How do at ms work.ppt
- 2. CONTENTS • Introduction • History • Locations • Hardware • Software • Settlement • Alternative uses • Reliability
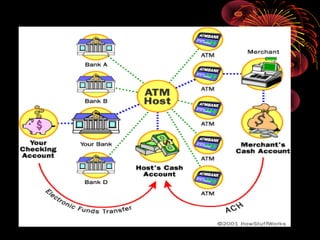
- 3. An ATM is simply a data terminal with two input and four output devices. Like any other data terminal, the ATM has to connect to, and communicate through, a host processor . The host processor is analogous to an Internet service provider (ISP) in that it is the gateway through which all the various ATM networks become available to the cardholder (the person wanting the cash).
- 4. British actor Reg Varney using the world's first ATM in 1967, located at a branch of Barclays Bank, Enfield. The system was developed by De La Rue • A mechanical cash dispenser was developed and built by Luther George Simjian and installed in 1939 in New York City by the City Bank of New York, but removed after 6 months due to the lack of customer acceptance.[1] • The ATM got smaller, faster and easier over the years. Thereafter, the history of ATMs paused for over 25 years, until De La Rue developed the first electronic ATM, which was installed first in Enfield Town in North London, United Kingdom [2] on 27 June 1967 by Barclays Bank.[3] However, the modern, networked ATM was invented in Dallas, Texas, by Don Wetzel in 1968. Wetzel was a department head at an automated baggage- handling company called Docutel. In 1995 the Smithsonian's National Museum of American History recognized Docutel and Wetzel as the inventors of the ATM.
- 5. ATMs are placed not only near or inside the premises of banks, but also in locations such as shopping centers/malls, airports, grocery stores, petrol/gas stations, restaurants, or any place large numbers of people may gather. These represent two types of ATM installations: on and off premise. On premise ATMs are typically more advanced, multi-function machines that complement an actual bank branch's capabilities and thus more expensive. Off premise machines are deployed by financial institutions and also ISOs (or Independent Sales Organizations) where there is usually just a straight need for cash, so they typically are the cheaper mono-function devices. In Canada, when an ATM is not operated by a financial institution it is known as a "White Label ATM". •
- 6. HARDWARE •Card reader - The card reader captures the account information stored on the magnetic stripe on the back of an ATM/debit or credit card. The host processor uses this information to route the transaction to the cardholder's bank. •You're probably one of the millions who has used an ATM. As you know, an ATM has two input devices: •Keypad - The keypad lets the cardholder tell the bank what kind of transaction is required (cash withdrawal, balance inquiry, etc.) and for what amount. Also, the bank requires the cardholder's personal identification number (PIN) for verification. Federal law requires that the PIN block be sent to the host processor in encrypted form. •
- 7. OUTPUT DEVICES: •Speaker - The speaker provides the cardholder with auditory feedback when a key is pressed. •Display screen - The display screen prompts the cardholder through each step of the transaction process. Leased-line machines commonly use a monochrome or color CRT (cathode ray tube) display. Dial-up machines commonly use a monochrome or color LCD. •Receipt printer - The receipt printer provides the cardholder with a paper receipt of the transaction. •Cash dispenser - The heart of an ATM is the safe and cash-dispensing mechanism. The entire bottom portion of most small ATMs is a safe that contains the cash.
- 9. SOFTWARE Typical platforms used in ATM development include RMX, OS/2, and Microsoft operating systems (such as MS-DOS, PC-DOS, Windows NT, Windows 2000, Windows XP Professional, or Windows XP Embedded). Java, Linux and Unix may also be used in these environments. Linux is also finding some reception in the ATM marketplace.
- 10. Settlement Funds When a cardholder wants to do an ATM transaction, 1) He or she provides the necessary information by means of the card reader and keypad. 2) The ATM forwards this information to the host processor, which routes the transaction request to the cardholder's bank or the institution that issued the card. 3) If the cardholder is requesting cash, the host processor causes an electronic funds transfer to take place from the customer's bank account to the host processor's account. 4) Once the funds are transferred to the host processor's bank account, the processor sends an approval code to the ATM authorizing the machine to dispense the cash.
- 12. ALTERNATIVES USES: Although ATMs were originally developed as just cash dispensers, they have evolved to include many other bank-related functions. In some countries, ATMs include many functions which are not directly related to the management of one's own bank account, such as: •Deposit currency recognition, acceptance, and recycling •Paying routine bills, fees, and taxes (utilities, phone bills, social security, legal fees, taxes, etc.) •Printing bank statements •Updating passbooks •Purchasing •Postage stamps. •Lottery tickets •train tickets •Shopping mall gift certificates. •Games and promotional features •Donating to charities
- 13. RELIABILITY Before an ATM is placed in a public place, it typically has undergone extensive testing with both test money and the backend computer systems that allow it to perform transactions. ATMs and the supporting electronic financial networks are generally very reliable, with industry benchmarks typically producing 98.25% customer availability for ATMs and up to 99.999% availability for host systems. If ATMs do go out of service, customers could be left without the ability to make transactions until the beginning of their bank's next time of opening hours.
- 14. THANK YOU




![British actor Reg Varney using the world's first ATM in 1967,
located at a branch of Barclays Bank, Enfield. The system was
developed by De La Rue
• A mechanical cash dispenser was developed and built by
Luther George Simjian and installed in 1939 in New York City by
the City Bank of New York, but removed after 6 months due to
the lack of customer acceptance.[1]
• The ATM got smaller, faster and easier over the years.
Thereafter, the history of ATMs paused for over 25 years, until
De La Rue developed the first electronic ATM, which was
installed first in Enfield Town in North London, United Kingdom
[2]
on 27 June 1967 by Barclays Bank.[3] However, the modern,
networked ATM was invented in Dallas, Texas, by Don Wetzel in
1968. Wetzel was a department head at an automated baggage-
handling company called Docutel. In 1995 the Smithsonian's
National Museum of American History recognized Docutel and
Wetzel as the inventors of the ATM.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howdoatmswork-ppt-130330014014-phpapp01/85/How-do-at-ms-work-ppt-4-320.jpg)