Introduction of ram ddr3
- 1. By Jatin Goyal Computer memory
- 2. 3. What are Upgrade limitation of system? 1.What is Computer memory and Why Do We Need It? 2. What are the Type of Computer memory and how they compared? 4. What they mean by multiple channel memory? 5. How to identify memory of pc? RAM Slot flash ROM and CMOS RAM
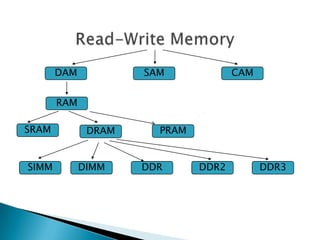
- 3. Read-Only Memory Read-Write Memory • non-volatile • volatile Volatile Memory losses contents when power is removed PROM EPROM EEPROM EAROM Flash CAMDAM SAM
- 4. DAM SAM CAM SRAM DRAM SIMM DIMM DDR DDR2 DDR3 RAM PRAM
- 5. DAM (Direct Access Memory) - direct access to all memory cells - RAM SAM (Sequential Access Memory) - data reading in sequence - HDD, optical discs CAM (Content Addressable Memory) - associative memory - returns value according to supplied word
- 6. The computer can access information held anywhere in RAM by addressing that part of the RAM directly. e.g if information stored in the 1000th location in memory the system does not have to read the information in the preceding 999 locations to get there, instead it can access the 1000th location simply by specifying it. RAM (Random Access Memory) Holds data and instructions used by CPU any piece of data can be returned in a constant time
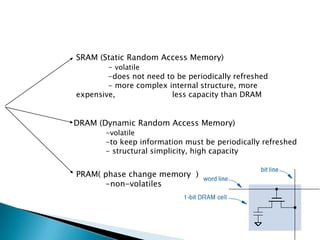
- 7. SRAM (Static Random Access Memory) - volatile -does not need to be periodically refreshed - more complex internal structure, more expensive, less capacity than DRAM DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory) -volatile -to keep information must be periodically refreshed - structural simplicity, high capacity PRAM( phase change memory ) -non-volatiles
- 8. SIMMs Single Inline Memory Module Pins on opposite sides form a single set of contacts 1987
- 9. EDO DRAM EDO = Extended Data Out Resides on SIMMs Sends and receives data simultaneously Maximum transfer rate to L2 cache is approximately 264 megabytes per second. 1990
- 10. DIMM(dual in-line memory module) Small Outline DIMM(SO-DIMM) DIMM mean module has Ics or chips and connection b/w both side in single line. DIMMs 1993
- 11. Buffered memory put less strain on the electrical load in Memory controller allowing a stable System that has several memory module. ECC code ability to detect and correct the error during data transmission. ECC/ Registered DIMM Non-ECC/ Non-Registered DIMM
- 12. SDRAM SDRAM PC66 transfer 533MB/s at 66Mhz SDRAM PC100 Desktop Memory transfer 800MB/s at 100Mhz SDRAM PC100 Server Memory (ECC) transfer 800MB/s at 100Mhz SDRAM PC133 Desktop Memory transfer 1,066MB/s at 133 Mhz SDRAM PC133 Server Memory (ECC) transfer 1,066MB/s at 133 Mhz 1999
- 13. Double data rate SDRAM 2002
- 14. DDR 2 2006
- 15. DDR 3 within the module and has the added advantage of a 30% reduction in power consumption dropping the voltage from 1.8V to 1.5V 2010
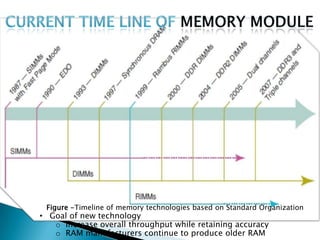
- 19. Figure -Timeline of memory technologies based on Standard Organization • Goal of new technology o Increase overall throughput while retaining accuracy o RAM manufacturers continue to produce older RAM
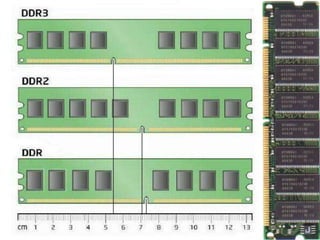
- 20. Cl or CAS rating Over Clocking Nomenclature(Identification of module) Ranking Comparison of DDR module notch
- 25. SGRAM Synchronous Graphics RAM SGRAM is a variant of SDRAM SGRAM makes use of block-writes to increase video processing speeds. SGRAM is single-ported so the CPU cannot write to it at the same time the image is being refreshed. SGRAM is used in high-end graphics cards
- 26. Open the case and look at memory slots How many slots? How many filled? Review module imprint Examine module for physical size and notch position Read motherboard documentation See if board supports dual channels or triple channels Last resort Take motherboard and old memory modules to a good computer parts store for conformation
- 28. Virtual Memory Virtual memory takes the place of RAM memory You should have a 2:1 ratio of RAM to Virtual Memory
- 29. Modifying Virtual Memory in Windows 8
- 30. Major Manufacturers • Corsair Memory • Crucial Technology • EDGE Tech Corp • GEIL • G.Skill • Hynix • Infineon Technologies • Kingston Technologies • Micron Technology • PNY • OCZ Technology • Rambus • Samsung • SimpleTech