Green generation. Science Olympiad preparation.
- 2. GENERAL CONCEPTS ECOLOGY • Individual: a single organism. • Population: a group of organisms of the same specie in a common location. • Biological community: an interacting group of various populations of several species in a common location (biotic). • Ecosystem: a biological community of interacting organisms (biotic) and their physical environment (abiotic). • Biome: A major ecological community of organisms adapted to a particular climatic or environmental condition on a large geographic area
- 5. ECOLOGY OF COMMUNITIES TROPHIC CHAIN TROPHIC WEB
- 6. ECOLOGY OF COMMUNITIES TROPHIC PYRAMID NUMBERS PYRAMID Compares the number of individuals in each trophic level. BIOMASS PYRAMID Compares the total dry weight of the organisms in each trophic level. ENERGY PYRAMID Compares the total amount of energy available in each trophic level, measured in kilocalories.
- 8. Condensation: process in which water vapor in the air cools and turns into liquid water. Precipitation: The droplets in the cloud become bigger and heavier and fall down. Infiltration: the downward movement of water from the land surface into soil or porous rock. Percolation: process in which liquid passes through a filter (could be different layers of soil). Water is stored in aquifers. Evaporation: the liquid water heats up and turns into atmospheric water vapor. Transpiration: the water released by the plants, it escapes through the stomata and then evaporates and turns into atmospheric water vapor.
- 10. No new water is created unless under artificial conditions. The water is being constantly recycled. The water that you drink could be the same one that dinosaurs drank! Best solvent found in nature
- 11. We all live in a watershed Area of land that drains to a common body of water.
- 12. FRESHWATER Makes aprox. 3% of all the water in the world, only 1% avalaible to us. It must have < 0.5% of dissolved salts. Freshwater wildflife shows extintion rates 15 times greater than marine wildlife! Ice caps Icebergs Glaciers Groundwater Vernal pools Ponds Lakes Marshes Bogs Fens Rivers Streams Underground aquifers
- 13. 1- WATER DIVERSION • To modify the natural course of a river flow. • Dams are a major factor in water diversion. They are built along rivers to produce reservoirs • They could cause habitat loss, habitat fragmentation, loss of biodiversity and alteration of life cycle of some species of fishes –anadromous-.
- 14. 2- OVERFISHING Fish catch has risen from 20 million tons/year to over 90 million tons / year 3- INTRODUCTION OF INVASIVE SPECIES
- 15. 4-THERMAL POLLUTION • Change in the water temperatures of lakes, rivers, and oceans caused by man-made industries or practices: water as coolant is warmed returned & to body of water • Produces alterations in the natural balance of the ecosystems, causes melting of ice caps and rises the level of water.
- 16. 5-POLLUTION Contamination of water bodies producing a degradation of the ecosystems.
- 17. 5-POLLUTION Industrial, residential, commercial, and environmental POINT SOURCE POLLUTION NON POINT SOURCE POLLUTION Source is clearly identificable Source is not clearly identificable or there is more than one.
- 19. Pollutants Organic compounds Decomposition of living organisms and their bi-products. Manure, oil, plastic, gasoline Inorganic pollutants Dissolved and suspended solids such as… silt, salts, and minerals Toxic substances Substances that are lethal to living organisms. Metals, chemical compounds
- 20. Pollutants Microorganisms and parasits Disease causing pollutants that spread through animal waste Bacteria, viruses, protozoa and parasitic worms Radioactive waste Elements that cause radiation and may lead to the mutation and death of the organisms exposed Uranium, radium, radon…
- 21. ALTERATIONS IN THE NUTRIENT CYCLE
- 23. EUTROPHICATION!!
- 24. PH WATER QUALITY
- 29. WATER QUALITY BIOINDICATORS A living organism that gives us an idea of the health of an ecosystem.
- 30. • Environmental Remediation Strategies • Sustainability Strategies • Nonrenewable vs. Renewable Energy Sources and Alternate Energy Sources • Everyday Solutions as recycling and composting • Legislation and Economic Opportunity for Solving Problems SOLUTIONS
- 31. WATER TREATMENT Coagulation Sedimentation Filtration Disinfection Environmental Remediation Strategies
- 33. Nonrenewable vs Renewable Energy Sources
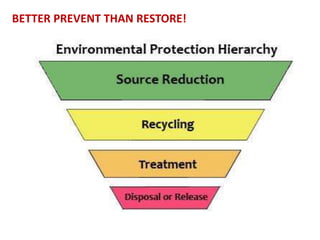
- 35. BETTER PREVENT THAN RESTORE!
- 36. TIPS •Review the water and the nutrients cycles, and each one of the different events and processes really well. •Review the trophic chains, webs and pyramids of every kind –biomass, numbers, energy-. Also the interaction between organisms! Learn how to read the graphs. •Types of pollution and pollutants. Water Quality indexes. •Research about richness, diversity, survivorship and mortality graphs. Learn about ecology of populations, communities and ecosystems. •Learn about water management and legislation. Measures taken to decrease water pollution. Research about solutions.
Editor's Notes
- #3: ECOLOGY – how organisms interact with one another and with their environment Put as example the people from Chesterton.
- #8: This is a really simplify version but you can see the most essential steps. The sunlight heats the surface of a body of water and the water evaporates and goes to the atmosphere. It could stay for a while in the atmosphere as water vapor, one powerful greenhouse gas –keeps the warmth- until it gets colder and heavier through the process known as condensation. When the droplets in the cloud become too big and heavy they fall down through the process known as precipitation. Once in the surface, it could infiltrate (infiltration) and experiment percolation and get stored in underground aquifers or it could glide all along the surface (surface runoff) until reaching a body of water. I emphasize in this as I bet it is going to appear in your competition exam. * Greenhouse Effect - warming that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space. VIDEO: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=al-do-HGuIk
- #10: Here we have two diagrams that show the differences between natural and urban water cycle. We can see two main differences. One is regarding the infiltration. In a natural environment the infitration is higher but what happens in a city? Concrete, pavement, roofs…all these materials keep water away from the ground. Consequently in natural environments there are rivers receiving large amount of water from rivers and streams while in cities those rivers will dry out. But there is another think hapenning, in natural environments the surface runoff, for the same reasons, is not too high while in cities there is after a storm an excess of surface water that will be probably dumped in a body of water, transporting all the obnoxious stuff with it.
- #11: They call it the Mickey Mouse molecule and as you can see it has two hydrogens atoms and one oxygen atom. Hydrogen atoms carry a positive charge while oxygen carry a negative charge. These atoms are able to stick to other substances and steal atoms from them causing dissolution of the substance. The substance is mixed with water and is really difficult to detect unless it has a weird color. This property makes the water the best solvent found in nature. But this property make it difficult for us to detect pollutants.
- #12: As you can see, in Indiana there are 5 main watersheds, though everything depends on the prespective. We are right now in the Lake Michigan Watershed, but if we look more closely or locally, we could consider being in the Calumet Watershed. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QOrVotzBNto
- #13: Ask them if they remember what an ecosystem is. Talk briefly about each of the systems. Remind percolation.
- #14: The water diversion could alter the cycle of some fishes, like anadromous fishes such as trouts and salmons, that are bornt in rivers, go to the ocean or the lakes to grow, eat and gain weight and they return back to the same river to spawn. Sometimes with the dams they can never return. They are fish ladders that help them jump in some of them, but not in the big ones.
- #16: One example of air thermal pollution is the climate change.
- #17: ENVIROSCAPE ACTIVITY
- #20: Organic compounds. Stuff that hass nitrogen and derivates and carbon and derivates, would affect the nutrient cycle. Inorganic. Mineral source or something that hasn´t got any organic compound on it. Toxic. Elements taht are lethal to us and affect our lifes directly. Metals and things that make us bleed, that melt tissues, that burn…etc etc
- #21: ENVIROSCAPE ACTIVITY.
- #25: Study the physical, chemical and biological conditions of water. Talk about the difference anaylisis and perform them.
- #29: Talk about turbidity and temperature.
- #32: To kill bacteria and other microorganisms, chlorine has been demonstrated to be the most effective of all the treatments. Today this chlorine treatment represents the 98% of all the water treatments while the remainder uses other methods such as ozone or ultraviolet light. Coagulation: first of the process once water enters the treatment plant. Chemicals including alum are added to the water. They neutralize the charge of suspended particles in the water and allow the particles suspended in the water to stick or clump together with the coagulant, forming floc. Sedimentation: the floc is heavier than the water, so it settles in the bottom. Filtration: the rest of the water is the only one stepping to the next part of the process. The water passes through sand, charcoal and gravel to remove very small particles. Disinfection: kills microorganisms in the water. It consists in ozonation, chlorination or ultraviolet radiation. In the USA they may include fluoride in the water to prevent tooth decay.
- #33: Primary treatment: large debris is filtered up with screens. After removing the largest elements, the water is sent to a chamber in which smaller solid materials such as sand and grit can settle to the bottom. Smaller particles can settle out in a sedimentation tank. Solids that settle down in the bottom are called primary sludge or biosolids. These last ones could be used for composting or fertilizer. Secondary treatment: biological treatment process that removes dissolved organic material from wastewater. Then the treated water flows by gravity into an aeration tank. Here it is treated with solids with microorganisms that consume the remaining organic material, the aeration tank provides bubbles and air that allow microorganisms to multiply. Tertiary treatments: additional. Sand or carbon filtration. It includes denitrification which reduces ammonia and nitrate levels. Additionally, microfiltration and osmosis to remove pathogens.