Introduction to HDF5 Data Model, Programming Model and Library APIs
- 1. Introduction to HDF5 Data Model, Programming Model and Library APIs HDF and HDF-EOS Workshop IX November 30, 2005 1
- 2. Goals • Introduce HDF5 • Provide a basic knowledge of how data can be organized in HDF5 & how it is used by applications. • To provide some examples of how to read and write HDF5 files 2
- 4. What is HDF5? • File format for storing scientific data – To store and organize all kinds of data – To share data , to port files from one platform to another – To overcome a limit on number and size of the objects in the file • Software for accessing scientific data – – – – – Flexible I/O library (parallel, remote, etc.) Efficient storage Available on almost all platforms C, F90, C++ , Java APIs Tools (HDFView, utilities) 4
- 5. Example HDF5 file “/” (root) “/foo” 3-D array lat | lon | temp ----|-----|----12 | 23 | 3.1 15 | 24 | 4.2 17 | 21 | 3.6 Table palette Raster image Raster image 2-D array
- 6. Viewing an HDF5 File with HDFView 6
- 7. 7
- 8. Example HDF5 Application #include<stdio.h> #include "H5IM.h" #define WIDTH 57 #define HEIGHT 57 #define RANK 2 int main (void) { hid_t file; herr_t status; unsigned char data[WIDTH][HEIGHT]; int i, j, num, val; FILE *fp; fp = fopen ("storm110.txt", "r"); for (i=0; i<WIDTH; i++) for (j=0; j<HEIGHT; j++) { num = fscanf (fp, "%d ", &val); data[i][j] = val; } /* dataset dimensions */ /* file handle */ /* data to write */ /* Open ASCII file */ /* Read Values into ‘data’ buffer */ file = H5Fcreate ("storm.h5", H5F_ACC_TRUNC, H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT); /* Create File */ status = H5IMmake_image_8bit (file, "Storm_Image", WIDTH, HEIGHT, (const unsigned char *)data); status = H5Fclose (file); } /* Create Image */ /* Close File */ 8
- 10. HDF5 file • HDF5 file – container for storing scientific data • Primary Objects – Groups – Datasets • Additional means to organize data – Attributes – Sharable objects – Storage and access properties 10
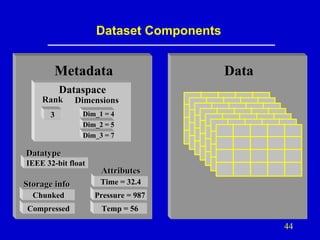
- 11. HDF5 Dataset • HDF5 dataset – data array and metadata • Data array – ordered collection of identically typed data items distinguished by their indices • Metadata – Dataspace – rank, dimensions, other spatial info about dataset – Datatype – Attribute list – user-defined metadata – Special storage options – how array is organized 11
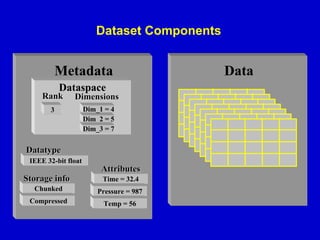
- 12. Dataset Components Metadata Dataspace Rank Dimensions 3 Dim_1 = 4 Dim_2 = 5 Dim_3 = 7 Datatype IEEE 32-bit float Attributes Storage info Time = 32.4 Chunked Pressure = 987 Compressed Temp = 56 Data
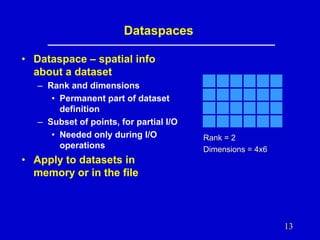
- 13. Dataspaces • Dataspace – spatial info about a dataset – Rank and dimensions • Permanent part of dataset definition – Subset of points, for partial I/O • Needed only during I/O operations Rank = 2 Dimensions = 4x6 • Apply to datasets in memory or in the file 13
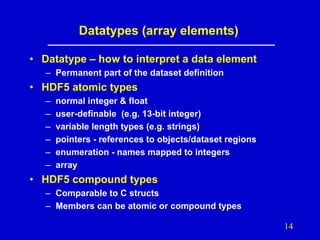
- 14. Datatypes (array elements) • Datatype – how to interpret a data element – Permanent part of the dataset definition • HDF5 atomic types – – – – – – normal integer & float user-definable (e.g. 13-bit integer) variable length types (e.g. strings) pointers - references to objects/dataset regions enumeration - names mapped to integers array • HDF5 compound types – Comparable to C structs – Members can be atomic or compound types 14
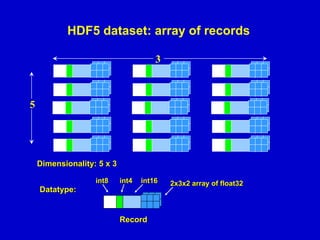
- 15. HDF5 dataset: array of records 3 5 Dimensionality: 5 x 3 int8 int4 int16 Datatype: Record 2x3x2 array of float32
- 16. Attributes • Attribute – data of the form “name = value”, attached to an object • Operations are scaled-down versions of the dataset operations – Not extendible – No compression – No partial I/O • Optional for the dataset definition • Can be overwritten, deleted, added during the “life” of a dataset 16
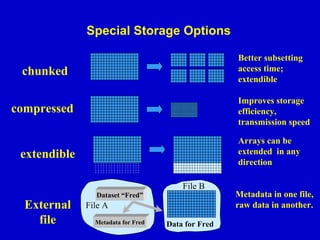
- 17. Special Storage Options Better subsetting access time; extendible chunked Improves storage efficiency, transmission speed compressed Arrays can be extended in any direction extendible File B Dataset “Fred” External file File A Metadata for Fred Data for Fred Metadata in one file, raw data in another.
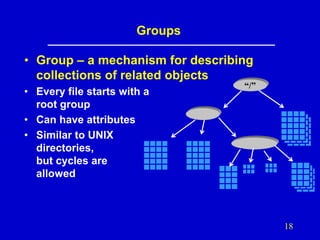
- 18. Groups • Group – a mechanism for describing collections of related objects • Every file starts with a root group • Can have attributes • Similar to UNIX directories, but cycles are allowed “/” 18
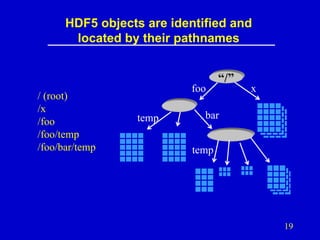
- 19. HDF5 objects are identified and located by their pathnames / (root) /x /foo /foo/temp /foo/bar/temp foo temp “/” x bar temp 19
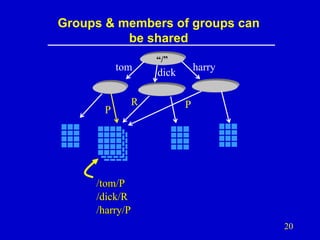
- 20. Groups & members of groups can be shared tom P R “/” harry dick P /tom/P /dick/R /harry/P 20
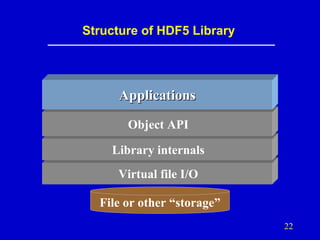
- 22. Structure of HDF5 Library Applications Object API Library internals Virtual file I/O File or other “storage” 22
- 23. Structure of HDF5 Library Object API (C, Fortran 90, Java, C++) • Specify objects and transformation and storage properties • Invoke data movement operations and data transformations Library internals (C) • Performs data transformations and other prep for I/O • Configurable transformations (compression, etc.) Virtual file I/O (C only) • Perform byte-stream I/O operations (open/close, read/write, seek) • User-implementable I/O (stdio, network, memory, etc.) 23
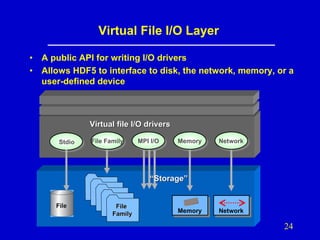
- 24. Virtual File I/O Layer • • A public API for writing I/O drivers Allows HDF5 to interface to disk, the network, memory, or a user-defined device Virtual file I/O drivers Stdio File Family MPI I/O Memory Network “Storage” File File Family Memory Network 24
- 25. Intro to HDF5 API Programming model for sequential access 25
- 26. Goals • Describe the HDF5 programming model • Give a feel for what it’s like to use the general HDF5 API • Review some of the key concepts of HDF5 26
- 27. General API Topics • • • • General info about HDF5 programming Creating an HDF5 file Creating a dataset Writing and reading a dataset 27
- 28. The General HDF5 API • Currently has C, Fortran 90, Java and C++ bindings. • C routines begin with prefix H5*, where * is a single letter indicating the object on which the operation is to be performed. • Full functionality Example APIs: H5D : Dataset interface e.g.. H5Dread H5F : File interface e.g.. H5Fopen H5S : dataSpace interface e.g.. H5Sclose 28
- 29. The General Paradigm • Properties (called creation and access property lists) of objects are defined (optional) • Objects are opened or created • Objects then accessed • Objects finally closed 29
- 30. Order of Operations • The library imposes an order on the operations by argument dependencies Example: A file must be opened before a dataset because the dataset open call requires a file handle as an argument • Objects can be closed in any order, and reusing a closed object will result in an error 30
- 31. HDF5 C Programming Issues For portability, HDF5 library has its own defined types: hid_t: hsize_t: object identifiers (native integer) size used for dimensions (unsigned long or unsigned long long) hssize_t: for specifying coordinates and sometimes for dimensions (signed long or signed long long) herr_t: function return value hvl_t: variable length datatype For C, include #include hdf5.h at the top of your HDF5 application. 31
- 32. h5dump Command-line Utility for Viewing HDF5 Files h5dump [--header] [-a ] [-d <names>] [-g <names>] [-l <names>] [-t <names>] <file> --header -a <names> -d <names> -g <names> -l <names> -t <names> Display header only; no data is displayed. Display the specified attribute(s). Display the specified dataset(s). Display the specified group(s) and all the members. Displays the value(s) of the specified soft link(s). Display the specified named datatype(s). <names> is one or more appropriate object names. 32
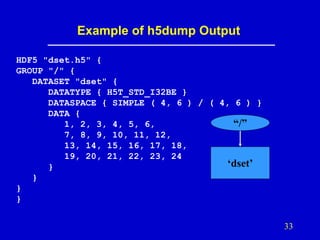
- 33. Example of h5dump Output HDF5 "dset.h5" { GROUP "/" { DATASET "dset" { DATATYPE { H5T_STD_I32BE } DATASPACE { SIMPLE ( 4, 6 ) / ( 4, 6 ) } DATA { “/” 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24 ‘dset’ } } } } 33
- 34. Creating an HDF5 File
- 35. Steps to Create a File 1. 2. 3. Specify File Creation and Access Property Lists, if necessary Create a file Close the file and the property lists, if necessary 35
- 36. Property Lists • A property list is a collection of values that can be passed to HDF5 functions at lower layers of the library • File Creation Property List – Controls file metadata – Size of the user-block, sizes of file data structures, etc. – Specifying H5P_DEFAULT uses the default values • Access Property List – Controls different methods of performing I/O on files – Unbuffered I/O, parallel I/O, etc. – Specifying H5P_DEFAULT uses the default values. 36
- 37. hid_t H5Fcreate (const char *name, unsigned flags, hid_t create_id, hid_t access_id) name flags create_id access_id IN: IN: IN: IN: Name of the file to access File access flags File creation property list identifier File access property list identifier
- 38. herr_t H5Fclose (hid_t file_id) file_id IN: Identifier of the file to terminate access to
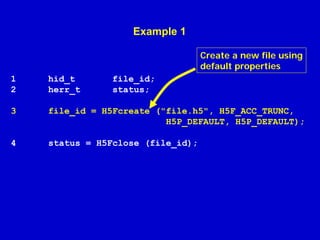
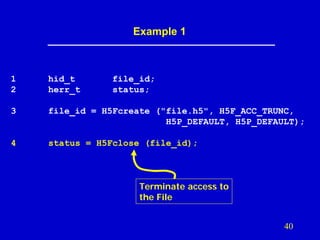
- 39. Example 1 Create a new file using default properties 1 2 hid_t herr_t file_id; status; 3 file_id = H5Fcreate ("file.h5", H5F_ACC_TRUNC, H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT); 4 status = H5Fclose (file_id);
- 40. Example 1 1 2 hid_t herr_t file_id; status; 3 file_id = H5Fcreate ("file.h5", H5F_ACC_TRUNC, H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT); 4 status = H5Fclose (file_id); Terminate access to the File 40
- 41. h5_crtfile.c 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 #include <hdf5.h> #define FILE "file.h5" main() { hid_t herr_t file_id; status; /* file identifier */ /* Create a new file using default properties. */ file_id = H5Fcreate (FILE, H5F_ACC_TRUNC, H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT); /* Terminate access to the file. */ status = H5Fclose (file_id); }
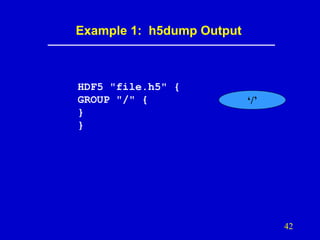
- 42. Example 1: h5dump Output HDF5 "file.h5" { GROUP "/" { } } ‘/’ 42
- 43. Create a Dataset
- 44. Dataset Components Metadata Data Dataspace Rank Dimensions 3 Dim_1 = 4 Dim_2 = 5 Dim_3 = 7 Datatype IEEE 32-bit float Attributes Storage info Time = 32.4 Chunked Pressure = 987 Compressed Temp = 56 44
- 45. Steps to Create a Dataset 1. Obtain location ID where dataset is to be created 2. Define dataset characteristics (datatype, dataspace, dataset creation property list, if necessary) 3. Create the dataset 4. Close the datatype, dataspace, and property list, if necessary 5. Close the dataset 45
- 46. Step 1 Step 1. Obtain the location identifier where the dataset is to be created Location Identifier: the file or group identifier in which to create a dataset 46
- 47. Step 2 Step 2. Define the dataset characteristics – datatype (e.g. integer) – dataspace (2 dimensions: 100x200) – dataset creation properties (e.g. chunked and compressed) 47
- 48. Standard Predefined Datatypes Examples: H5T_IEEE_F64LE Eight-byte, little-endian, IEEE floating-point H5T_IEEE_F32BE Four-byte, big-endian, IEEE floating point H5T_STD_I32LE Four-byte, little-endian, signed two's complement integer H5T_STD_U16BE Two-byte, big-endian, unsigned integer NOTE: • These datatypes (DT) are the same on all platforms • These are DT handles generated at run-time 48
- 49. Standard Predefined Datatypes Examples: H5T_IEEE_F64LE Eight-byte, little-endian, IEEE floating-point H5T_IEEE_F32BE Four-byte, big-endian, IEEE floating point H5T_STD_I32LE Four-byte, little-endian, signed two's complement integer H5T_STD_U16BE Two-byte, big-endian, unsigned integer Architecture Programming Type 49
- 50. Native Predefined Datatypes Examples of predefined native types in C: H5T_NATIVE_INT H5T_NATIVE_FLOAT H5T_NATIVE_UINT H5T_NATIVE_LONG H5T_NATIVE_CHAR (int) (float ) (unsigned int) (long ) (char ) NOTE: • These datatypes are NOT the same on all platforms • These are DT handles generated at run-time 50
- 51. Dataspaces • Dataspace: size and shape of dataset and subset – Dataset • Rank: number of dimension • Dimensions: sizes of all dimensions • Permanent – part of dataset definition – Subset • Size, shape and position of selected elements • Needed primarily during I/O operations • Not permanent • (Subsetting not covered in this tutorial) • Applies to arrays in memory or in the file 51
- 52. Creating a Simple Dataspace hid_t H5Screate_simple (int rank, const hsize_t * dims, const hsize_t *maxdims) rank dims maxdims IN: Number of dimensions of dataspace IN: An array of the size of each dimension IN: An array of the maximum size of each dimension A value of H5S_UNLIMITED specifies the unlimited dimension. A value of NULL specifies that dims and maxdims are the same.
- 53. Dataset Creation Property List The dataset creation property list contains information on how to organize data in storage. Chunked Chunked & compressed 53
- 54. Property List Example • Creating a dataset with ``deflate'' compression create_plist_id = H5Pcreate(H5P_DATASET_CREATE); H5Pset_chunk(create_plist_id, ndims, chunk_dims); H5Pset_deflate(create_plist_id, 9); 54
- 55. Remaining Steps to Create a Dataset 3. Create the dataset 4. Close the datatype, dataspace, and property list, if necessary 5. Close the dataset 55
- 56. hid_t H5Dcreate (hid_t loc_id, const char *name, hid_t type_id, hid_t space_id, hid_t create_plist_id) loc_id IN: Identifier of file or group to create the dataset within name IN: The name of (the link to) the dataset to create type_id IN: Identifier of datatype to use when creating the dataset space_id IN: Identifier of dataspace to use when creating the dataset create_plist_id IN: Identifier of the dataset creation property list (or H5P_DEFAULT)
- 57. Example 2 – Create an empty 4x6 dataset 1 2 3 hid_t hsize_t herr_t file_id, dataset_id, dataspace_id; dims[2]; status; Create a new file 4 file_id = H5Fcreate ("dset.h5", H5F_ACC_TRUNC, H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT); 5 6 7 dims[0] = 4; dims[1] = 6; dataspace_id = H5Screate_simple (2, dims, NULL); 8 dataset_id = H5Dcreate(file_id,"dset",H5T_STD_I32BE, dataspace_id, H5P_DEFAULT); 9 status = H5Dclose (dataset_id); 10 status = H5Sclose (dataspace_id); 11 status = H5Fclose (file_id);
- 58. Example 2 – Create an empty 4x6 dataset 1 2 3 hid_t hsize_t herr_t file_id, dataset_id, dataspace_id; dims[2]; status; 4 file_id = H5Fcreate ("dset.h5", H5F_ACC_TRUNC, H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT); Create a dataspace 5 6 7 8 current dims rank dims[0] = 4; dims[1] = 6; dataspace_id = H5Screate_simple (2, dims, NULL); dataset_id = H5Dcreate(file_id,"dset",H5T_STD_I32BE, dataspace_id, H5P_DEFAULT); 9 status = H5Dclose (dataset_id); 10 status = H5Sclose (dataspace_id); 11 status = H5Fclose (file_id); Set maxdims to current dims
- 59. Example 2 – Create an empty 4x6 dataset 1 2 3 hid_t hsize_t herr_t file_id, dataset_id, dataspace_id; dims[2]; status; 4 file_id = H5Fcreate ("dset.h5", H5F_ACC_TRUNC, H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT); 5 6 7 Pathname dims[0] = 4; dims[1] = 6; dataspace_id = H5Screate_simple (2, dims, NULL); Create a dataset 8 Datatype dataset_id = H5Dcreate(file_id,"dset",H5T_STD_I32BE, dataspace_id, H5P_DEFAULT); Dataspace 9 status = H5Dclose (dataset_id); 10 status = H5Sclose (dataspace_id); 11 status = H5Fclose (file_id); Property list (default)
- 60. Example 2 – Create an empty 4x6 dataset 1 2 3 hid_t hsize_t herr_t file_id, dataset_id, dataspace_id; dims[2]; status; 4 file_id = H5Fcreate ("dset.h5", H5F_ACC_TRUNC, H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT); 5 6 7 dims[0] = 4; dims[1] = 6; dataspace_id = H5Screate_simple (2, dims, NULL); 8 dataset_id = H5Dcreate(file_id,"dset",H5T_STD_I32BE, dataspace_id, H5P_DEFAULT); Terminate access to dataset, dataspace, & file 9 status = H5Dclose (dataset_id); 10 status = H5Sclose (dataspace_id); 11 status = H5Fclose (file_id);
- 61. Example2: h5dump Output An empty 4x6 dataset HDF5 "dset.h5" { GROUP "/" { DATASET "dset" { DATATYPE { H5T_STD_I32BE } DATASPACE { SIMPLE ( 4, 6 ) / ( 4, 6 ) } DATA { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 } } } } “/” ‘dset’ 61
- 62. Writing and Reading Datasets
- 63. Dataset I/O • Dataset I/O involves – reading or writing – all or part of a dataset – Compressed/uncompressed • During I/O operations data is translated between the source & destination (file-memory, memoryfile) – Datatype conversion • data types (e.g. 16-bit integer => 32-bit integer) of the same class – Dataspace conversion • dataspace (e.g. 10x20 2d array => 200 1d array) 63
- 64. Partial I/O • Selected elements (called selections) from source are mapped (read/written) to the selected elements in destination • Selection – Selections in memory can differ from selection in file – Number of selected elements is always the same in source and destination • Selection can be – Hyperslabs (contiguous blocks, regularly spaced blocks) – Points – Results of set operations (union, difference, etc.) on hyperslabs or points 64
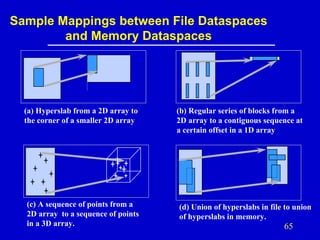
- 65. Sample Mappings between File Dataspaces and Memory Dataspaces (a) Hyperslab from a 2D array to the corner of a smaller 2D array (c) A sequence of points from a 2D array to a sequence of points in a 3D array. (b) Regular series of blocks from a 2D array to a contiguous sequence at a certain offset in a 1D array (d) Union of hyperslabs in file to union of hyperslabs in memory. 65
- 66. Reading Dataset into Memory from File File Memory 2D array of 16-bit ints 3D array of 32-bit ints 2-d array Regularly spaced series of cubes The only restriction is that the number of selected elements on the left be the same as on the right. 66
- 67. Reading Dataset into Memory from File File Memory 2D array of 16-bit ints 3D array of 32-bit ints Read 67
- 68. Steps for Dataset Writing/Reading 1. 2. 3. If necessary, open the file to obtain the file ID Open the dataset to obtain the dataset ID Specify – – – – – 4. 5. Memory datatype ! Library “knows” file datatype – do not need to specify ! Memory dataspace File dataspace Transfer properties (optional) Perform the desired operation on the dataset Close dataspace, datatype and property lists 68
- 69. Data Transfer Property List The data transfer property list is used to control various aspects of the I/O, such as caching hints or collective I/O information. 69
- 70. hid_t H5Dopen (hid_t loc_id, const char *name) loc_id IN: name IN: Identifier of the file or group in which to open a dataset The name of the dataset to access NOTE: File datatype and dataspace are known when a dataset is opened
- 71. herr_t H5Dwrite (hid_t dataset_id, hid_t mem_type_id, hid_t mem_space_id, hid_t file_space_id, hid_t xfer_plist_id, const void * buf ) dataset_id mem_type_id mem_space_id file_space_id xfer_plist_id buf IN: Identifier of the dataset to write to IN: Identifier of memory datatype of the dataset IN: Identifier of the memory dataspace (or H5S_ALL) IN: Identifier of the file dataspace (or H5S_ALL) IN: Identifier of the data transfer properties to use (or H5P_DEFAULT) IN: Buffer with data to be written to the file
- 72. Example 3 – Writing to an existing dataset 1 2 3 hid_t herr_t int file_id, dataset_id; status; i, j, dset_data[4][6]; Initialize buffer 4 5 6 for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) for (j = 0; j < 6; j++) dset_data[i][j] = i * 6 + j + 1; 7 8 file_id = H5Fopen ("dset.h5", H5F_ACC_RDWR, H5P_DEFAULT); dataset_id = H5Dopen (file_id, "dset"); 9 status = H5Dwrite (dataset_id, H5T_NATIVE_INT, H5S_ALL, H5S_ALL, H5P_DEFAULT, dset_data);
- 73. Example 3 – Writing to an existing dataset 1 2 3 hid_t herr_t int file_id, dataset_id; status; i, j, dset_data[4][6]; 4 5 6 for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) for (j = 0; j < 6; j++) dset_data[i][j] = i * 6 + j + 1; Open existing file and dataset 7 8 file_id = H5Fopen ("dset.h5", H5F_ACC_RDWR, H5P_DEFAULT); dataset_id = H5Dopen (file_id, "dset"); 9 status = H5Dwrite (dataset_id, H5T_NATIVE_INT, H5S_ALL, H5S_ALL, H5P_DEFAULT, dset_data);
- 74. Example 3 – Writing to an existing dataset 1 2 3 hid_t herr_t int file_id, dataset_id; status; i, j, dset_data[4][6]; 4 5 6 for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) for (j = 0; j < 6; j++) dset_data[i][j] = i * 6 + j + 1; 7 8 file_id = H5Fopen ("dset.h5", H5F_ACC_RDWR, H5P_DEFAULT); dataset_id = H5Dopen (file_id, "dset"); Write to dataset 9 status = H5Dwrite (dataset_id, H5T_NATIVE_INT, H5S_ALL, H5S_ALL, H5P_DEFAULT, dset_data);
- 75. Example 3: h5dump Output HDF5 "dset.h5" { GROUP "/" { DATASET "dset" { DATATYPE { H5T_STD_I32BE } DATASPACE { SIMPLE ( 4, 6 ) / ( 4, 6 ) } DATA { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24 } } } } 75
- 76. HDF5 High Level APIs 76
- 77. High Level APIs • Make HDF5 easier to use • Encourage standard ways to store objects • Included with HDF5 library However: • Currently available in C • Still need HDF5 calls (H5Fopen/H5Fclose…) 77
- 78. High Level APIs • HDF5 Lite (H5LT): Functions that simply the steps need to create/read datasets and attributes • HDF5 Image (H5IM): Functions for creating images in HDF5. • HDF5 Table (H5TB): Functions for creating tables (collections of records) in HDF5. • Others … (dimension scales, packet) 78
- 79. HDF5 LT Programming model file_id = H5Fcreate( "test.h5", ……. ); /* Call some High Level function */ H5LTsome_function( file_id, ...extra parameters ); status = H5Fclose( file_id ); 79
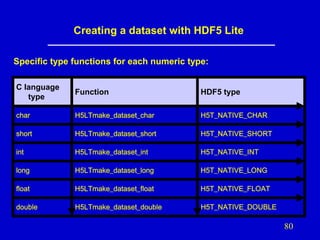
- 80. Creating a dataset with HDF5 Lite Specific type functions for each numeric type: C language type Function HDF5 type char H5LTmake_dataset_char H5T_NATIVE_CHAR short H5LTmake_dataset_short H5T_NATIVE_SHORT int H5LTmake_dataset_int H5T_NATIVE_INT long H5LTmake_dataset_long H5T_NATIVE_LONG float H5LTmake_dataset_float H5T_NATIVE_FLOAT double H5LTmake_dataset_double H5T_NATIVE_DOUBLE 80
- 81. Reading a dataset with HDF5 Lite Specific type functions also for reading: C language type Function HDF5 type char H5LTread_dataset_char H5T_NATIVE_CHAR short H5LTread_dataset_short H5T_NATIVE_SHORT int H5LTread_dataset_int H5T_NATIVE_INT long H5LTread_dataset_long H5T_NATIVE_LONG float H5LTread_dataset_float H5T_NATIVE_FLOAT double H5LTread_dataset_double H5T_NATIVE_DOUBLE 81
- 82. HDF5 Image (H5IM) • Purpose: to defines a standard storage for HDF5 datasets that are intended to be interpreted as images • 2 types of images (8bit indexed to a palette, and 24bit with 3 color planes (RGB)) • Also palette functions 82
- 84. HDF5 Image Palette functions • H5IMmake_palette • H5IMlink_palette • H5IMunlink_palette • H5IMget_npalettes • H5IMget_palette_info • H5IMget_palette • H5IMis_palette 84
- 85. HDF5 Image (H5IM) Programming example file_id = H5Fcreate ( "ex_image1.h5", H5F_ACC_TRUNC, H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT ); /* Write image */ status = H5IMmake_image_8bit ( file_id, "Image1", WIDTH, HEIGHT, data ); /* Make a palette */ status = H5IMmake_palette ( file_id, "Palette", pal_dims, pal ); /* Attach a palette to the image dataset */ status = H5IMlink_palette ( file_id, "Image1", "Palette" ); /* Close the file. */ status = H5Fclose ( file_id ); 85
- 86. For more information… HDF • HDF website – http://hdf.ncsa.uiuc.edu/ 5 • HDF5 Information Center – http://hdf.ncsa.uiuc.edu/HDF5/ • HDF Helpdesk – hdfhelp@ncsa.uiuc.edu or help@hdfgroup.org 86
- 87. Thank you This presentation is based upon work supported in part by a Cooperative Agreement with the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) under NASA grant NNG05GC60A. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of NASA. Other support provided by NCSA and other sponsors and agencies (http://hdf.ncsa.uiuc.edu/acknowledge.html). 87








![Example HDF5 Application
#include<stdio.h>
#include "H5IM.h"
#define WIDTH
57
#define HEIGHT 57
#define RANK 2
int main (void)
{
hid_t
file;
herr_t
status;
unsigned char data[WIDTH][HEIGHT];
int
i, j, num, val;
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen ("storm110.txt", "r");
for (i=0; i<WIDTH; i++)
for (j=0; j<HEIGHT; j++) {
num = fscanf (fp, "%d ", &val);
data[i][j] = val;
}
/* dataset dimensions */
/* file handle */
/* data to write */
/* Open ASCII file */
/* Read Values into ‘data’ buffer */
file = H5Fcreate ("storm.h5", H5F_ACC_TRUNC, H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT);
/* Create File */
status = H5IMmake_image_8bit (file, "Storm_Image", WIDTH, HEIGHT,
(const unsigned char *)data);
status = H5Fclose (file);
}
/* Create Image */
/* Close File */
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdf5-intro-jones-pourmal-140218130351-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-HDF5-Data-Model-Programming-Model-and-Library-APIs-8-320.jpg)













![h5dump
Command-line Utility for Viewing HDF5 Files
h5dump [--header] [-a ] [-d <names>] [-g <names>]
[-l <names>] [-t <names>] <file>
--header
-a <names>
-d <names>
-g <names>
-l <names>
-t <names>
Display header only; no data is displayed.
Display the specified attribute(s).
Display the specified dataset(s).
Display the specified group(s) and all the members.
Displays the value(s) of the specified soft link(s).
Display the specified named datatype(s).
<names> is one or more appropriate object names.
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdf5-intro-jones-pourmal-140218130351-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-HDF5-Data-Model-Programming-Model-and-Library-APIs-32-320.jpg)



















![Example 2 – Create an empty 4x6 dataset
1
2
3
hid_t
hsize_t
herr_t
file_id, dataset_id, dataspace_id;
dims[2];
status;
Create a new file
4
file_id = H5Fcreate ("dset.h5", H5F_ACC_TRUNC,
H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT);
5
6
7
dims[0] = 4;
dims[1] = 6;
dataspace_id = H5Screate_simple (2, dims, NULL);
8
dataset_id = H5Dcreate(file_id,"dset",H5T_STD_I32BE,
dataspace_id, H5P_DEFAULT);
9 status = H5Dclose (dataset_id);
10 status = H5Sclose (dataspace_id);
11 status = H5Fclose (file_id);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdf5-intro-jones-pourmal-140218130351-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-HDF5-Data-Model-Programming-Model-and-Library-APIs-57-320.jpg)
![Example 2 – Create an empty 4x6 dataset
1
2
3
hid_t
hsize_t
herr_t
file_id, dataset_id, dataspace_id;
dims[2];
status;
4
file_id = H5Fcreate ("dset.h5", H5F_ACC_TRUNC,
H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT);
Create a dataspace
5
6
7
8
current dims
rank
dims[0] = 4;
dims[1] = 6;
dataspace_id = H5Screate_simple (2, dims, NULL);
dataset_id = H5Dcreate(file_id,"dset",H5T_STD_I32BE,
dataspace_id, H5P_DEFAULT);
9 status = H5Dclose (dataset_id);
10 status = H5Sclose (dataspace_id);
11 status = H5Fclose (file_id);
Set maxdims
to current
dims](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdf5-intro-jones-pourmal-140218130351-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-HDF5-Data-Model-Programming-Model-and-Library-APIs-58-320.jpg)
![Example 2 – Create an empty 4x6 dataset
1
2
3
hid_t
hsize_t
herr_t
file_id, dataset_id, dataspace_id;
dims[2];
status;
4
file_id = H5Fcreate ("dset.h5", H5F_ACC_TRUNC,
H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT);
5
6
7
Pathname
dims[0] = 4;
dims[1] = 6;
dataspace_id = H5Screate_simple (2, dims, NULL);
Create a dataset
8
Datatype
dataset_id = H5Dcreate(file_id,"dset",H5T_STD_I32BE,
dataspace_id, H5P_DEFAULT);
Dataspace
9 status = H5Dclose (dataset_id);
10 status = H5Sclose (dataspace_id);
11 status = H5Fclose (file_id);
Property list
(default)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdf5-intro-jones-pourmal-140218130351-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-HDF5-Data-Model-Programming-Model-and-Library-APIs-59-320.jpg)
![Example 2 – Create an empty 4x6 dataset
1
2
3
hid_t
hsize_t
herr_t
file_id, dataset_id, dataspace_id;
dims[2];
status;
4
file_id = H5Fcreate ("dset.h5", H5F_ACC_TRUNC,
H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT);
5
6
7
dims[0] = 4;
dims[1] = 6;
dataspace_id = H5Screate_simple (2, dims, NULL);
8
dataset_id = H5Dcreate(file_id,"dset",H5T_STD_I32BE,
dataspace_id, H5P_DEFAULT);
Terminate access to dataset, dataspace, & file
9 status = H5Dclose (dataset_id);
10 status = H5Sclose (dataspace_id);
11 status = H5Fclose (file_id);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdf5-intro-jones-pourmal-140218130351-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-HDF5-Data-Model-Programming-Model-and-Library-APIs-60-320.jpg)










![Example 3 – Writing to an existing dataset
1
2
3
hid_t
herr_t
int
file_id, dataset_id;
status;
i, j, dset_data[4][6];
Initialize buffer
4
5
6
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 6; j++)
dset_data[i][j] = i * 6 + j + 1;
7
8
file_id = H5Fopen ("dset.h5", H5F_ACC_RDWR, H5P_DEFAULT);
dataset_id = H5Dopen (file_id, "dset");
9
status = H5Dwrite (dataset_id, H5T_NATIVE_INT,
H5S_ALL, H5S_ALL, H5P_DEFAULT, dset_data);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdf5-intro-jones-pourmal-140218130351-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-HDF5-Data-Model-Programming-Model-and-Library-APIs-72-320.jpg)
![Example 3 – Writing to an existing dataset
1
2
3
hid_t
herr_t
int
file_id, dataset_id;
status;
i, j, dset_data[4][6];
4
5
6
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 6; j++)
dset_data[i][j] = i * 6 + j + 1;
Open existing file and dataset
7
8
file_id = H5Fopen ("dset.h5", H5F_ACC_RDWR, H5P_DEFAULT);
dataset_id = H5Dopen (file_id, "dset");
9
status = H5Dwrite (dataset_id, H5T_NATIVE_INT,
H5S_ALL, H5S_ALL, H5P_DEFAULT, dset_data);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdf5-intro-jones-pourmal-140218130351-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-HDF5-Data-Model-Programming-Model-and-Library-APIs-73-320.jpg)
![Example 3 – Writing to an existing dataset
1
2
3
hid_t
herr_t
int
file_id, dataset_id;
status;
i, j, dset_data[4][6];
4
5
6
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 6; j++)
dset_data[i][j] = i * 6 + j + 1;
7
8
file_id = H5Fopen ("dset.h5", H5F_ACC_RDWR, H5P_DEFAULT);
dataset_id = H5Dopen (file_id, "dset");
Write to dataset
9
status = H5Dwrite (dataset_id, H5T_NATIVE_INT,
H5S_ALL, H5S_ALL, H5P_DEFAULT, dset_data);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdf5-intro-jones-pourmal-140218130351-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-HDF5-Data-Model-Programming-Model-and-Library-APIs-74-320.jpg)