ketogroups in steroids by formation of methoximes. Cyclization: Cyclization is performed on compounds containing two functional groups in close proximity so that 5 or 6 membered Heterocyclic rings can be formed.
- 119. • Heterocycles formed are ketals, boronates, triazines & phosphites. E.g: Cyclization of α – OH ketones (present in corticosteroids) with formaldehyde forms bismethylene dioxy derivatives which are thermally stable & permit resolution of corticosterone from a mixture of steroids.
- 120. applications Qualitativeanalysis: Retention time data should be usefulfor identification of mixtures. Comparing the retention time of the sample as well asthe standard. Checking the purity of acompound: comparthe standard and sample. Additional peaksare obtained…..impurities are present….compoundis not pure.
- 121. Elementalanalysis Determination of C,H ,O ,S and N . Determination of mixture of drugs Isolation and identification of drugs Isolation and identification of mixture of components(amino acids ,plant extracts ,volatile oils) GS-MSis one of the most powerful tool in siologicaland chemical studies. Other app…like Analysis of dairy prod.., aldehydes, ketones etc.. Whichare present in pharm..,Rancidity in fattyacids. Assayof drugs, purity of compounds, determinationof foreign or relatedcompounds.
- 122. Quantitation Introdution • Sampling techniques for practical quantitative capillary GC have to meet certain principal requirements. Both the absolute and the relative peak areas (e.g. column loads) must be reproducible with high precision and at high accuracy; discrimination of certain constituents according to their volatility should not take place on sampling. On the basis of systematic studies, the three most reliable sampling techniques used for GC analyses with the aim of achieving precise and accurate quantitative data proved to be the following: On‐column, injection, splitless PTV injection, and an optimized version of split sampling called “cooled needle split” injection. The on‐column technique can be optimized by using precolumns with wider internal diameters and without stationary phase coatings to overcome the problems of large liquid sampling volumes and for automation. The PTV technique should only be used in the splitless mode because discrimination cannot be suppressed completely with the split mode. All three of the techniques can be operated automatically, either to avoid “human interference”, i.e. to improve precision or for unattended operation to save man‐power.
- 123. What is Area Normalization method • Normalization is a technique used for quantitatively assessing a chromatogram to provide a quantitative analysis of the mixture being separated. ... The quantitative results are obtained by expressing the area of a given peak as a percentage of the sum of the areas of all the peaks. •
- 124. Internal Standard Method • Description – In this approach, an internal standard is added to the sample, and the response from the analyte peak is compared to the internal standard. This approach corrects for minor variations in the injection volume. • Response Factor (RF) – The response factor accounts for differences in the detector response between the analyte and standard. – Conc-sample = [( AreaIScalibrator) / ( AreaISsample)] x [Areasample / Areacalibrator] * (Conccalibrator) 124
- 125. Sample Chromatogram and Integration Report 126 IS X AIS = 17.80 AX = 27.01 isx isx isx cc AA R /
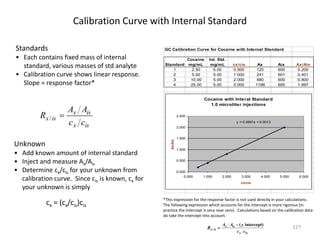
- 126. Calibration Curve with Internal Standard 127 Standards • Each contains fixed mass of internal standard, various masses of std analyte • Calibration curve shows linear response. Slope = response factor* Unknown • Add known amount of internal standard • Inject and measure Ax/Ais • Determine cx/cis for your unknown from calibration curve. Since cis is known, cx for your unknown is simply cx = (cx/cis)cis isx isx isx cc AA R / GC Calibration Curve for Cocaine with Internal Standard Standard Cocaine mg/mL Int. Std. mg/mL cx/cis Ax Aix Ax/Ais 1 2.50 5.00 0.500 120 600 0.200 2 5.00 5.00 1.000 241 601 0.401 3 10.00 5.00 2.000 480 600 0.800 4 25.00 5.00 5.000 1198 600 1.997 Cocaine with Interal Standard 1.0 microliter injections y = 0.3991x + 0.0013 0.000 0.500 1.000 1.500 2.000 2.500 0.000 1.000 2.000 3.000 4.000 5.000 6.000 cx/cis Ax/Ais *This expression for the response factor is not used directly in your calculations. The following expression which accounts for the intercept is more rigorous (in practice the intercept is very near zero). Calculations based on the calibration data do take the intercept into account. / ( intercept)x is x is x is A A y R c c
- 127. Area Percent Method • Area percent is the simplest quantitation method. This method assumes that the detector responds identically to all compounds. This assumption, however, is not valid. This method provides a rough estimate of the amounts of analytes present. • Gas chromatography is a technique used to analyze mixtures. The instrument allows mixtures to be separated and the amount of each component to be determined. ... Using the chromatogram, the identity and the percent composition of each component in the mixture can be determined. •
- 128. Single Point Internal Standard • The Single Point Internal Standard method requires at least two analyses. The first analysis contains a known amount of internal standard and the compounds of interest. Calculate the response factor using • Internal Response • Factor = area IS x amount SC amount IS x areaSC IS = Internal Standard SC = Specific Compound of Interest
- 129. Single Point External Standard • Unlike the area percent method, the Single Point External Standard method requires the analysis of more than just the sample of interest. Analyze a sample containing a known amount of analyte or analytes and record the peak area. Then calculate a response factor using • response factor = peak area/ sample amount
- 130. Gas Chromatography Quantitative Analysis Chromatogram The response must be linear Concentration Mass The response factor of each compound is different for each compound Parameters that can be used: Peak Height Peak Area
- 131. External standard • For an external standard quantitation, known data from a calibration standard and unknown data from the sample are combined to generate a quantitative report. It is called external standard because the standard or known material is separate orexternal to the unknown material.
- 132. areas %g PeakAreag 100 g 100g (areai fi ) PeakArea f %g Gas Chromatography Quantitative Analysis Chromatogram Area Normalization The sum of the areas of all the peaks corresponds to 100% of the solutes separated. Only true if: All the compounds are eluted Same sensitivity As the compounds usually do not have the same sensitivity a correction factor should be applied Calibration curve area fg mass
- 133. Chromatogram Internal Standard An internal standard is a compound, not present in the sample, that is added in a constant amount to samples and calibration standards. The peak of compound must not overlap with the peaks of the analytes. SI Method y=0.9978x R2 = 0.9991 y=0.497x R2 =0.999 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 2 10 124 6 8 masscompound/mass SI Areacompound/area SI compoundA compoundB Lineal (compound A) Lineal (compoundB) Advantages: manual injection Disadvantages: To analyse great number of analytes To find a good IS
- 134. Chromatogram External Standard Advantages: simpler than IS. Disadvantages: Sample injection reproducibility Preferable Automatic injection or sample valve ES Method y = 1.9841x R2 = 0.9991 y = 0.9981x R2 = 0.9993 2 1 0 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 4 5 63 mass compound Areacompound compound A compound B Lineal (compound A) Lineal (compound B)
- 135. Derivatization is the process of chemically modifying a compound to produce a new compound which has properties that are suitable for analysis using a GC WHY? To permit analysis of compounds not directly amenable to analysis due to, for example, inadequate volatility or stability Improve chromatographic behavior or detectability. Derivatization is a useful tool allowing the use of GC and GC/MS to be done on samples that would otherwise not be possible in various areas of chemistry such as medical, forensic, and environmental
- 136. •Increases volatility (i.e. sugars): –Eliminates the presence of polar OH, NH, & SH groups –Derivatization targets O,S, N and P functional groups (with hydrogens available Increases detectability, I.e. steroids/ cholesterol •Increases stability •Enhances sensitivity for ECD (Electron Capture Detection). The introduction of ECD detectable groups, such as halogenated acyl groups, allows detection of previously undetectable compounds •in some cases: derivatization can also be used to decrease volatility to allow analysis of very low molecular weight compounds, to minimize losses in manipulation and to help separate sample peaks from solvent peak.
- 137. Gas Chromatography DERIVATIZATION Comments Advantages Disadvantages Silylation Readily volitizes the sample - Wide variety of compounds -Large number of silylating reagents available -Easily prepared -Moisture sensitive -Organic solvents must be aprotic (no protons available) -WAX type columns cannot be used Acylation -Used as the first step to further derivatizations or as a method of protection of certain active hydrogens. -Reduces the polarity of amino, hydroxyl, and thiol groups and adds halogenated functionalities. -Increased detectability by ECD -Derivatives are hydrolytically stable - Increased sensitivity by adding molecular weight -Acylation can be used as a first step to activate carboxylic acids prior to esterfication (alkylation) -Difficult to prepare. -Reaction products often need to be removed before analysis -Moisture sensitive -Reagents are hazardous and odorous Alkylation -Reduces molecular polarity by replacing active hydrogens with an alkyl group. - modify compounds with acidic hydrogens, such as carboxylic acids and phenols. -Reagents containing fluorinated benzoyl groups can be used for ECD -Wide range of alkylation reagents. -Reaction conditions can vary from strongly acidic to strongly basic -Some reactions can be done in aqueous solutions -Alkylation derivatives are generally stable -Limited to amines and acidic hydroxyls -Reaction conditions are frequently severe - Reagents are often toxic Formation of perfluoro- derivatives Reagents containing fluorinated benzoyl groups can be used for ECD Wide range of application Easy to prepare Selectivity GC-Quiral Derivatiz.
- 138. Gas Chromatography DERIVATIZATION Derivatization Reaction Common Derivatizing Agent Methylation of carboxylic acids Diazomethane, methanol/sulfuric acid Oxime formation of carbonyl functionality PFBHA N-hexyl carbonate, carbamate, and ester formation from hydroxylic, aminic, and carboxylic functionality N-hexyl chloroformate Heptafluorobutyramide formation from aromatic amines Heptafluorobutyramide Some examples And much more…
- 139. Thank you








































































































![anticonvulsants and barbiturates.
Themost common derivative is
methyl imide, which canbe formed
on column by using trimethyl
ammonium hydroxide.[TMAH]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gc-181128164613/85/Gas-Chromatography-105-320.jpg)


















![Internal Standard Method
• Description
– In this approach, an internal standard is added to the sample, and the
response from the analyte peak is compared to the internal standard. This
approach corrects for minor variations in the injection volume.
• Response Factor (RF)
– The response factor accounts for differences in the detector response
between the analyte and standard.
– Conc-sample = [( AreaIScalibrator) / ( AreaISsample)] x [Areasample /
Areacalibrator] * (Conccalibrator)
124](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gc-181128164613/85/Gas-Chromatography-124-320.jpg)