HTML Basics, Web Development Part-2.pptx
- 1. W E B S Y S T E M A N D T E C H N O L O G I E S LECTURE 2
- 2. HTML TABLES • Tables are defined with the <table> tag. • A table is divided into rows (with the <tr> tag), and each row is divided into data cells (with the <td> tag). td stands for "table data," and holds the content of a data cell. A <td> tag can contain text, links, images, lists, forms, other tables, etc. Table Example • <table border="1"> <tr> <td>row 1, cell 1</td> <td>row 1, cell 2</td> </tr> <tr> <td>row 2, cell 1</td> <td>row 2, cell 2</td> </tr> </table> How the HTML code above looks in a browser: Row 1 ,cell1 Row1,cell2 Row2.cell1 Row2,cell2
- 3. TABLE ELEMENTS • Each table cell is defined by a <td> and a </td> tag. • td stands for table data. • Everything between <td> and </td> are the content of the table cell. • Sometimes you want your cells to be table header cells. In those cases use the <th> tag instead of the <td> tag:
- 4. COLUM SPAN • To make a cell span more than one column, use the colspan attribute: • Example <table border=”1”> <tr> <th>Name</th> <th colspan="2">Telephone</th> </tr> <tr> <td>Bill Gates</td> <td>555 77 854</td> <td>555 77 855</td> </tr> </table>
- 5. ROW SPAN • To make a cell span more than one row, use the rowspan attribute: • Example <table border= “1” > <tr> <th>First Name:</th> <td>Bill Gates</td> </tr> <tr> <th rowspan="2">Telephone:</th> <td>555 77 854</td> </tr> <tr> <td>555 77 855</td> </tr> </table>
- 6. CELL PADDING AND CELL SPACING Cell padding property of tables is used to set blank space between cell border and cell content Cell spacing is the space between each cell. Example <table border="1" cellpadding="40“ style=“border-spacing:10”> <tr> <td>First</td> <td>Row</td></tr> <tr> <td>Second</td> <td>Row</td></tr> </table>
- 7. TABLE BORDER HTML tables can have borders of different styles and shape Example: <table style=“border: 1px solid black”> <tr> <td>First</td> <td>Row</td></tr> <tr> <td>Second</td> <td>Row</td></tr> </table>
- 8. TABLE CAPTION • To add a caption to a table, use the <caption> tag: • Example <table style="width:100%“ > <caption>Monthly savings</caption> <tr><th>Month</th> <th>Savings</th> </tr> <tr> <td>January</td><td>$100</td> </tr> <tr> <td>February</td><td>$50</td> </tr> </table>
- 9. GROUPING OF COLUMNS • The <colgroup> tag specifies a group of one or more columns in a table for formatting. • The <colgroup> tag is useful for applying styles to entire columns, instead of repeating the styles for each cell, for each row. <table> <colgroup> <col span="2" style="background-color:red"> <col style="background-color:yellow"> </colgroup> <tr> <th>ISBN</th> <th>Title</th> <th>Price</th> </tr> <tr> <td>3476896</td> <td>My first HTML</td> <td>$53</td> </tr> <tr> <td>5869207</td> <td>My first CSS</td> <td>$49</td> </tr></table> Note: The <colgroup> tag must be a child of a <table> element, after any <caption> elements and before any <thead>, <tbody>, <tfoot>, and <tr> elements.
- 10. SECTIONS OF HTML TABLE • The <thead> tag is used to group header content in an HTML table. • The <tbody> tag is used to group the body content in an HTML table. • The <tfoot> tag is used to group footer content in an HTML table. • The <thead>, <tbody>and <tfoot> element are used in conjunction elements to specify each part of a table (footer, header, body) for formatting a table.
- 11. EXAMPLE <table border= "1"> <thead style="color:green"> <tr> <th>Month</th> <th>Savings</th> </tr> </thead> <tfoot style="color:red" > <tr> <td>Sum</td> <td>$180</td> </tr></tfoot> <tbody style="background-color:grey"> <tr> <td>January</td> <td>$100</td> </tr> <tr> <td>February</td> <td>$80</td> </tr> </tbody></table> For more styling we will learn CSS later in this course
- 12. HTML LISTS • The most common HTML lists are ordered and unordered lists: • HTML Unordered Lists • An unordered list starts with the <ul> tag. Each list item starts with the <li> tag. • The list items are marked with bullets (typically small black circles). • <ul> <li>Coffee</li> <li>Milk</li> </ul> • How the HTML code above looks in a browser: • Coffee • Milk
- 13. STYLE ATTRIBUTE • A style attribute can be added to an unordered list, to define the style of the marker: Style Description list-style-type:disc The list items will be marked with bullets (default) list-style-type:circle The list items will be marked with circles list-style-type:square The list items will be marked with squares list-style-type:none The list items will not be marked
- 14. STYLE ARRTIBUTE • <ul style="list-style-type:square"> <li>Coffee</li> <li>Tea <li>Milk</li> </ul> • Output Coffee Tea Milk
- 15. ORDERED LISTS • HTML Ordered Lists • An ordered list starts with the <ol> tag. Each list item starts with the <li> tag. • The list items are marked with numbers. • <ol> <li>Coffee</li> <li>Milk</li> </ol> • How the HTML code above looks in a browser: 1 Coffee 2 Milk
- 16. STYLE ATTRIBUTE • A style attribute can be added to an ordered list, to define the style of the marker: Style Description 1 The list items will be marked with numeric (default) A The list items will be marked with uppercase alphabets a The list items will be marked with lowercase alphabets I The list items will be marked with uppercase roman letters i The list items will be marked with lowercase romans
- 17. HTML DEFINITION LISTS • A definition list is a list of items, with a description of each item. • The <dl> tag defines a definition list. • The <dl> tag is used in conjunction with <dt> (defines the item in the list) and <dd> (describes the item in the list): <dl> <dt>Coffee</dt><dd>black hot drink</dd> <dt>Milk</dt><dd>white cold drink</dd> </dl> How the HTML code above looks in a browser: Coffee black hot drink Milk white cold drink
- 18. NESTED LISTS • List can be nested (lists inside lists). • Example <ul> <li>Coffee</li> <li>Tea <ul> <li>Black tea</li> <li>Green tea</li> </ul> </li> <li>Milk</li> </ul>
- 19. DIV ELEMENT • The HTML <div> Element – The HTML <div> element is a block level element that can be used as a container for grouping other HTML elements. – The <div> element has no special meaning. Except that, because it is a block level element, the browser will display a line break before and after it. – When used together with CSS, the <div> element can be used to set style attributes to large blocks of content. – Another common use of the <div> element, is for document layout. It replaces the "old way" of defining layout using tables. Using <table> elements for layout is not the correct use of <table>. The purpose of the <table> element is to display tabular data.
- 20. HTML LINKS HTML Links - Hyperlinks HTML links are hyperlinks. A hyperlink is a text or an image you can click on, and jump to another document. HTML Links - Syntax In HTML, links are defined with the anchor <a> tag: <a href="url">link text</a> Example <p><a href="http://www.w3schools.com/html/">Visit our HTML tutorial</a></p> • The href attribute specifies the destination address (http://www.w3schools.com/html/) • The link text is the visible part (Visit our HTML tutorial). • Clicking on the link text, will send you to the specified address.
- 21. LINK COLORS • When you move the mouse over a link, two things will normally happen: The mouse arrow will turn into a little hand The color of the link element will change • By default, a link will appear like this (in all browsers): An unvisited link is underlined and blue A visited link is underlined and purple An active link is underlined and red • You can change the default colors, by using styles
- 22. CONT. <!DOCTYPE html> <html><head> <style> a:link {color: yellow; background-color:transparent} a:visited {color:green; background-color:transparent} a:hover {color:blue; background-color:yellow; text-decoration:underline} a:active {color:red; background-color:transparent; text-decoration:underline} </style></head><body> <p> Default colors of links can be changed</p> <a href="https://www.yahoo.com.pk" target="_blank">Open yahoo.com</a> </body></html>
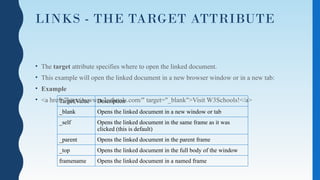
- 23. LINKS - THE TARGET ATTRIBUTE • The target attribute specifies where to open the linked document. • This example will open the linked document in a new browser window or in a new tab: • Example • <a href="http://www.w3schools.com/" target="_blank">Visit W3Schools!</a> Target Value Description _blank Opens the linked document in a new window or tab _self Opens the linked document in the same frame as it was clicked (this is default) _parent Opens the linked document in the parent frame _top Opens the linked document in the full body of the window framename Opens the linked document in a named frame
- 24. HTML IMAGE AS LINK • It is common to use images as links: • Example <a href="default.asp"> <img src="smiley.gif" alt="HTML tutorial" style="width:42px;height:42px;border:0"> </a> • A mail link can be set as: <a href="mailto:someone@example.com?Subject=Hello%20again" target="_top">Send Mail</a>
- 25. BOOKMARK • HTML bookmarks are used to allow readers to jump to specific parts of a Web page. • Bookmarks are practical if your website has long pages. • To make a bookmark, you must first create the bookmark, and then add a link to it. • When the link is clicked, the page will scroll to the location with the bookmark.
- 26. CONT. <!DOCTYPE html><html><body> <p><a href="#C5">Jump to Chapter 5</a></p> <h2>Chapter 1</h2> <p>This chapter explains ba bla bla</p> <h2>Chapter 2</h2> <p>This chapter explains ba bla bla</p> <h2>Chapter 3</h2> <p>This chapter explains ba bla bla</p> <h2>Chapter 4</h2> <p>This chapter explains ba bla bla</p> <h2 id="C5">Chapter 5</h2> <p>This chapter explains ba bla bla</p>
- 27. HTML IFRAME • The <iframe> tag specifies an inline frame. • An inline frame is used to embed another document within the current HTML document. <iframe name=“abc” src=http://www.w3schools.com width="200" height="200" ></iframe>
- 28. IMAGES • In HTML, images are defined with the <img> tag. • The <img> tag is empty, it contains attributes only, and does not have a closing tag. • The src attribute specifies the address of the image. • <img src="url" alt="some_text"> • Example <h1>You can insert images to your web page with img tag.</h1> <img src= "planets-o.jpg">
- 29. IMAGE ATTRIBUTES • Style attribute can be used to specify height and width of the image. • The alt attribute provides alternative information for an image if a user for some reason cannot view it (because of slow connection, an error in the src attribute, or if the user uses a screen reader). • If a browser cannot find an image, it will display the alt text • Example <img src= "planets-o.jpg" alt="Image not found" style="width:110px;height:110px"> • Or <img src= "planets-o.jpg" alt="Image not found" width="128" height="128">
- 30. CONT. • Image Address: if the image is in different folder than your html file. You must then include the folder name in the src attribute. You can also include images from internet using URL of images. • <img src= "C:UsersfarzanaDownloadsimages.jpg" alt="Image not found“ style="width:110px;height:110px"> • <img src= "http://res1.windows.microsoft.com/resbox/en/windows/main/7e03ffcf- d91d-4787-80fd-2e3e2affb127_4.jpg" alt="Image not found“ style="width:110px;height:110px">
- 31. IMAGES AS LINK • It is common to use images as links: • Example <a href="default.asp"> <img src="smiley.gif" alt="HTML tutorial" style="width:42px;height:42px;border:0"> </a> • Animated images: • The GIF standard allows animated images <img src= "LIGHTNINGgif-new.GIF" alt="Image not found" width="128" height="128">
- 32. IMAGE FLOAT • You can use float to align your image to the right or to the left of a text: <p> <img src= "C:UsersfarzanaDownloadsLIGHTNINGgif-new.gif" alt="Smiley face" style="float:right;width:42px;height:42px;"> A paragraph with a floating image. A paragraph with a floating image. A paragraph with a floating image. </p>
- 33. BACKGROUND IMAGE To add a background image on an HTML element, use the HTML style attribute and the CSS background-image property Example: <p style="background-image: url('img_girl.jpg');"> You can specify background images<br> for any visible HTML element.<br> In this example, the background image<br> is specified for a p element.<br> </p>
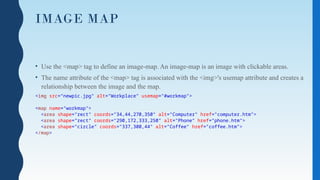
- 34. IMAGE MAP • Use the <map> tag to define an image-map. An image-map is an image with clickable areas. • The name attribute of the <map> tag is associated with the <img>'s usemap attribute and creates a relationship between the image and the map. <img src=“newpic.jpg" alt="Workplace" usemap="#workmap"> <map name="workmap"> <area shape="rect" coords="34,44,270,350" alt="Computer" href="computer.htm"> <area shape="rect" coords="290,172,333,250" alt="Phone" href="phone.htm"> <area shape="circle" coords="337,300,44" alt="Coffee" href="coffee.htm"> </map>