Head injury ppt
- 1. HEAD INJURY MANALI H. SOLANKI F.Y. M.SC. NURSING J G COLLEGE OF NURSING
- 2. ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF HEAD:
- 6. CLASSIFICATION SCALP INJURY: The scalp has many blood vessels, so any scalp injury may bleed profusely. Control bleeding with direct pressure SKULL INJURY: Skull injury includes fracture to cranium and the face. If severe enough there can be injury to the brain. BRAIN INJURY: Brain injury can be classified as direct or indirect. Direct injuries to the brain can occur in open head injuries
- 7. CONCUSION Concussions result from direct blows to the head, gunshot wounds, violent shaking of the head, or through a whiplash type of injury.
- 8. CONTUSION A contusionis a bleeding bruise to the brain caused by a direct impact to the head.
- 12. RISK FACTORS: Colour blindness Alcohol addiction Youngsters Vertigo Males (about 1.5 times as likely as females to sustain a brain injury) Young children or teenagers (especially infants to 4- year-olds and 15–19-year-olds) Certain military personnel (for example, paratroopers) African Americans (who have the highest death rate from brain injury)
- 13. ETIOLOGY: Common causes of head injury include traffic accidents, falls, physical assault, and accidents at home, work, outdoors, or while playing sports.
- 14. SIGN AND SYMPTOMS: Dilatedpupils Changes in behaviour, such as irritability or confusion Trouble walking or speaking Drainage of bloody or clear fluids from ears or nose Vomiting Seizures Weakness or numbness in the arms or legs
- 15. DIAGNOSTIC INVESTIGATIONS: Complete blood count (e.g. Hb, RBC, WBC) Normal values: Hb: in male 13-18gm/dl Platelet: 1, 50,000-4, 50,000/cu mm WBC: 4,000-10,000 /cu mm S. NA+:135-145mEq/l S.k+:3.5-4.5mEq/l Arterial blood gas level PaO2:85-95 mm of Hg PaCO2:35-45 mm of Hg
- 16. CT SCAN:
- 17. MRI:
- 18. Brain Scans Electroencephalography (EEG) Nerve Conduction Velocity (NCV) Electronystagmography (ENG) Ultrasound Imaging
- 19. COMPLICATIONS: Coma Chronic headaches Loss of or change in sensation, hearing, vision, taste, or smell Paralysis Seizures Speech and language problems Death
- 20. INITIAL MANAGEMENT A: Airway control including cervical spine immobilisation with a stiff collar. B: Breathing C: Circulation D: Dysfunction or Disability E: External Examination
- 21. SURGICAL MANAGEMENT: CLOSED HEAD INJURY: OPEN HEAD INJURY: DEPRESSED SKULL FRACTURE:
- 22. NURSING MANAGEMENT: Ineffective Cerebral tissue perfusion related to increased ICP and decreased CPP Fluid volume deficit related to decrease LOC and hormonal dysfunction. Risk for injury related to decreased level of consciousness. Knowledge deficit regarding the treatment modalities and current situation.
- 23. Ineffective thermoregulation related to damage to hypothalamic centres. Risk for Impaired skin integrity related to compromised circulation shifting of fluid from intra vascular to interstitial space. Anxiety related to outcome of diseases as evidenced by poor concentration on work, isolation from others, rude behaviour
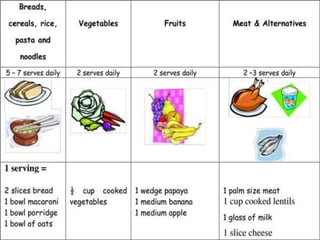
- 24. DIET PLAN Amino Acids Protein is used for the growth, repair and maintenance of nearly every tissue in the body and is composed of amino acids. Those with traumatic brain injuries require 0.55 to 0.73 grams of protein per pound of body weight
- 25. Other Foods A person living with a brain injury should consume a rounded diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Avoid saturated fat, hydrogenated fats and sodium because they may increase your risk of suffering a stroke.
- 26. CALORIE REQUIREMENTS The Glasgow Coma Scale is a tool used by medical professionals to measure someone's level of consciousness. Someone with a GCS of 4 to 5 needs 22.7 to 27.3 calories per pound of body weight per day. Someone with a GCS of 6 to 7 needs 18.2 to 22.7 calories. Those with less-severe injuries who have a GCS of 8 to 12 require 13.6 to 16 calories.
- 28. JOURNALS: Nutrition Considerations in Traumatic Brain Injury Nutritional treatment of patients with severe traumatic brain injury during the first six months after injury
- 29. REHABILITATION:
- 30. Cognitive Rehabilitation Therapy Physical Therapy Speech Therapy Mental Rehabilitation Physical Exercise Occupational Therapy