Heart development
- 1. DEVELOPMENT OF HEART TUBE SHREEYA NAIK ROLL NO. -141
- 2. • Development of blood cells and circulatory system – later part of 3rd week of gestation • Heart and blood vessels are mesodermal in origin • Progenitor heart cells lie in the epiblast, adjacent to the cranial end of the primitive streak. From there, they migrate through the streak and into the splanchnic layer of lateral plate mesoderm where they form a horseshoe-shaped cluster of cells called the primary heart field (PHF) .
- 3. PHF induced by the underlying endoderm to form cardiac myoblasts and blood islands that will form blood cells and vessels by the process of vasculogenesis. With time, the islands unite and form a horseshoe-shaped endothelial-lined heart tube surrounded by myoblasts. This region is known as the cardiogenic region.
- 4. • CRANIOCAUDAL FOLDING • LATERAL FOLDING Initially the cardiogenic area was anterior to oropharyngeal membrane ,as a result of growth CNS system and CRANIOCAUDAL FOLDING of the embryo the oropharyngeal membrane is pulled forward ,while the heart and pericardial cavity move to the cervical region and gradually to the thorax The lateral folding cause the two heart tubes to fuse except at the caudal most ends .
- 5. • Thus the heart becomes a continuous expanded tube having inner endothelial lining and outer myocardial layer. • Heart tube attached dorsal side of pericardial cavity by fold of mesocardium tissue –DORSAL MESOCARDIUM. • With futher development the dorsal mesocardium disappears ,creating the transverse pericardial sinus that connects both side of pericardial cavity • HEART TUBE consist of 3 layers 1. Inner ENDOTHELIUM 2. Myocardium,muscular wall 3. Epicardium/visceral pericardium
- 7. The cephalic portion of the tube bends ventrally, caudally, and to the right and the atrial (caudal) portion shifts dorsocranially and to the left. This bending, creates the cardiac loop. LOOPING OF HEART
- 8. Development Of Right Atrium Roll No - 143
- 9. •The main part of Right Atrium is derived from Right half of Primitive Atrium •The Sinus Venosus is absorbed into the Right Atrium
- 10. •The left horn of the Sinus Venosus becomes Coronary Sinus •The Right common Cardinal vein becomes part of Superior Vena Cava •The right Vitelline vein forms the Inferior Vena Cava
- 11. Development Of The Conducting System Of The Heart
- 12. •After fusion of the two tubes the pacemaker lies in the Sinus Venosus •Afterwards it comes to lie near the opening of SVC
- 13. •Similarly the AV Node and the AVBundle form in the left wall of Sinus Venosus and afterwards it comes to lie near the Interatrial Septum
- 17. Development Of Left Atrium Roll no - 144 The left atrium is derived from :- Left half of primitive atrial chamber Left half of AV canal Absorbed proximal parts of pulmonary veins
- 18. Absorption of Pulmonary Veins into Left Atrium At first only one pulmonary vein enters the atria The proximal part of vein is gradually absorbed and is incorporated into the wall of the atrium As a result , four vein (two on each side) finally open into atrium
- 20. Development of the ventricles The part of the heart tube lying within the pericardial cavity grows rapidly and, therefore, becomes folded on itself to form a “U”-shaped bulboventricular loop.
- 21. Bulboventricular sulcus gradually becomes shallower so that the conus, the proximal part of the bulbus cordis, and the ventricle, come to form one chamber which communicates with the truncus arteriosus.
- 22. DEVELOPMENT OF INTER-ATRIAL SEPTUM Beginning at the end of the fourth week, the primordial atrium is divided into right and left atria by the formation and subsequent modification and fusion of two septa
- 23. Septum primum Begins at the end of the fourth week Septum primum, a thin crescent shaped membrane
- 24. Grows toward the fusing endocardial cushions from the roof of the primordial atrium, partially dividing the common atrium into right and left halves. Fused endocardial cushion
- 25. Before the foramen primum disappears, perforations, produced by apoptosis, appear in the central part of the septum primum.
- 26. During the fifth and sixth weeks septum secundum, a thick crescentic muscular fold, grows from the ventrocranial wall of the right atrium, immediately adjacent to the septum primum
- 27. How does this septum formation helps to prevent backflow of oxygenated blood? Septum Primum - thin and mobile Septum Secundum - thick and rigid
- 29. INTERVENTRICULAR SEPTUM Roll No. 150
- 30. Interventricular Septum Divided into :-
- 31. • Muscular Part :- • The Medial Walls of the expanding ventricles become apposed and gradually merge forming the muscular interventricular septum • Membranous Part :- • Derived from Endocardial Cushions. • Derived from Conus Septum.
- 32. Conus Septum :- Heart Tube is divided into Bulbar Cordis , Primitive Ventricle , Primitive Atrium , Sinus Venosus. • Bulbus Cordis gets further divided into 3 parts :- Truncus Arteriosus , Conus Cordis and proximal part of Bulbus Cordis Conus Cordis further develop Conus Swellings which gets further developed into Conus Septum. *Trunkus Arteriosus of Bulbus Cordis give rise to aorta and Pulmonary Trunk seperated by Spiral Septum. *Proximal part of Bulbus Cordis give rise to smooth parts of ventricle :- Vestibule and Infundibulum.
- 34. Applied :- Tetralogy of Fallot Anterior Displacement of Spiral Septum
- 36. Congenital anomalies of the heart Roll no.146
- 37. (I) DEXTROCARDIA - (i) with situs inversus (ii) with laterality 1. CARDIAC LOOPING ANOMALIES
- 39. 2. ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT (asd)
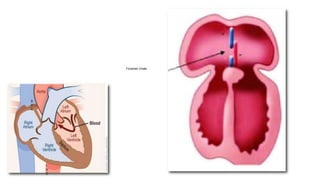
- 40. Normal Interatrial Septum Formation
- 42. 1. Excess Resorption of Septum Primum 90% ASDs- Ostium Secundum Defects Foramen Ovale Ostium Secundum
- 43. 2. Incomplete Development of Septum Secundum ASDs- Ostium Secundum Defects Foramen Ovale Ostium Secundum
- 46. 3. Ventricular septal defect (VSd) Normal Interventricular Septum Development Muscular Region Membranous Region
- 47. (I) Muscular region of IV Septum (II) Membranous region of IV Septum Muscular Region Membranous Region
- 48. 5. Tricuspid atresia Normal Development of Atrioventricular Valves
- 49. (1) Underdevelopment of Right Ventricle (3) Ventricular Septal Defect (4) Patent Foramen Ovale Absence/Fusion of Tricuspid Valves Normal Abnormal (2) Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
- 50. THANK YOU !