Healthy lifestyle Akniyet.pdf
- 1. DETERMINANTS OF HEALTH DR. MAHESWARI JAIKUMAR. maheswarijaikumar2103@gmail.com
- 3. BIOLOGICAL DETERMINANTS • The physical & mental traits of every human being are determined by the nature of his genes at the moment of conception.
- 4. • The genetic makeup is unique in the sense it cannot be altered after conception. • A number of diseases are now known to be of genetic origin, E.g., Chromosomal anomalies, errors of metabolism, mental retardation.
- 6. • Medical genetics offers hope for prevention & treatment of a wide spectrum of diseases, thus the prospect of better medicine & longer & healthier life.
- 7. • A positive health advocated by WHO implies that a person should be able to express as completely as possible the potentialities of his genetic heritage.
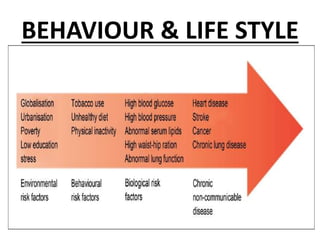
- 8. BEHAVIOURAL & SOCIO CULTURAL CONDITIONS • Life style denotes “ the way that people live”, reflecting a whole range of social values, attitudes & activities.
- 9. • It is composed of cultural & behavioural patterns & life long personal habits (Alcoholism,smoking)that have developed through the process of socialization.
- 10. BEHAVIOUR & LIFE STYLE
- 11. • Life styles are learnt through social interaction with parents & peer groups, friends, siblings & through school & mass media. • Many current health problems such as coronary heart disease, obesity, lung cancer, drug addiction are associated with life style.
- 13. • In countries like India risk of illness & death are connected with lack of sanitation, poor nutrition, personal hygiene, elementary human habits, customs & cultural patterns.
- 14. ENVIRONMENT • It was Hippocrates who first related disease to environment, climate, water, & air. • Later Pettenkoffer in Germany revived the concept of disease – environment association.
- 15. THE ENVIRONMENT
- 16. • Environment is classified as “internal” & “external”. • Internal environment of a man pertains to each & every component part, every tissue organ & organ system & their harmonious functioning within the system.
- 17. • External or macro environment consists of those things to which man is exposed after conception. • It is defined as “all that which is external to the individual human host”.
- 18. • It can be divided into physical, biological & psychosocial components , any or all of which affect can affect the health of man & his susceptibility to illness.
- 19. • Some epidemiologists use the term “micro environment” or domestic environment or personal environment which reflects a person’s way of living & lifestyle. E.g., eating habits, personal habits.
- 20. • The other environment includes occupational environment, socio economic environment, moral environment.
- 21. • SOCIO ECONOMIC CONDITIONS • The health of a person is primarily dependent upon the level of socio economic development. • E.g., Per Capita income, GNP, education, nutrition, employment, housing & political system of the country.
- 23. • ECONOMIC STATUS: The per capita GNP is the most widely accepted measure of general economic performance. • The economic progress of many countries has been a major factor in reducing the morbidity, mortality, increase in life expectancy & improving of the quality of life, family size, & the pattern of disease & deviant behaviour in the community.
- 24. EDUCATION • Education is the second major influencing factor in affecting the health of the population.
- 25. • The world map of illiteracy closely coincides with the maps of poverty, malnutrition, ill health, high infant & child mortality rates. • Studies indicate that education to some extent compensates the effects of poverty on health, irrespective of the availability of health facilities.
- 26. OCCUPATION • Un employment usually shows a higher incidence of ill health & death. • For many, loss of work may mean loss of income & status.
- 28. • It can cause psychological & social damage. • The very state of being employed in productive work promotes health.
- 29. POLITICAL SYSTEM • Health is closely related to the political system of a country. • Often the main obstacles to the implementation of health technologies are not technical rather political.
- 30. • Decisions concerning resource allocation, man power policy, choice of technology & the degree to which health services are made available & accessible to different segments of the society are examples of the manner in which the political system can shape community health services.
- 31. • The percentage of GNP spent on health is About 3%
- 32. HEALTH SERVICES • Health services are seen as essential for social & economic development. There is a strong correlation between GNP & Expectation of life at birth & the overall health status of the given population.
- 33. • Health &Family welfare services aim at improving the health condition of the population. • India being a signatory member , to realize Heath For All has chalked out strategies like the PHC, CHC, HSc, & other peripheral infrastructure.
- 34. The National preventive programmes such as Immunization programme, AIDS Control programme, Malaria Eradication Prog, Filaria Control Prog, ICDS, The Mid day Meal programme, Family Welfare programmes & Other non communicable disease programmes aim at prevention, promotion & maintenance of the health status of the population.
- 35. AGING OF THE POPULATION • By the year 2020 the world will have more than one billion people aged 60 & over. • More than two thirds of them living in the developing countries.
- 36. • A major concern of rapid population aging is the increased prevalence of chronic disease & disabilities. • Therefore aging process needs a special attention
- 37. GENDER • The 1990 have witnessed a increase concentration on women’s issues. In 1993 The Global Commission on women’s Health was established.
- 38. • The Commission drew up an agenda for action on women’s health covering nutrition, reproductive health, the health consequences of violence, aging, life style related conditions & occupational environment. • Inclusion of women’s health issues is a major breakthrough in the developmental plans.
- 40. OTHER FACTORS • The revolution in information & Communication Technology offers tremendous opportunities in providing an easy & instant access to medical information once difficult to retrieve.
- 41. • It contributes to the dissemination of information world wide, serving the needs of many physicians, health professionals, bio medical scientists & researchers, the mass media & the public.
- 42. • Health is not the sole contributor to the health & wellbeing of population, the potential of inter sectoral contributions to the health of communities is increasingly recognized.
- 44. THANK YOU